Paralanguage refers to the non-verbal elements of communication such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate that convey meaning beyond words. Understanding these vocal cues enhances your ability to interpret emotions and intentions accurately during conversations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how paralanguage influences everyday communication.
Table of Comparison
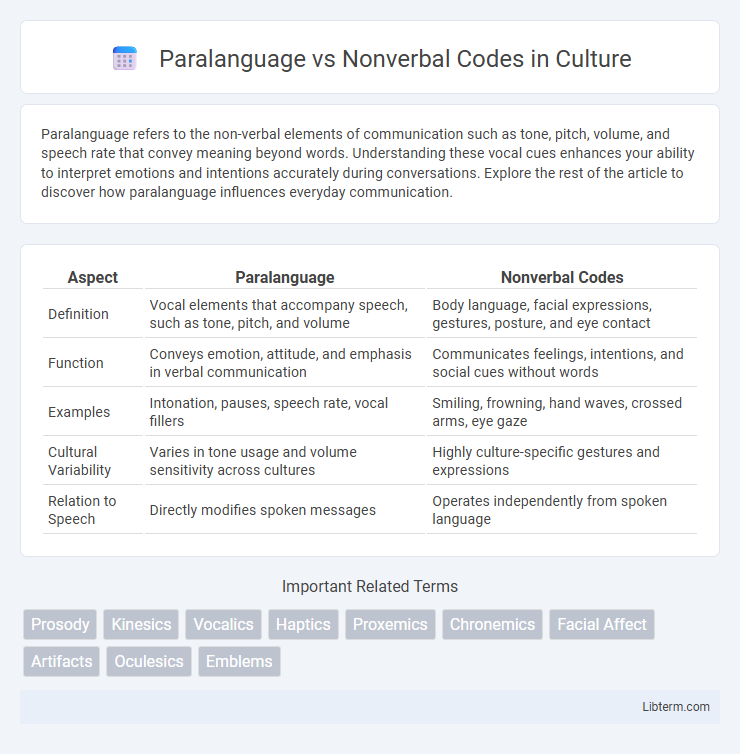
| Aspect | Paralanguage | Nonverbal Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vocal elements that accompany speech, such as tone, pitch, and volume | Body language, facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact |
| Function | Conveys emotion, attitude, and emphasis in verbal communication | Communicates feelings, intentions, and social cues without words |
| Examples | Intonation, pauses, speech rate, vocal fillers | Smiling, frowning, hand waves, crossed arms, eye gaze |
| Cultural Variability | Varies in tone usage and volume sensitivity across cultures | Highly culture-specific gestures and expressions |
| Relation to Speech | Directly modifies spoken messages | Operates independently from spoken language |
Introduction to Paralanguage and Nonverbal Codes
Paralanguage encompasses vocal elements such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate that convey meaning beyond spoken words, playing a crucial role in communication. Nonverbal codes include body language, facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact, which collectively express emotions and intentions without verbal articulation. Understanding both paralanguage and nonverbal codes enhances effective interpersonal communication by providing deeper insight into the speaker's true message and emotional state.
Defining Paralanguage: Beyond Words
Paralanguage encompasses the vocal elements of communication that go beyond spoken words, such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate, which convey emotions and intentions. These vocal cues play a crucial role in interpreting meaning, often revealing attitudes or feelings not explicit in the verbal message. Unlike nonverbal codes, which include gestures, facial expressions, and body language, paralanguage specifically relates to how something is said rather than what is said.
Understanding Nonverbal Codes
Nonverbal codes encompass a broad range of communication methods including facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact, which convey emotions and intentions beyond spoken words. Unlike paralanguage, which refers to vocal elements such as tone, pitch, and volume, nonverbal codes rely primarily on physical behaviors to express meaning and regulate social interactions. Understanding these codes enhances the ability to interpret unspoken messages and improves interpersonal communication effectiveness.
Key Elements of Paralanguage
Paralanguage encompasses vocal elements such as pitch, tone, volume, and speech rate, which convey emotions and clarify meaning beyond spoken words. These key paralanguage components influence listener perception and enhance understanding by providing context and emotional cues. Unlike nonverbal codes like gestures or facial expressions, paralanguage specifically refers to vocal nuances that modify verbal communication.
Types of Nonverbal Codes
Nonverbal codes include kinesics, proxemics, haptics, chronemics, and appearance, each conveying meaning without spoken words. Kinesics involves gestures, facial expressions, and body movements that express emotions and intentions, while proxemics deals with personal space and physical distance in communication. Haptics refers to touch, chronemics to timing and punctuality, and appearance encompasses clothing and physical traits, all crucial for interpreting messages beyond paralanguage.
Differences Between Paralanguage and Nonverbal Codes
Paralanguage refers to vocal elements such as pitch, tone, volume, and speech rate that accompany spoken language, while nonverbal codes encompass a broader range of communication methods including gestures, facial expressions, body posture, and eye contact. Unlike paralanguage, which modifies verbal messages, nonverbal codes can convey meaning independently without spoken words. Understanding these differences enhances the interpretation of communication nuances in contexts like interpersonal interactions and cross-cultural exchanges.
Functions and Importance in Communication
Paralanguage involves vocal elements such as tone, pitch, and volume that convey emotions and clarify meaning beyond spoken words, enhancing interpersonal understanding. Nonverbal codes include gestures, facial expressions, posture, and eye contact, which regulate interactions and communicate attitudes or intentions effectively. Both paralanguage and nonverbal codes play crucial roles in reinforcing messages, managing conversational flow, and building rapport in diverse communication contexts.
Cultural Variations in Paralanguage and Nonverbal Codes
Cultural variations in paralanguage, such as tone, pitch, and speech rate, significantly influence how messages are interpreted across different societies, with some cultures valuing expressive intonation while others prefer a more subdued vocal delivery. Nonverbal codes, including gestures, facial expressions, and proxemics, also vary widely; for example, eye contact may be considered respectful in Western cultures but intrusive in some Asian cultures. Understanding these cultural differences is crucial for effective intercultural communication and helps prevent misinterpretations in both personal and professional interactions.
Common Misinterpretations and Communication Barriers
Paralanguage, which includes vocal elements like tone, pitch, and volume, is often misinterpreted as conveying emotions or attitudes that may not align with the speaker's intent, creating communication barriers. Nonverbal codes, such as body language, facial expressions, and gestures, vary significantly across cultures and can lead to misunderstandings when interpreted through the lens of different cultural norms. These misinterpretations disrupt effective communication by causing receivers to misconstrue messages, highlighting the importance of context and cultural awareness in decoding paralinguistic and nonverbal signals accurately.
Conclusion: Integrating Paralanguage and Nonverbal Codes in Effective Communication
Integrating paralanguage and nonverbal codes enhances communication by providing a holistic understanding of the speaker's intent and emotions, as vocal tone, pitch, and volume complement facial expressions, gestures, and body language. Effective communicators leverage this synergy to reinforce messages, reduce misunderstandings, and build stronger interpersonal connections. Mastery of both paralanguage and nonverbal cues is essential for achieving clarity and emotional resonance in personal and professional interactions.
Paralanguage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com