Homogeneity ensures consistency and uniformity across datasets or materials, which is crucial for accurate analysis and reliable results. Maintaining homogeneity can improve the quality of processes and strengthen the validity of conclusions drawn from your work. Explore the full article to understand how homogeneity impacts various fields and how to achieve it effectively.
Table of Comparison
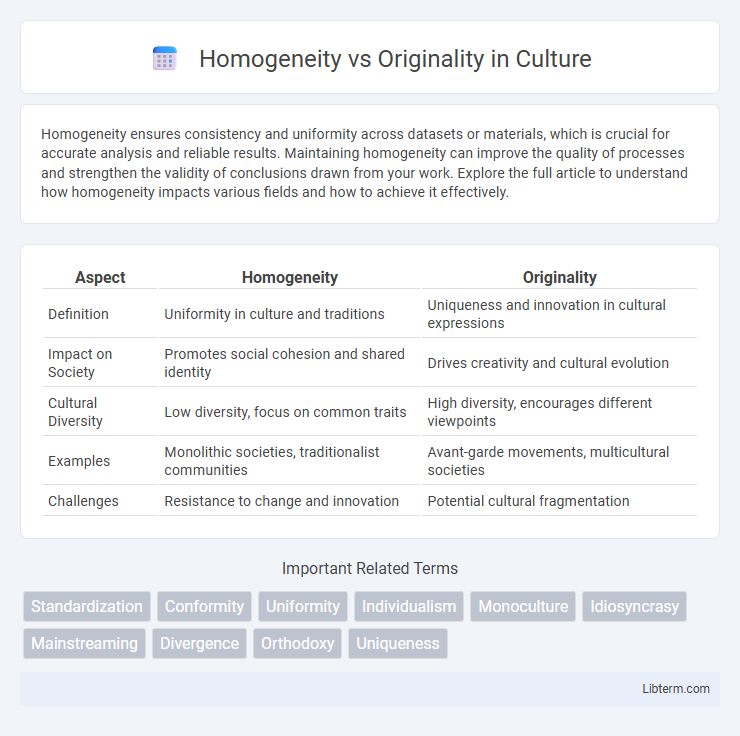
| Aspect | Homogeneity | Originality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniformity in culture and traditions | Uniqueness and innovation in cultural expressions |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social cohesion and shared identity | Drives creativity and cultural evolution |
| Cultural Diversity | Low diversity, focus on common traits | High diversity, encourages different viewpoints |
| Examples | Monolithic societies, traditionalist communities | Avant-garde movements, multicultural societies |
| Challenges | Resistance to change and innovation | Potential cultural fragmentation |
Understanding Homogeneity: Definition and Concepts
Homogeneity refers to the quality of being uniform or similar in composition, structure, or characteristics within a group or system. In various contexts such as chemistry, sociology, or linguistics, homogeneity implies consistent traits that promote predictability and cohesion. Understanding homogeneity involves recognizing patterns of sameness that contrast sharply with originality, which emphasizes uniqueness and diversity.
The Essence of Originality in Creative Work
The essence of originality in creative work lies in the unique synthesis of ideas, perspectives, and expressions that distinguish it from homogeneity. While homogeneity offers familiarity and consistency, originality drives innovation and cultural evolution by challenging conventional boundaries. Genuine originality is rooted in authentic personal experiences and novel insights that resonate on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Historical Perspectives on Homogeneity and Originality
Historical perspectives on homogeneity emphasize cultural conformity and the preservation of established traditions, often seen in societies valuing collective identity. In contrast, originality has been historically celebrated as a driver of innovation, artistic expression, and societal progress, challenging uniform norms. Philosophers like Kant and Hegel explored originality as a manifestation of individual creativity against homogeneous cultural frameworks.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Homogeneity
Homogeneity in groups fosters easier communication and faster decision-making by minimizing conflicts and ensuring shared values and perspectives. It can enhance efficiency and cohesion but limits creativity and innovation due to a lack of diverse ideas and viewpoints. Overreliance on homogeneity risks groupthink, reducing adaptability and problem-solving capabilities in dynamic environments.
The Value of Originality in Modern Society
Originality fuels innovation by encouraging unique ideas that drive cultural and technological progress, setting individuals and organizations apart in competitive markets. In modern society, the value of originality lies in its ability to spark creativity, solve complex problems, and foster diverse perspectives that challenge conventional thinking. Homogeneity limits growth by promoting conformity, whereas originality cultivates dynamic environments essential for advancement and change.
Homogeneity vs Originality: Key Differences
Homogeneity emphasizes uniformity and consistency across elements, promoting cohesion and predictability in design, culture, or products. Originality prioritizes uniqueness and innovation, fostering creativity and distinctiveness that set ideas or items apart from conventional norms. The key differences lie in homogeneity's focus on standardization versus originality's drive for new and diverse expressions.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Homogeneity and Originality
Culture profoundly influences the balance between homogeneity and originality by shaping collective values, norms, and creative expressions. Societies with strong cultural cohesion often prioritize homogeneity to preserve traditions and social harmony, while more pluralistic cultures encourage originality by fostering diversity and innovation. The interplay between cultural heritage and openness to new ideas determines how communities navigate conformity and uniqueness in artistic, social, and intellectual domains.
Impact on Innovation: Homogeneous vs Original Approaches
Homogeneous approaches often streamline processes but limit diversity in ideas, resulting in incremental innovation rather than breakthrough solutions. Original approaches foster diverse perspectives and unconventional thinking, driving radical innovations and competitive advantages in dynamic markets. Companies embracing originality typically see higher rates of disruptive innovation, which can reshape industries and create new market opportunities.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Homogeneity and Originality
Striking a balance between homogeneity and originality involves blending familiar elements that create cohesion with unique aspects that foster innovation. Homogeneity provides structural consistency and predictability, essential for user experience and brand identity, while originality drives creativity, differentiation, and engagement. Integrating these dimensions strategically cultivates environments that are both relatable and refreshingly distinct, maximizing appeal and effectiveness.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Homogeneity and Originality
Future trends indicate a dynamic shift in the balance between homogeneity and originality as industries increasingly leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to generate creative content. Advances in algorithmic personalization allow for mass customization, blending uniformity in production with unique user experiences, driving innovation across sectors like marketing, entertainment, and design. This evolution fosters hybrid models where standardized processes coexist with distinctive, original outputs, reshaping consumer expectations and competitive strategies.
Homogeneity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com