Individualism emphasizes personal freedom and self-expression as fundamental values, promoting the importance of individual rights and independence. It encourages people to pursue their own goals and make decisions based on their unique beliefs and desires. Explore the rest of this article to understand how individualism shapes society and impacts your personal growth.
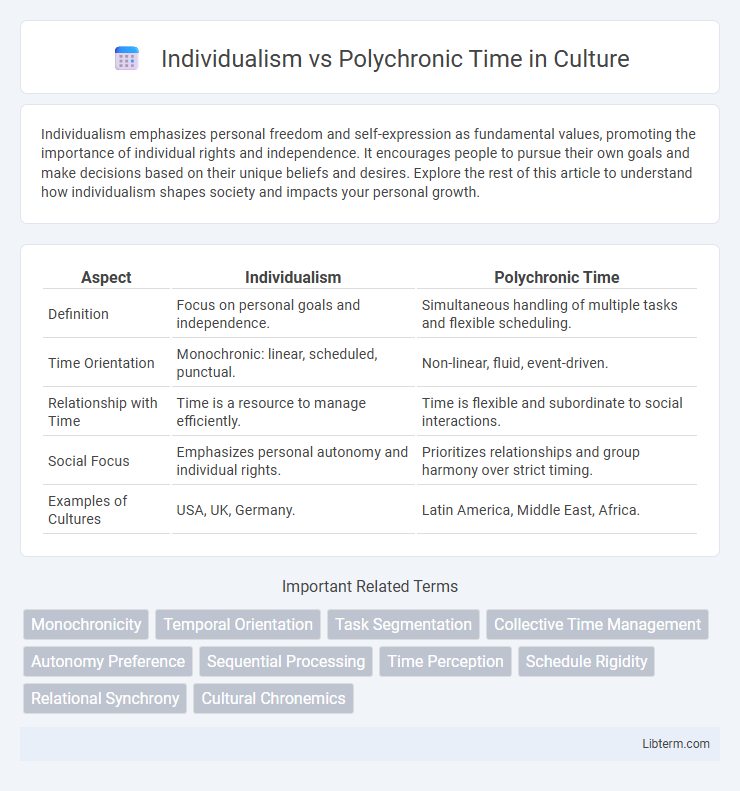
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Individualism | Polychronic Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal goals and independence. | Simultaneous handling of multiple tasks and flexible scheduling. |
| Time Orientation | Monochronic: linear, scheduled, punctual. | Non-linear, fluid, event-driven. |
| Relationship with Time | Time is a resource to manage efficiently. | Time is flexible and subordinate to social interactions. |
| Social Focus | Emphasizes personal autonomy and individual rights. | Prioritizes relationships and group harmony over strict timing. |
| Examples of Cultures | USA, UK, Germany. | Latin America, Middle East, Africa. |
Understanding Individualism: Core Concepts
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-expression, and the prioritization of individual goals over collective interests, forming a core principle in cultural studies and social psychology. In individualistic societies, time is often perceived linearly and rigidly, aligning with monochronic time patterns that value punctuality and task completion. Understanding these concepts is crucial for navigating cross-cultural communication, especially in contexts where polychronic time--a flexible and relational approach to time--is predominant.
What is Polychronic Time Orientation?
Polychronic time orientation refers to a cultural perspective where people view time as flexible and multi-dimensional, often engaging in multiple tasks simultaneously and valuing relationships over strict schedules. This contrasts sharply with individualistic cultures that prioritize punctuality, linear time management, and personal achievement. Understanding polychronic time is crucial for interpreting social interactions and business practices in collectivist societies that emphasize group harmony and interconnectedness.
Key Differences Between Individualism and Polychronic Cultures
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and individual goals, while polychronic cultures prioritize relationships, group harmony, and multitasking. Individualistic cultures tend to view time linearly, valuing punctuality and schedules, whereas polychronic cultures experience time fluidly, often managing multiple activities simultaneously. These differences influence communication styles, decision-making processes, and work ethics, with individualism favoring directness and planning, and polychronic cultures embracing flexibility and relational interactions.
Communication Styles: Direct vs Multitasking
Individualistic cultures prioritize direct communication, emphasizing clear, explicit messages to ensure personal accountability and clarity. Polychronic time orientations favor multitasking, managing multiple conversations or tasks simultaneously, often resulting in flexible, context-dependent communication. Balancing these styles requires awareness of cultural preferences to enhance effective interactions in diverse environments.
Time Management: Prioritizing Self or Relationships
Individualism in time management emphasizes prioritizing personal goals and schedules, reflecting a monochronic approach that values punctuality and task completion. Polychronic time prioritizes relationships, allowing for flexible and simultaneous engagement in multiple activities, often placing social connections above strict adherence to deadlines. Balancing these perspectives requires adapting time management strategies to align either with individual responsibilities or relational commitments depending on cultural or situational contexts.
Workplace Dynamics and Productivity
Individualism in workplace dynamics promotes personal accountability and task-focused productivity, aligning well with monochronic time management where tasks are approached sequentially and deadlines are strictly adhered to. Polychronic time orientation values multitasking and flexible scheduling, emphasizing relationships and collective teamwork over rigid timelines, which can enhance collaboration but potentially reduce individual task efficiency. Balancing individualistic work styles with polychronic time practices requires adaptive management strategies to optimize both productivity and interpersonal harmony.
Conflict Resolution in Individualistic vs Polychronic Settings
Conflict resolution in individualistic cultures emphasizes direct communication and timely problem-solving to respect personal autonomy and individual goals. Polychronic settings prioritize relational harmony and flexibility, often addressing conflicts through ongoing dialogue and mutual understanding over extended periods. Recognizing these differing approaches enables more effective mediation by aligning strategies with cultural time perceptions and social values.
Impact on Personal Relationships and Social Structures
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and schedules, often aligning with monochronic time that values punctuality and sequential task completion. Polychronic time, common in collectivist cultures, prioritizes multitasking and fluid interactions, fostering flexible social structures and deeper relational connections. The contrast influences personal relationships by shaping communication expectations and social obligations, where individualistic, monochronic societies may experience transactional interactions, and polychronic, collectivist environments promote interdependence and communal harmony.
Globalization: Bridging Individualism and Polychronic Approaches
Globalization facilitates the integration of individualistic cultures that prioritize linear, monochronic time with polychronic societies valuing multi-tasking and relational flexibility. Multinational corporations implement cross-cultural training to enhance collaboration by respecting diverse temporal orientations, improving project management and communication. Embracing these time perspectives fosters innovation and efficiency, bridging cultural gaps in global business environments.
Practical Strategies for Navigating Cultural Differences
Understanding individualism helps recognize the emphasis on personal goals and autonomy, while polychronic time orientation values multitasking and flexible scheduling. Practical strategies include adapting communication styles to respect personal space and time perceptions, scheduling meetings with buffer periods for spontaneity, and fostering patience in collaborative environments. Emphasizing active listening and cultural awareness reduces misunderstandings and enhances cross-cultural cooperation.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com