Proxemics studies how people use space in communication, revealing cultural and personal boundaries that influence interactions. Understanding proxemics enhances your awareness of nonverbal cues and improves relationships in personal and professional settings. Discover more about how proxemics shapes everyday communication by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
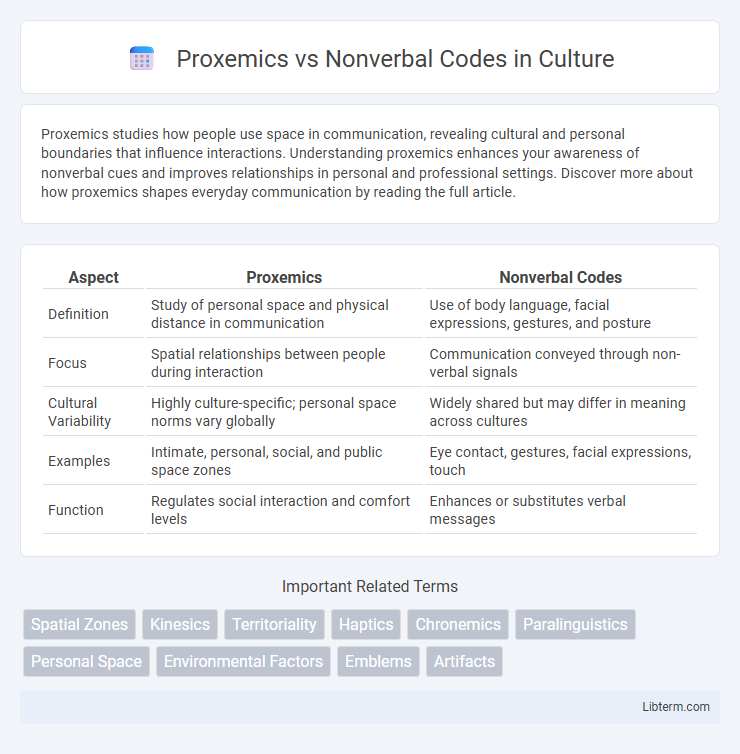
| Aspect | Proxemics | Nonverbal Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of personal space and physical distance in communication | Use of body language, facial expressions, gestures, and posture |
| Focus | Spatial relationships between people during interaction | Communication conveyed through non-verbal signals |
| Cultural Variability | Highly culture-specific; personal space norms vary globally | Widely shared but may differ in meaning across cultures |
| Examples | Intimate, personal, social, and public space zones | Eye contact, gestures, facial expressions, touch |
| Function | Regulates social interaction and comfort levels | Enhances or substitutes verbal messages |
Understanding Proxemics: The Language of Space
Understanding proxemics involves analyzing the use of personal and social space to communicate nonverbally. It encompasses spatial zones such as intimate, personal, social, and public distances that convey varying levels of comfort, power, and relational dynamics. Proxemics reveals how physical distance and spatial arrangement influence perceptions and interactions within different cultural contexts.
Defining Nonverbal Codes in Communication
Nonverbal codes in communication encompass various forms of nonverbal behavior such as facial expressions, gestures, posture, eye contact, and proxemics that convey meaning without spoken words. These codes function as essential complements to verbal communication, influencing interpretation, emotional tone, and relational dynamics in interactions. Understanding nonverbal codes like kinesics, haptics, and chromatics enhances the ability to decode unspoken messages and improves overall communicative effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Proxemics and Other Nonverbal Codes
Proxemics studies the use of personal space and physical distance in communication, whereas other nonverbal codes include gestures, facial expressions, and posture to convey meaning. Key differences lie in how proxemics emphasizes spatial relationships and cultural variations in personal space, while nonverbal codes focus on specific body movements and signals. Proxemics also influences interaction dynamics and context interpretation more broadly than isolated nonverbal cues.
Types of Proxemics: Intimate, Personal, Social, Public
Proxemics, the study of spatial distances in communication, includes intimate (0-18 inches), personal (18 inches to 4 feet), social (4 to 12 feet), and public (12 feet or more) distances, each signaling different levels of relational closeness. Intimate space is reserved for close relationships, while personal space supports conversations among friends. Social distance facilitates interactions in professional or casual settings, and public space accommodates formal or impersonal communication.
Common Forms of Nonverbal Codes Beyond Proxemics
Common forms of nonverbal codes beyond proxemics include kinesics, which studies body movements such as gestures, facial expressions, and posture, as well as haptics, the use of touch to communicate. Vocalics, or paralanguage, encompasses tone, pitch, and volume variations that convey emotional states and intentions without words. Chronemics, the study of time in communication, reflects cultural attitudes towards punctuality and interaction pacing, influencing the interpretation of messages.
The Role of Culture in Proxemics and Nonverbal Codes
Culture significantly shapes proxemics and nonverbal codes by defining spatial behavior and interpretive norms that vary across societies. For example, personal space preferences differ widely; Western cultures often favor larger interpersonal distances compared to many Asian cultures that value closer proximity. Nonverbal cues such as eye contact, gestures, and body orientation are also culturally regulated, influencing communication effectiveness and social interactions globally.
How Proxemics Influences Interpersonal Relationships
Proxemics significantly influences interpersonal relationships by regulating personal space, which affects comfort levels and emotional connection between individuals. Cultural norms dictate proxemic preferences, shaping interactions and nonverbal communication such as eye contact, touch, and body orientation, all of which contribute to relationship dynamics. Understanding proxemic behavior enhances social bonding and conflict resolution by aligning physical distance with relational context and emotional needs.
Nonverbal Codes: Gestures, Facial Expressions, and Posture
Nonverbal codes encompass gestures, facial expressions, and posture, serving as crucial channels for conveying emotions and intentions beyond spoken language. Gestures such as hand movements and nods communicate specific messages, while facial expressions reveal feelings like happiness, anger, or surprise across cultures. Posture indicates attitude and social status, with open stances often signifying confidence and closed postures reflecting discomfort or defensiveness.
Practical Examples: Proxemics vs. Other Nonverbal Behaviors
Proxemics, which studies personal space and physical distance in communication, presents practical examples such as maintaining an arm's length distance during casual conversations versus a closer proximity in intimate settings. Other nonverbal codes include facial expressions, gestures, and posture, such as a smile signaling friendliness or crossed arms indicating defensiveness. Understanding the differences helps interpret social cues accurately--proxemics provides spatial context, while other nonverbal behaviors convey emotional states and intentions.
The Impact of Proxemics and Nonverbal Codes on Communication Effectiveness
Proxemics, the study of personal space and physical distance in communication, significantly shapes interaction outcomes by influencing comfort levels and perceived intimacy. Nonverbal codes, including body language, facial expressions, and gestures, complement proxemic cues to convey emotions and intentions more accurately. Understanding the interplay between proxemics and nonverbal codes enhances communication effectiveness by reducing misunderstandings and fostering clearer, more engaging exchanges.
Proxemics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com