Economic violence undermines financial stability by controlling or restricting access to money, employment, or resources, often within intimate relationships or households. This form of abuse limits Your ability to make independent decisions and traps victims in cycles of dependency and vulnerability. Explore the rest of the article to understand the signs, impacts, and ways to address economic violence effectively.
Table of Comparison
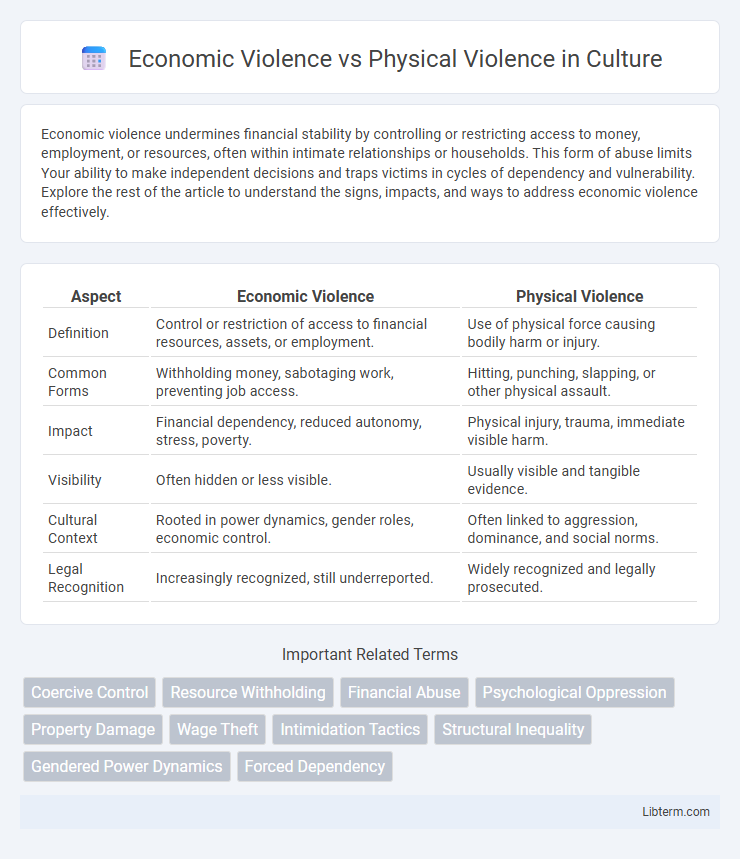
| Aspect | Economic Violence | Physical Violence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control or restriction of access to financial resources, assets, or employment. | Use of physical force causing bodily harm or injury. |
| Common Forms | Withholding money, sabotaging work, preventing job access. | Hitting, punching, slapping, or other physical assault. |
| Impact | Financial dependency, reduced autonomy, stress, poverty. | Physical injury, trauma, immediate visible harm. |
| Visibility | Often hidden or less visible. | Usually visible and tangible evidence. |
| Cultural Context | Rooted in power dynamics, gender roles, economic control. | Often linked to aggression, dominance, and social norms. |
| Legal Recognition | Increasingly recognized, still underreported. | Widely recognized and legally prosecuted. |
Defining Economic Violence
Economic violence involves controlling or limiting a person's access to financial resources, employment, or education, resulting in dependency and financial insecurity. It includes tactics such as withholding money, restricting work opportunities, or sabotaging financial stability to exert power. Unlike physical violence, which inflicts bodily harm, economic violence undermines autonomy and long-term well-being through financial control.
Understanding Physical Violence
Physical violence involves the use of force causing bodily harm, injury, or trauma to an individual, including actions such as hitting, slapping, or choking. It results in visible injuries and immediate physical pain, often requiring medical attention and posing long-term health risks. Unlike economic violence, which manipulates financial resources and restricts access to economic independence, physical violence directly impacts a person's physical safety and well-being.
Key Differences Between Economic and Physical Violence
Economic violence involves controlling or restricting access to financial resources, assets, or economic opportunities, whereas physical violence entails inflicting bodily harm or injury. Economic violence often manifests through behaviors like withholding money, sabotaging employment, or limiting financial independence, while physical violence includes acts such as hitting, slapping, or physical assault. The key difference lies in the mode of harm: economic violence targets financial stability and autonomy, whereas physical violence targets physical safety and health.
Forms and Manifestations of Economic Violence
Economic violence manifests through controlling access to financial resources, restricting employment opportunities, and sabotaging economic independence, often limiting victims' ability to make autonomous decisions. Forms include withholding money, preventing access to bank accounts, imposing debt, and sabotaging work or education efforts to generate income. Unlike physical violence, economic violence exerts power by systematically undermining a person's financial stability and security, frequently serving as a tool for prolonged control.
Common Types of Physical Violence
Common types of physical violence include hitting, slapping, punching, kicking, choking, and using weapons to cause bodily harm. These actions result in visible injuries such as bruises, cuts, fractures, and internal damage. Physical violence often leaves immediate and tangible evidence, distinguishing it sharply from economic violence, which targets financial resources and economic stability.
Impact of Economic Violence on Victims
Economic violence severely undermines victims' autonomy by restricting access to financial resources, leading to increased dependence and diminished ability to escape abusive situations. This form of violence often results in long-term psychological stress, poverty, and reduced opportunities for education and employment. Unlike physical violence, the impact of economic violence can be less visible but equally devastating, perpetuating cycles of abuse and social marginalization.
Physical Violence: Consequences and Effects
Physical violence leads to severe physical injuries, psychological trauma, and long-term emotional distress in victims. It increases the risk of chronic health issues such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression, significantly impacting overall well-being and quality of life. The societal costs include increased healthcare expenses, reduced productivity, and strain on social support systems.
Legal Responses to Economic and Physical Violence
Legal responses to economic violence often involve protective orders, financial restitution, and enforcement of property rights to address damaging control over resources and income. Physical violence laws prioritize criminal prosecution and immediate protective measures such as restraining orders and emergency shelters to ensure victim safety. Both forms of violence necessitate tailored legal frameworks to effectively mitigate harm and provide comprehensive victim support within civil and criminal justice systems.
Addressing Economic Violence in Policy and Practice
Economic violence, including financial control, deprivation of resources, and employment sabotage, undermines victims' autonomy and long-term wellbeing. Effective policy responses involve integrating economic abuse indicators into legal frameworks, ensuring access to financial resources, and providing targeted support services such as financial counseling and employment programs. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, social services, and financial institutions are crucial for addressing economic violence comprehensively and preventing its escalation into physical violence.
Prevention and Support Strategies for All Types of Violence
Prevention and support strategies for economic violence and physical violence require tailored approaches focused on empowerment and protection. Economic violence prevention involves financial literacy programs, access to independent income sources, and legal frameworks ensuring economic rights while physical violence prevention emphasizes community awareness, safe shelters, and law enforcement training. Comprehensive support systems integrate counseling, emergency assistance, and advocacy services to address the multifaceted needs of survivors of all types of violence.
Economic Violence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com