Customs influence global trade by regulating the import and export of goods, ensuring compliance with national laws and international agreements. Efficient customs processes reduce delays and costs, enhancing your business competitiveness in global markets. Explore the full article to understand how customs impact your trade operations and what measures you can take to streamline them.
Table of Comparison
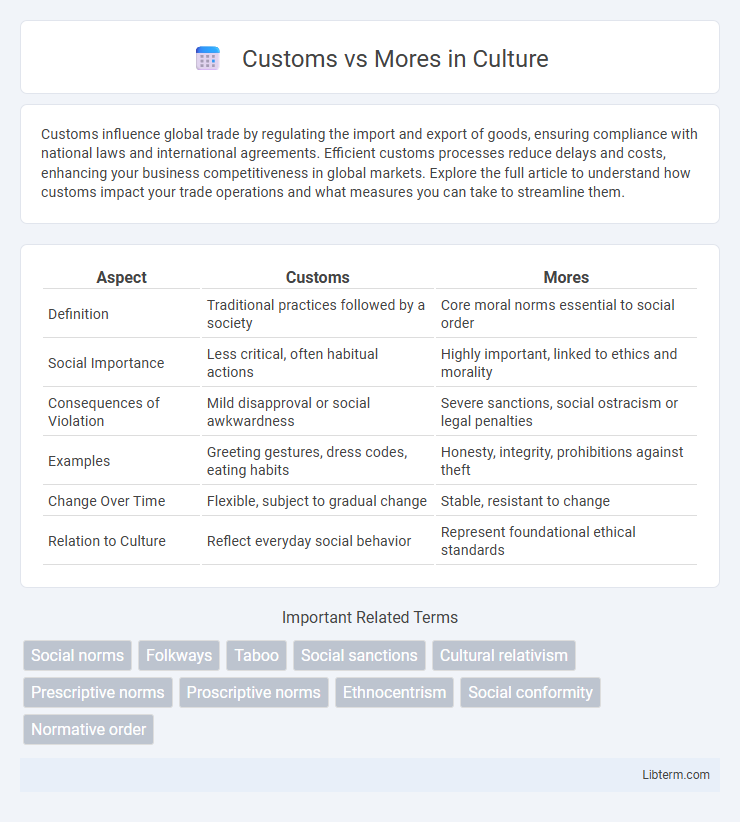
| Aspect | Customs | Mores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional practices followed by a society | Core moral norms essential to social order |
| Social Importance | Less critical, often habitual actions | Highly important, linked to ethics and morality |
| Consequences of Violation | Mild disapproval or social awkwardness | Severe sanctions, social ostracism or legal penalties |
| Examples | Greeting gestures, dress codes, eating habits | Honesty, integrity, prohibitions against theft |
| Change Over Time | Flexible, subject to gradual change | Stable, resistant to change |
| Relation to Culture | Reflect everyday social behavior | Represent foundational ethical standards |
Understanding Customs and Mores: Key Definitions
Customs refer to traditional practices and behaviors that are widely accepted and followed within a particular culture or society, often passed down through generations. Mores are stronger social norms that embody the moral views and principles of a community, with violations typically resulting in severe social sanctions. Understanding the distinction between customs and mores is essential for analyzing cultural norms, as customs guide everyday conduct while mores enforce fundamental ethical standards.
Historical Origins of Customs and Mores
Customs and mores both stem from historical social practices that shape cultural norms and values, with customs originating from long-standing habitual behaviors passed down through generations. Mores, emerging from moral and ethical codes deeply rooted in religious or philosophical traditions, reflect society's foundational beliefs about right and wrong. The distinction lies in customs being practical social conventions, while mores command stronger societal enforcement due to their association with collective moral standards.
The Role of Customs in Shaping Social Behavior
Customs play a crucial role in shaping social behavior by establishing accepted patterns of conduct within a community. They provide predictability and order, influencing daily interactions and reinforcing cultural identity. Through consistent practice, customs help individuals learn societal expectations and maintain social cohesion.
Mores as Moral Guidelines in Society
Mores are deeply ingrained moral guidelines that govern acceptable behavior within a society, reflecting core values and ethical standards. Unlike customs, which are traditional practices or habitual actions, mores carry a stronger moral significance and violations often result in social disapproval or sanctions. These moral norms shape collective conscience and ensure social order by defining what is considered right and wrong in a cultural context.
Differences Between Customs and Mores
Customs are traditional practices followed by a specific group or society, typically involving everyday social behaviors such as greetings or dress codes, whereas mores are stronger norms tied to moral and ethical values, governing behaviors critical to social order. The violation of customs usually results in mild social disapproval, while breaking mores can lead to severe sanctions, including legal penalties or social ostracism. Customs tend to be flexible and evolve over time, but mores are more rigid and central to a culture's core beliefs and identity.
Examples of Customs Across Cultures
Customs vary widely across cultures, reflecting diverse social practices like greeting gestures, dress codes, and eating habits. For instance, bowing is a common greeting custom in Japan, while handshakes are prevalent in Western societies. In India, removing shoes before entering a home is a customary sign of respect, contrasting with the Western practice of wearing shoes indoors.
Notable Mores and Their Societal Impact
Notable mores, such as prohibitions against theft, murder, and incest, serve as fundamental ethical standards that maintain social order and cohesion in communities worldwide. These deeply ingrained moral norms shape legal systems, influence social policies, and foster a collective sense of right and wrong, ensuring stability and predictability within societies. Violations of mores typically provoke strong societal reactions, including sanctions or ostracism, which reinforce shared values and promote cultural continuity.
Adaptation and Evolution of Customs and Mores
Customs and mores both evolve through societal adaptation, reflecting changes in cultural values and social norms over time. Customs, as traditional practices, adapt more flexibly to technological advances and globalization, while mores, which are deeply rooted moral rules, evolve more gradually to maintain social cohesion and ethical standards. This dynamic transformation highlights how societies balance innovation with preserving core principles in their behavioral expectations.
Influence of Customs and Mores on Law and Order
Customs shape societal expectations through repetitive behaviors that become unwritten rules influencing community conduct and social harmony. Mores embody the moral standards critical to a society, often underpinning formal legal systems and guiding legislative frameworks to uphold ethical norms. The interplay between customs and mores directly impacts law enforcement and judicial decisions by embedding cultural values into the fabric of legal order and governance.
The Future of Customs and Mores in Changing Societies
Customs and mores evolve continuously as societies undergo technological advancements and globalization, prompting shifts in social norms and values. Emerging trends in digital communication and cultural exchange accelerate the adaptation of traditional customs while challenging established mores, resulting in dynamic social frameworks. The future of customs and mores lies in balancing respect for heritage with openness to change, fostering inclusive communities that reflect diverse cultural identities.
Customs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com