Folk culture preserves traditional customs, beliefs, and practices passed down through generations, reflecting the identity and values of a community. It often includes music, dance, storytelling, crafts, and festivals that connect people to their heritage and foster a sense of belonging. Discover how your understanding of folk culture deepens by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
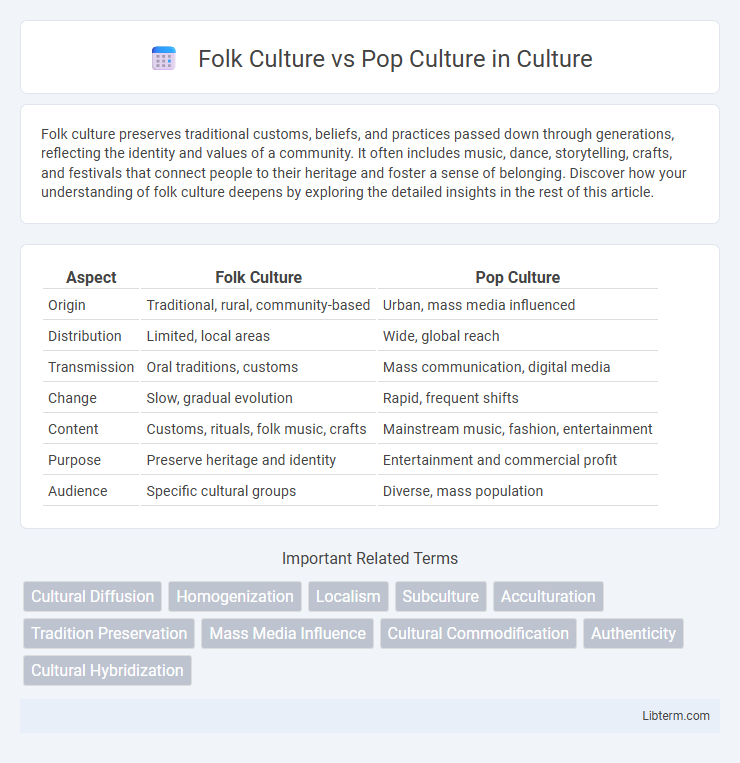
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Folk Culture | Pop Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Traditional, rural, community-based | Urban, mass media influenced |
| Distribution | Limited, local areas | Wide, global reach |
| Transmission | Oral traditions, customs | Mass communication, digital media |
| Change | Slow, gradual evolution | Rapid, frequent shifts |
| Content | Customs, rituals, folk music, crafts | Mainstream music, fashion, entertainment |
| Purpose | Preserve heritage and identity | Entertainment and commercial profit |
| Audience | Specific cultural groups | Diverse, mass population |
Defining Folk Culture and Pop Culture
Folk culture refers to the traditional practices, customs, and expressions shared among small, homogeneous groups often rooted in rural or isolated communities, characterized by oral traditions, handcrafted artifacts, and localized rituals. Pop culture encompasses the mainstream ideas, trends, music, fashion, and entertainment widely disseminated through mass media and embraced by heterogeneous urban populations globally. While folk culture emphasizes historical continuity and community identity, pop culture evolves rapidly, influenced by technology, commercialization, and global connectivity.
Historical Origins of Folk and Pop Traditions
Folk culture originates from localized communities with traditions passed down orally and shaped by historical contexts such as agricultural practices and regional beliefs. Pop culture emerges from mass media and promotes widespread trends influenced by urbanization and technological advancements since the 20th century. The historical origins of folk culture reflect slow cultural evolution tied to specific ethnic groups, while pop culture evolves rapidly from commercial entertainment industries and globalization.
Characteristics of Folk Culture
Folk culture is characterized by its strong connection to traditional practices, local communities, and customs passed down through generations, often rooted in rural environments. It emphasizes collective identity, oral traditions, and handcrafted artifacts that reflect the values and beliefs of specific cultural groups. This culture tends to resist rapid change, maintaining continuity through rituals, festivals, and folk songs that reinforce community cohesion.
Characteristics of Pop Culture
Pop culture is characterized by its widespread appeal and rapid diffusion through mass media, making trends in music, fashion, and entertainment accessible globally. It is dynamic, constantly evolving with consumer preferences and technological advances, often reflecting current societal norms and commercial interests. Unlike folk culture, pop culture values mass production and commercialization, emphasizing novelty and mainstream popularity over tradition and localized practices.
Transmission and Spread of Culture
Folk culture is transmitted mainly through oral tradition, family, and community interactions, preserving customs within localized, homogeneous groups. Pop culture spreads rapidly and widely via mass media, technology, and globalization, influencing diverse, heterogeneous populations across regions and countries. This swift diffusion results in continuous cultural exchange and adaptation, distinguishing it from the slower, more stable transmission of folk traditions.
Geographic Distribution and Local Identity
Folk culture is typically confined to specific geographic regions, often rural or isolated areas, preserving traditional practices that reinforce local identity and community cohesion. Pop culture, by contrast, spreads rapidly across vast geographic areas through mass media and globalization, leading to more homogenized cultural expressions and diminished emphasis on local uniqueness. The geographic concentration of folk culture fosters strong regional identity, while the widespread distribution of pop culture promotes shared global trends.
Influence of Technology on Pop Culture
Technology profoundly shapes pop culture by accelerating the dissemination of trends through social media platforms, streaming services, and digital communication tools. This rapid exchange fosters global connectivity, enabling pop culture to evolve dynamically and reach diverse audiences instantly. Unlike folk culture, which is traditionally localized and transmitted orally, pop culture thrives on technological advancements that amplify its reach and influence worldwide.
Impact on Social Values and Norms
Folk culture preserves traditional social values and norms by emphasizing community-based practices and local customs, fostering a strong sense of identity and continuity. Pop culture, driven by mass media and commercialization, often challenges and reshapes these norms through widespread dissemination of new ideas, trends, and behaviors. The interaction between folk and pop cultures can lead to both the reinforcement of heritage and the evolution of social values in contemporary society.
Examples of Folk Culture in Modern Society
Folk culture in modern society is exemplified by traditional crafts like Amish quilting and Native American beadwork, which preserve ancestral techniques and cultural identity. Rural festivals such as Japan's Obon and Mexico's Day of the Dead celebrate age-old customs through music, dance, and rituals, reinforcing community bonds. Handcrafted folk music and storytelling, found in regions like Appalachia and Ireland, continue to pass down historical narratives and values amid globalized pop culture influences.
The Future of Folk and Pop Culture
The future of folk culture hinges on preserving traditional practices through digital archiving and community-driven initiatives, ensuring resilience amid globalization's influence on popular culture. Pop culture will continue evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovation, social media platforms, and global connectivity, shaping trends at an unprecedented scale. Both cultures increasingly intersect as folk elements are incorporated into mainstream media, creating hybrid identities that reflect diverse cultural expressions.
Folk Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com