Psychological violence inflicts emotional harm through manipulation, intimidation, and constant criticism, severely impacting mental health and self-esteem. It often leaves invisible scars that disrupt your sense of safety and well-being, making recognition and intervention crucial. Explore the rest of the article to understand the signs, effects, and strategies for coping with psychological violence.
Table of Comparison
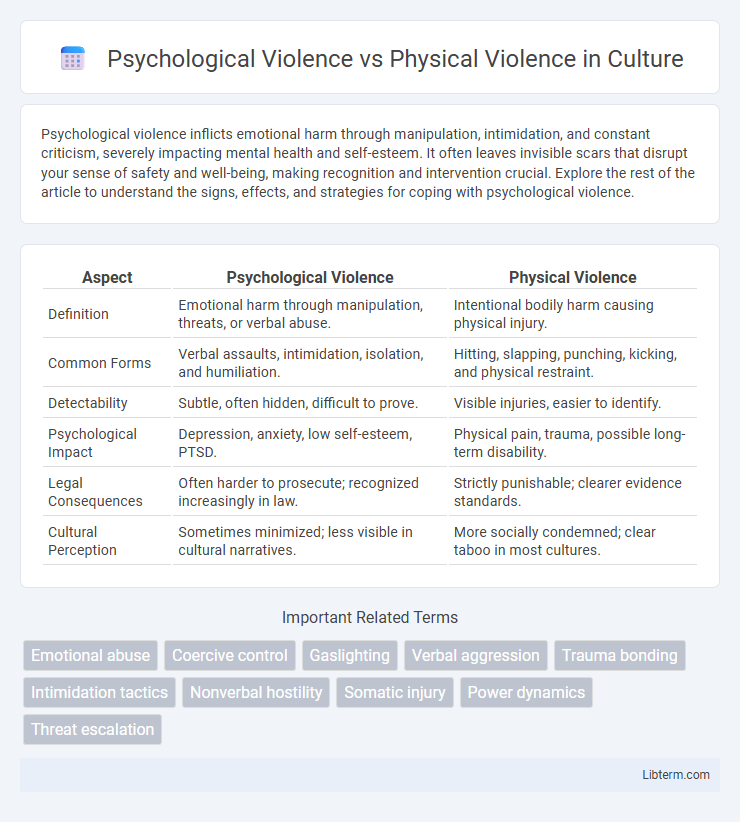
| Aspect | Psychological Violence | Physical Violence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional harm through manipulation, threats, or verbal abuse. | Intentional bodily harm causing physical injury. |
| Common Forms | Verbal assaults, intimidation, isolation, and humiliation. | Hitting, slapping, punching, kicking, and physical restraint. |
| Detectability | Subtle, often hidden, difficult to prove. | Visible injuries, easier to identify. |
| Psychological Impact | Depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, PTSD. | Physical pain, trauma, possible long-term disability. |
| Legal Consequences | Often harder to prosecute; recognized increasingly in law. | Strictly punishable; clearer evidence standards. |
| Cultural Perception | Sometimes minimized; less visible in cultural narratives. | More socially condemned; clear taboo in most cultures. |
Understanding Psychological Violence
Psychological violence involves patterns of behavior that cause emotional harm, such as intimidation, threats, manipulation, and humiliation, impacting mental health and self-esteem. Unlike physical violence, which inflicts bodily injury, psychological violence targets the mind, often leaving invisible scars that can lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Recognizing signs of psychological abuse is essential for early intervention and support, as its effects are profound and long-lasting.
Defining Physical Violence
Physical violence refers to intentional acts causing bodily harm, injury, or physical pain to another person, including hitting, slapping, punching, or use of weapons. It is distinguishable from psychological violence, which targets mental and emotional well-being through threats, intimidation, or verbal abuse without physical contact. Physical violence leaves tangible evidence such as bruises, cuts, or broken bones, making it more readily identifiable than psychological violence.
Key Differences Between Psychological and Physical Violence
Psychological violence involves emotional harm through threats, manipulation, or verbal abuse, while physical violence entails bodily harm or physical force. Key differences include the invisibility of psychological wounds compared to visible injuries in physical violence, and the long-term mental health impact often associated with psychological abuse. Psychological violence can undermine self-esteem and cause trauma without leaving physical marks, whereas physical violence typically results in immediate, tangible harm.
Common Signs of Psychological Violence
Psychological violence often manifests through common signs such as constant criticism, humiliation, isolation from friends and family, and controlling behaviors that undermine a person's self-worth and autonomy. Victims may exhibit anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, and symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to prolonged emotional abuse. Recognizing these signs is crucial for early intervention and support, distinguishing psychological violence from the more visible injuries caused by physical violence.
Recognizable Signs of Physical Violence
Recognizable signs of physical violence include visible injuries such as bruises, cuts, burns, and fractures, often appearing in various stages of healing on different body parts. Victims may also exhibit symptoms like swelling, tenderness, or unexplained pain, along with behavioral changes such as flinching or avoiding certain individuals. Unlike psychological violence, these physical indicators provide tangible evidence that can be documented by healthcare professionals.
Short-Term Impacts on Victims
Psychological violence often causes immediate emotional distress, anxiety, and lowered self-esteem, impacting victims' mental well-being more swiftly than physical injuries. Physical violence typically results in visible wounds and pain that demand urgent medical attention, though psychological trauma may also develop concurrently. Short-term effects of both types of violence can significantly disrupt daily functioning, with psychological violence sometimes leading to acute symptoms like PTSD and emotional instability within days.
Long-Term Consequences of Each Type
Psychological violence leads to long-term mental health issues such as chronic anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder, often impairing emotional regulation and self-esteem. Physical violence results in lasting physical injuries, chronic pain, and increased risk of neurological damage, alongside psychological trauma that can exacerbate overall health decline. Both types of violence contribute to impaired social functioning and increased vulnerability to substance abuse and suicide.
Reporting and Seeking Help
Reporting psychological violence often faces challenges due to its invisible nature and emotional manipulation, leading many victims to underreport compared to physical violence, which typically leaves visible evidence and prompts immediate intervention. Mental health professionals and support organizations provide specialized resources for psychological abuse victims, emphasizing confidential counseling and safety planning. Legal systems increasingly recognize psychological violence, offering protection orders and tailored support services to encourage reporting and facilitate access to help.
Prevention Strategies and Interventions
Effective prevention strategies for psychological violence include promoting emotional intelligence and communication skills through school programs and community workshops, which empower individuals to recognize and address abusive behaviors early. Interventions for physical violence often involve law enforcement, medical treatment, and shelter services alongside counseling to ensure victim safety and recovery. Integrating multidisciplinary approaches that involve healthcare providers, social workers, and legal professionals enhances both prevention and intervention outcomes in violence cases.
Supporting Survivors: Resources and Approaches
Psychological violence survivors benefit from specialized counseling services that address trauma-induced anxiety, depression, and PTSD, emphasizing emotional healing and resilience-building. Physical violence support involves medical treatment, legal advocacy, and safe housing provisions to ensure immediate safety and recovery. Integrated support programs combining mental health therapy, legal assistance, and community resources enhance survivors' long-term recovery outcomes.
Psychological Violence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com