Rituals play a vital role in shaping daily habits and enhancing mindfulness, helping you create intentional moments that foster well-being and personal growth. By integrating meaningful practices into your routine, you can cultivate a sense of calm and purpose amid life's chaos. Discover how incorporating rituals into your life can transform your mindset and productivity by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
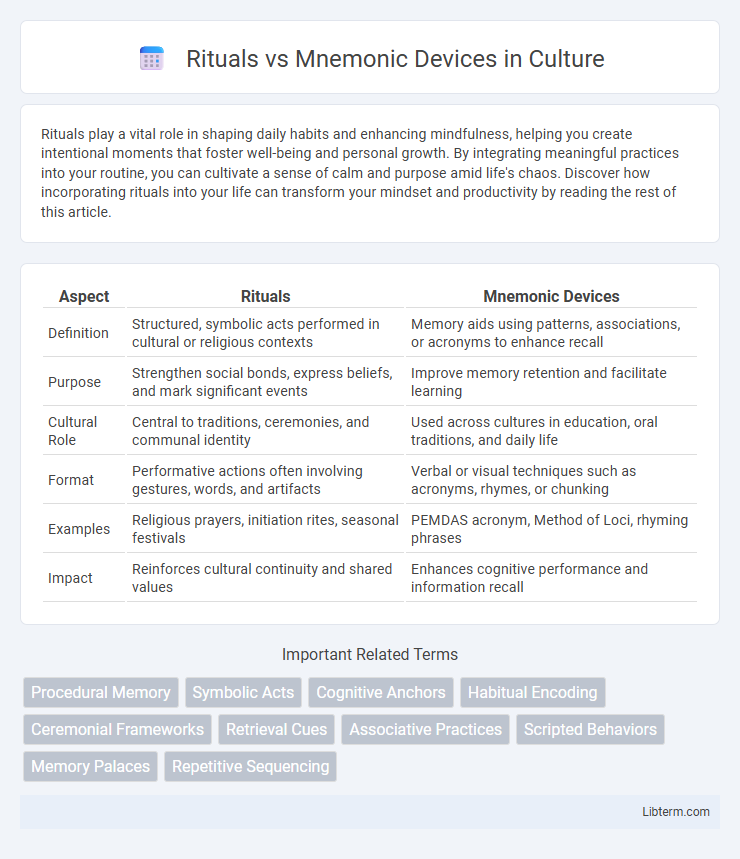
| Aspect | Rituals | Mnemonic Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured, symbolic acts performed in cultural or religious contexts | Memory aids using patterns, associations, or acronyms to enhance recall |
| Purpose | Strengthen social bonds, express beliefs, and mark significant events | Improve memory retention and facilitate learning |
| Cultural Role | Central to traditions, ceremonies, and communal identity | Used across cultures in education, oral traditions, and daily life |
| Format | Performative actions often involving gestures, words, and artifacts | Verbal or visual techniques such as acronyms, rhymes, or chunking |
| Examples | Religious prayers, initiation rites, seasonal festivals | PEMDAS acronym, Method of Loci, rhyming phrases |
| Impact | Reinforces cultural continuity and shared values | Enhances cognitive performance and information recall |
Introduction: Understanding Rituals and Mnemonic Devices
Rituals are structured, repetitive actions performed with symbolic meaning, often rooted in cultural or religious contexts to create a sense of order and identity. Mnemonic devices are cognitive tools or techniques designed to improve memory retention and recall by associating new information with familiar patterns, images, or phrases. Understanding the distinctions between rituals and mnemonic devices highlights how rituals emphasize behavioral and social functions, while mnemonic devices focus on enhancing individual cognitive processes.
Definition and Core Concepts
Rituals are structured, repeated actions imbued with symbolic meaning, often used to provide a sense of order and connection in cultural or personal contexts. Mnemonic devices are cognitive tools or techniques designed to enhance memory retention and recall by associating new information with familiar patterns, such as acronyms or rhymes. While rituals emphasize behavioral repetition and symbolic significance, mnemonic devices focus specifically on mental strategies to improve information encoding and retrieval.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Rituals trace back to ancient civilizations where symbolic actions reinforced social and religious cohesion, evolving through cultural transmission to maintain group identity and spiritual significance. Mnemonic devices originated in classical antiquity, notably with the Greek poet Simonides, who developed memory techniques such as the method of loci to enhance information recall, adapting over centuries into modern cognitive strategies. Both practices demonstrate an evolution rooted in human efforts to structure memory and meaning, with rituals emphasizing communal experience and mnemonic devices targeting individual memory optimization.
Psychological Mechanisms at Play
Rituals and mnemonic devices both engage memory through distinct psychological mechanisms; rituals leverage repetition and emotional significance to enhance encoding and retrieval, while mnemonic devices utilize structured associations and visualization techniques to improve recall. The habitual nature of rituals creates a consistent contextual framework, activating procedural memory systems and reducing cognitive load. Mnemonic devices stimulate episodic memory by linking new information to familiar cues, facilitating faster and more accurate information retrieval.
Differences in Purpose and Application
Rituals primarily serve to reinforce social cohesion and personal meaning through repeated symbolic actions, often tied to cultural or religious contexts. Mnemonic devices function as cognitive tools designed to enhance memory retention and recall by using associations, patterns, or acronyms. While rituals emphasize emotional and communal resonance, mnemonic devices focus on effective information processing and learning efficiency.
How Rituals Shape Memory and Focus
Rituals create structured environments that enhance memory retention by linking specific actions with meaningful contexts, reinforcing neural pathways involved in recall. The repetitive nature of rituals improves focus and attentional control by engaging sensory and motor systems, making the experience more immersive and less prone to distraction. Unlike mnemonic devices, rituals embed information within emotional and physical frameworks, strengthening both long-term memory and cognitive engagement.
Mnemonic Devices: Enhancing Memory Retention
Mnemonic devices significantly enhance memory retention by organizing information into easily retrievable formats such as acronyms, visual imagery, and rhymes. Techniques like the method of loci and chunking create strong associative links that improve recall efficiency. These memory aids leverage cognitive patterns, making complex data more accessible and durable over time.
Comparative Effectiveness: Rituals vs Mnemonics
Rituals enhance memory retention by creating consistent, emotionally charged patterns that engage multiple sensory pathways in the brain, while mnemonic devices improve recall by organizing information into structured, easily retrievable formats like acronyms or visualization. Studies show mnemonic devices often yield faster retrieval of discrete facts, whereas rituals support deeper, long-term learning through habitual reinforcement. The comparative effectiveness depends on the learning context, with rituals benefiting procedural memory and mnemonics excelling in declarative memory tasks.
Practical Examples in Daily Life
Rituals like morning meditation or a nightly skincare routine create consistent habits that reduce stress and improve mental clarity by engaging sensory and emotional cues. Mnemonic devices such as acronyms (e.g., HOMES for the Great Lakes) or visualization techniques help in memory retention for tasks like grocery lists or study material. Both methods enhance daily efficiency; rituals build automaticity through repetition, while mnemonics optimize cognitive recall.
Choosing the Right Approach for Optimal Outcomes
Selecting between rituals and mnemonic devices depends on the context and desired outcome, as rituals enhance emotional engagement and consistency, while mnemonic devices facilitate memory retention and recall efficiency. For tasks requiring habitual reinforcement and motivation, rituals create meaningful routines that embed behavior subconsciously. In contrast, mnemonic devices like acronyms or visualization techniques are optimal for learning complex information quickly and improving long-term memory accuracy.
Rituals Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com