Tradition shapes cultural identity by preserving customs and values passed down through generations. It influences daily life, community practices, and even celebrations, providing a sense of continuity and belonging. Explore the rest of the article to understand how tradition impacts your life and society.
Table of Comparison
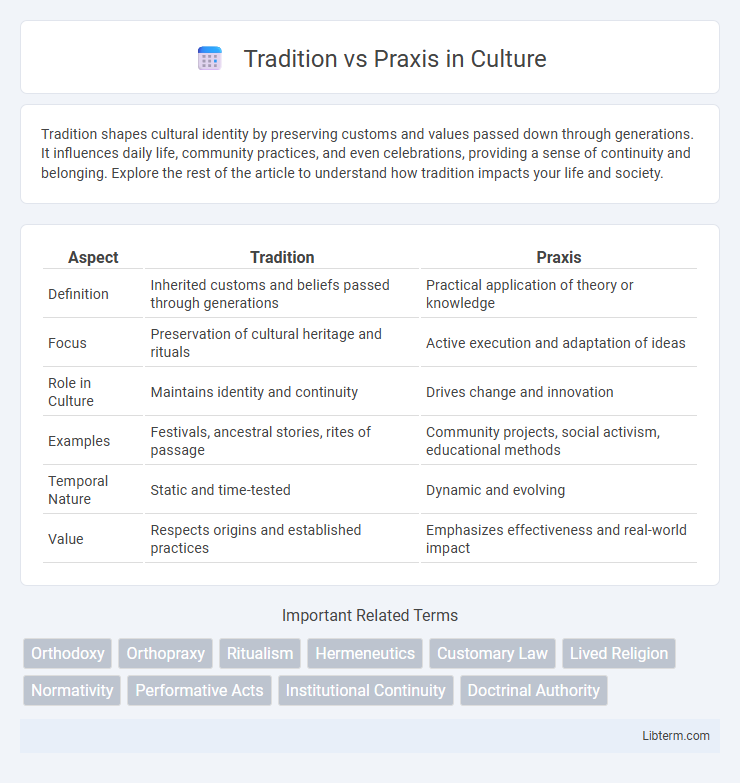
| Aspect | Tradition | Praxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inherited customs and beliefs passed through generations | Practical application of theory or knowledge |
| Focus | Preservation of cultural heritage and rituals | Active execution and adaptation of ideas |
| Role in Culture | Maintains identity and continuity | Drives change and innovation |
| Examples | Festivals, ancestral stories, rites of passage | Community projects, social activism, educational methods |
| Temporal Nature | Static and time-tested | Dynamic and evolving |
| Value | Respects origins and established practices | Emphasizes effectiveness and real-world impact |
Understanding Tradition: Foundations and Significance
Tradition encompasses the inherited customs, beliefs, and practices passed down through generations, serving as a foundational framework for cultural identity and social cohesion. Understanding tradition requires analyzing its historical roots, symbolic meanings, and role in shaping collective memory and values across societies. The significance of tradition lies in its ability to provide continuity, guide behavior, and influence contemporary praxis within diverse communities.
Defining Praxis: Concepts and Applications
Praxis refers to the process by which theory is enacted, embodied, and realized through practical action, emphasizing the dynamic interaction between reflection and practice. Unlike tradition, which embodies inherited customs and established methods, praxis involves critical engagement and adaptive application of knowledge to transform social and political realities. This concept is extensively applied in fields such as education, philosophy, and social activism to bridge the gap between abstract ideas and concrete outcomes.
The Historical Interplay Between Tradition and Praxis
The historical interplay between tradition and praxis reveals how longstanding cultural customs continuously adapt through practical application and lived experience. Traditions provide a foundational framework of inherited knowledge, while praxis embodies the dynamic process of implementing and modifying these traditions in response to changing social, political, and economic contexts. This reciprocal relationship drives societal evolution by balancing preservation with innovation, ensuring cultural continuity alongside progressive transformation.
Theoretical Perspectives: Key Thinkers on Tradition and Praxis
Theoretical perspectives on tradition and praxis are significantly shaped by key thinkers like Antonio Gramsci, who emphasized the role of cultural hegemony in sustaining tradition while advocating praxis as a form of transformative action. Michel Foucault analyzed how power relations embedded in traditions influence social practices and stressed the importance of praxis in challenging dominant discourses. Paulo Freire contributed to this discourse by framing praxis as reflective action aimed at liberation, contrasting it with static tradition that often perpetuates social inequalities.
Tradition as a Source of Cultural Identity
Tradition serves as a foundational source of cultural identity by preserving collective memories, customs, and values passed down through generations, strengthening social cohesion within communities. Rituals, folklore, and established practices embedded in tradition provide a shared sense of belonging and continuity that distinguishes one culture from another. Maintaining these inherited traditions supports cultural resilience and affirms a community's unique historical narrative amid changing societal dynamics.
Praxis: Bridging Theory and Practice
Praxis embodies the dynamic process of applying theoretical knowledge to practical action, ensuring that concepts are tested and refined in real-world contexts. By integrating reflection and iterative experimentation, praxis bridges the gap between abstract ideas and tangible outcomes, fostering continuous learning and adaptation. This approach enhances problem-solving effectiveness by grounding theoretical frameworks in lived experience and contextual nuances.
Conflicts Arising from Tradition vs Praxis in Society
Conflicts arising from tradition versus praxis in society often stem from the tension between established customs and evolving practices that challenge conventional norms. Traditional values, deeply embedded in cultural identity, may resist change brought by new methodologies or progressive ideologies, leading to disputes across generations or social groups. This clash can hinder social development, sparking debates on the legitimacy of customs versus the necessity for pragmatic adaptations in governance, education, and social behavior.
Adapting Traditions: Evolving Praxis in Modern Contexts
Adapting traditions involves reinterpreting established customs to align with contemporary societal values and technological advancements, ensuring their relevance and sustainability. Evolving praxis emphasizes the dynamic application of these traditions in modern contexts, fostering innovation while preserving cultural identity. Integrating historical knowledge with current practices allows communities to maintain continuity amid rapid social change.
Contemporary Case Studies: Tradition Challenged by Praxis
Contemporary case studies reveal how traditional cultural practices face challenges when pragmatic, context-driven praxis reshapes social norms, such as the disruption of caste-based rituals by grassroots social movements in India. In urban African communities, indigenous healing rituals encounter transformation through integration with modern medical practices, highlighting the tension between ancestral knowledge and empirical innovation. These examples underscore the dynamic interplay between entrenched traditions and evolving praxis, emphasizing the need for adaptive frameworks that respect heritage while promoting practical, ethical progress.
Finding Balance: Harmonizing Tradition and Praxis
Finding balance between tradition and praxis involves integrating time-honored customs with practical application to create adaptive and meaningful practices. Emphasizing contextual adaptability ensures that traditional values remain relevant while addressing contemporary challenges. This harmonization fosters sustainable development by respecting heritage and encouraging innovative problem-solving.
Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com