Popular religion often reflects the beliefs and practices embraced by the general population, influencing cultural traditions and social behaviors. State religion, on the other hand, is officially recognized and supported by the government, impacting legislation and public policies. Discover how your understanding of these concepts can deepen by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
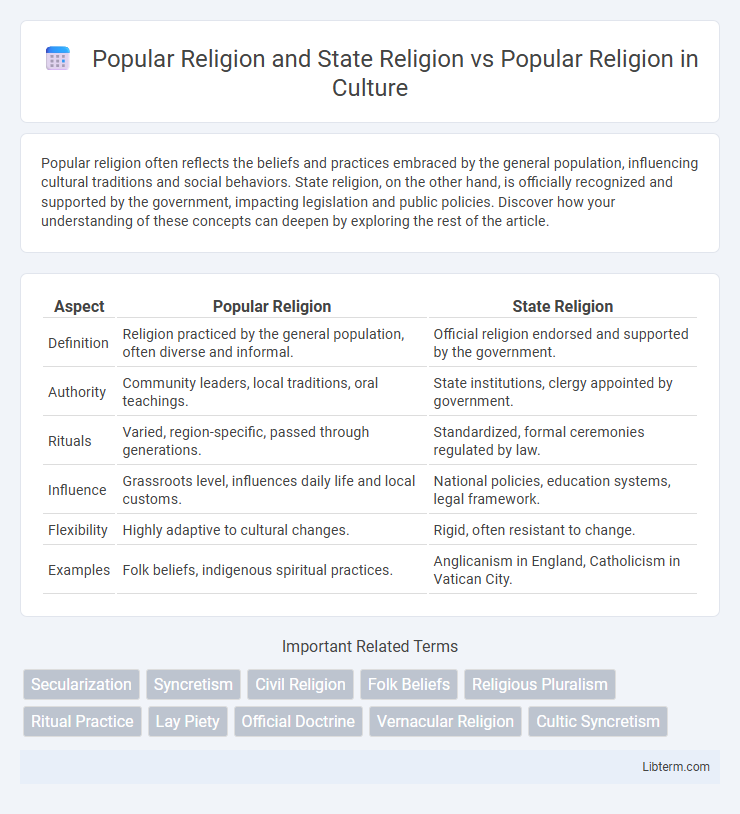
| Aspect | Popular Religion | State Religion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Religion practiced by the general population, often diverse and informal. | Official religion endorsed and supported by the government. |
| Authority | Community leaders, local traditions, oral teachings. | State institutions, clergy appointed by government. |
| Rituals | Varied, region-specific, passed through generations. | Standardized, formal ceremonies regulated by law. |
| Influence | Grassroots level, influences daily life and local customs. | National policies, education systems, legal framework. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptive to cultural changes. | Rigid, often resistant to change. |
| Examples | Folk beliefs, indigenous spiritual practices. | Anglicanism in England, Catholicism in Vatican City. |
Defining Popular Religion: Beliefs and Practices
Popular religion encompasses the everyday beliefs and practices of ordinary people, often blending official doctrines with local customs, rituals, and folk traditions. It emphasizes personal spirituality, magic, healing, and communal ceremonies that may diverge from formal theological teachings. This contrasts with state religion, which represents officially endorsed doctrines and institutionalized rituals sanctioned by political authorities.
Understanding State Religion: Official Faiths and Policies
State religion refers to an official faith or creed endorsed and supported by a government, often influencing national laws and cultural practices. Popular religion embodies the beliefs and rituals practiced by the general population, which may differ significantly from the state's officially sanctioned faith. Understanding state religion involves examining how government policies promote certain religious doctrines and regulate religious institutions to maintain social cohesion or assert political authority.
Historical Interactions Between State and Popular Religions
Historical interactions between state and popular religions often reveal a dynamic tension where state religions seek to institutionalize faith through official doctrines and rituals, while popular religions represent grassroots beliefs and practices shaped by local communities. State religions, such as Christianity in the Roman Empire or Buddhism in imperial China, were used to legitimize political authority, whereas popular religions maintained diverse, syncretic traditions that persisted despite official suppression. These interactions significantly influenced cultural development, social cohesion, and political control across civilizations.
Popular Religion vs State Religion: Key Differences
Popular religion refers to the grassroots religious practices and beliefs embraced by ordinary people, often reflecting local customs and traditions. State religion is officially endorsed and supported by the government, shaping laws and public policies to reflect its doctrines. The key differences lie in popular religion's decentralized, diverse nature versus state religion's centralized authority and formal integration into governance.
State-Endorsed Religion: Influence on Society and Culture
State-endorsed religion significantly shapes national identity and cultural norms by intertwining religious doctrines with government policies, often influencing education, legal systems, and public ceremonies. This fusion fosters social cohesion and legitimizes political authority, but can also marginalize minority beliefs and restrict religious freedom. The dominant religion's values permeate media, holidays, and moral frameworks, embedding itself into everyday social interactions and cultural expressions.
The Role of Popular Religion in Shaping Social Identity
Popular religion plays a crucial role in shaping social identity by reflecting the collective beliefs, rituals, and practices that resonate with everyday life, often independent of state-imposed religious frameworks. It fosters community cohesion and cultural continuity through shared narratives and local customs that reinforce group solidarity. Unlike state religions that may formalize religious expression, popular religion embodies the dynamic, lived experience of faith that deeply influences individual and collective identities.
Conflict and Cooperation: State Religion vs Popular Belief Systems
State religions often create institutional frameworks that both clash with and incorporate popular belief systems, leading to conflicts over authority and practice. Popular religions resist state control by adapting rituals and beliefs to local contexts, fostering grassroots movements that challenge official doctrines. Cooperation emerges when state authorities co-opt popular symbols and festivals, blending institutional power with grassroots spirituality to maintain social cohesion.
Secularism and Religious Pluralism: Impacts on Popular Religiosity
Secularism promotes a clear distinction between popular religion and state religion, fostering an environment where religious pluralism thrives and diverse faith expressions coexist without government endorsement, resulting in a more individualized popular religiosity. In contrast, when a state religion dominates, popular religiosity often aligns with official doctrines, potentially limiting religious diversity and personal freedom in belief. The impact of secularism on popular religiosity is significant, encouraging inclusivity and adaptation within societies marked by multiple religious traditions.
Case Studies: Popular Religion Flourishing Amid State Faith
Case studies reveal that popular religion often flourishes despite the dominance of state religion, exemplified by the persistent practice of Vodou in Haiti alongside Catholicism, and the growth of Sufism within predominantly Sunni Muslim states like Turkey and Egypt. These examples highlight how grassroots religious movements adapt and sustain diverse beliefs, rituals, and community practices independent from official state-endorsed religions. The coexistence underscores the dynamic interaction between institutional religion and popular faith, emphasizing local agency in religious expression.
The Future of Popular Religion in Changing Political Landscapes
The future of popular religion in changing political landscapes hinges on its adaptability to shifting state policies and societal values. As governments either endorse or suppress specific faiths, popular religion often morphs, maintaining its vitality through grassroots practices and community resilience. Emerging trends indicate that syncretism and digital platforms play crucial roles in sustaining popular religious expressions amid evolving state-religion dynamics.
Popular Religion and State Religion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com