Interculturalism promotes meaningful interactions and understanding between diverse cultural groups, fostering social cohesion and mutual respect. This approach emphasizes dialogue, inclusivity, and the celebration of cultural differences within communities and institutions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how interculturalism can enhance your relationships and social environments.
Table of Comparison
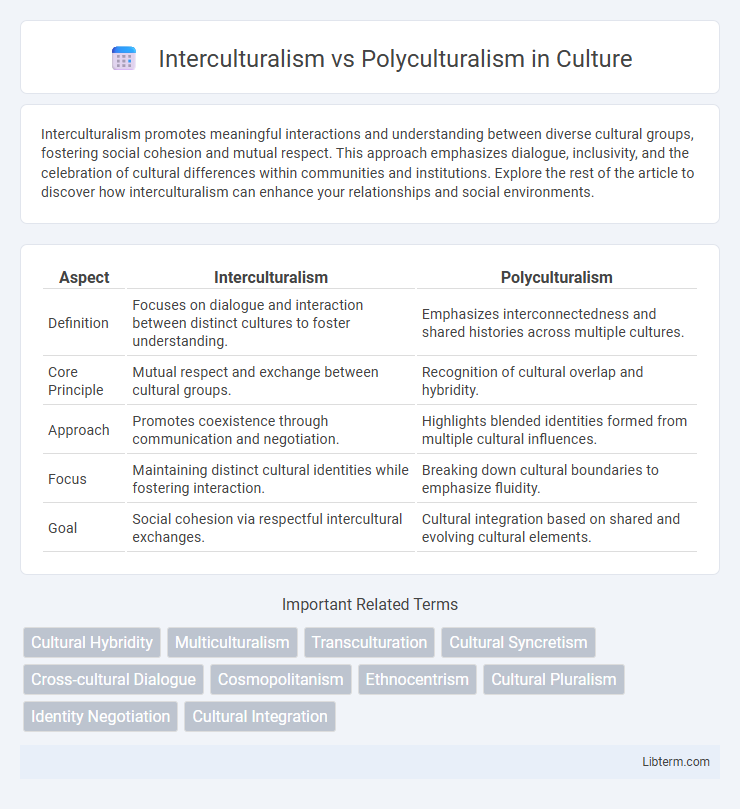
| Aspect | Interculturalism | Polyculturalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on dialogue and interaction between distinct cultures to foster understanding. | Emphasizes interconnectedness and shared histories across multiple cultures. |
| Core Principle | Mutual respect and exchange between cultural groups. | Recognition of cultural overlap and hybridity. |
| Approach | Promotes coexistence through communication and negotiation. | Highlights blended identities formed from multiple cultural influences. |
| Focus | Maintaining distinct cultural identities while fostering interaction. | Breaking down cultural boundaries to emphasize fluidity. |
| Goal | Social cohesion via respectful intercultural exchanges. | Cultural integration based on shared and evolving cultural elements. |
Understanding Interculturalism: Definitions and Origins
Interculturalism emphasizes meaningful dialogue and interaction between distinct cultural groups to foster mutual respect and social cohesion, originating primarily in Quebec's political discourse during the 1990s. This approach contrasts with polyculturalism, which highlights the fluid and overlapping nature of cultural identities without fixed boundaries. Understanding interculturalism involves recognizing its commitment to managing cultural diversity through structured engagement and institutional policies promoting integration.
Polyculturalism Explained: Key Concepts and Background
Polyculturalism emphasizes the interconnectedness and dynamic interactions between different cultures, highlighting shared histories and continuous cultural exchanges rather than viewing cultures as isolated entities. It challenges fixed cultural boundaries by promoting an understanding of cultures as fluid and mutually influencing each other, fostering cooperation and hybrid identities. Rooted in sociological and anthropological studies, polyculturalism provides a framework for analyzing multicultural societies through the lens of cultural blending and ongoing transformation.
Historical Contexts Shaping Interculturalism and Polyculturalism
Interculturalism emerged largely in Quebec during the late 20th century as a response to tensions between majority and minority cultures, emphasizing dialogue and shared values within a framework that respects cultural differences. Polyculturalism, rooted in postcolonial critiques and ethnic studies since the 1990s, challenges fixed cultural boundaries by highlighting overlapping histories and interactions across diverse groups. The historical development of interculturalism reflects efforts to manage cultural coexistence in plural societies, while polyculturalism centers on hybridity and dynamic cultural exchanges shaped by migration and globalization.
Core Principles: Interculturalism vs Polyculturalism
Interculturalism emphasizes dialogue, mutual respect, and interaction between diverse cultural groups within a society to foster social cohesion and understanding. Polyculturalism highlights the fluid, dynamic exchanges and interconnections among cultures, recognizing cultural hybridity and shared influences rather than isolated identities. Core principles of interculturalism prioritize integration and bridging cultural divides, whereas polyculturalism centers on the interconnectedness and complexity of cultural identities over time.
Comparative Analysis: Similarities and Differences
Interculturalism and polyculturalism both emphasize the dynamic interaction and mutual influence of diverse cultures within a society, promoting dialogue and shared understanding. Interculturalism focuses on fostering communication and cooperation between distinct cultural groups while maintaining their unique identities, whereas polyculturalism highlights the fluid, interconnected nature of cultures blending and evolving through continuous contact and exchange. Both frameworks challenge cultural essentialism, but interculturalism tends to prioritize coexistence and respect for difference, while polyculturalism underscores hybridity and cultural mixing as fundamental to identity formation.
Societal Impacts on Identity and Community
Interculturalism promotes dialogue and mutual respect among diverse cultural groups, fostering social cohesion while preserving distinct identities within communities. Polyculturalism emphasizes fluidity and shared cultural influences, encouraging hybrid identities that transcend traditional boundaries and enhance social integration. Both frameworks impact societal identity by shaping how individuals relate to their heritage and community, influencing inclusion, conflict resolution, and collective belonging.
Policy Implications in Multicultural Societies
Interculturalism emphasizes active dialogue and interaction between distinct cultural groups, promoting policies that foster social cohesion through mutual respect and shared public spaces. Polyculturalism advocates for recognizing the fluidity and interconnectedness of cultures, encouraging policies that highlight cultural hybridity and dynamic identities within multicultural societies. Both approaches influence integration strategies, with interculturalism prioritizing participatory governance and polyculturalism supporting adaptable educational curricula reflecting diverse cultural narratives.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Interculturalism faces challenges related to maintaining equitable dialogue while avoiding superficial exchanges that may overlook deeper systemic inequalities. Polyculturalism is criticized for oversimplifying cultural interactions by emphasizing blending and hybridity, which can obscure power dynamics and historical contexts. Both approaches struggle with balancing cultural respect and integration without reinforcing stereotypes or cultural dominance.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications and Outcomes
Case studies in interculturalism demonstrate effective integration policies in cities like Montreal, where emphasis on dialogue and mutual respect fosters social cohesion amid diversity. In contrast, polyculturalism, as observed in Singapore, highlights dynamic cultural intermixing that promotes innovation and hybrid identities through everyday interactions. These real-world applications reveal that interculturalism prioritizes structured engagement strategies, whereas polyculturalism thrives on fluid, organic cultural exchanges, each yielding distinct social outcomes.
Future Perspectives: Towards Inclusive Cultural Models
Interculturalism emphasizes dialogue and mutual respect among distinct cultural groups, promoting coexistence through structured interaction frameworks that foster societal cohesion. Polyculturalism highlights the dynamic blending and interconnectedness of cultures, encouraging fluid identities and continuous cultural exchange as drivers of social innovation. Future inclusive cultural models prioritize hybrid approaches integrating both intercultural dialogue and polycultural blending to enhance social integration, equity, and global citizenship in increasingly diverse societies.
Interculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com