Vernacular dialects embody the unique linguistic characteristics spoken by everyday people within a specific region or community, reflecting cultural identity and local traditions. These dialects often include distinct vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation that differentiate them from standard language forms. Discover how understanding vernacular dialects can enhance your appreciation of language diversity and cultural heritage in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
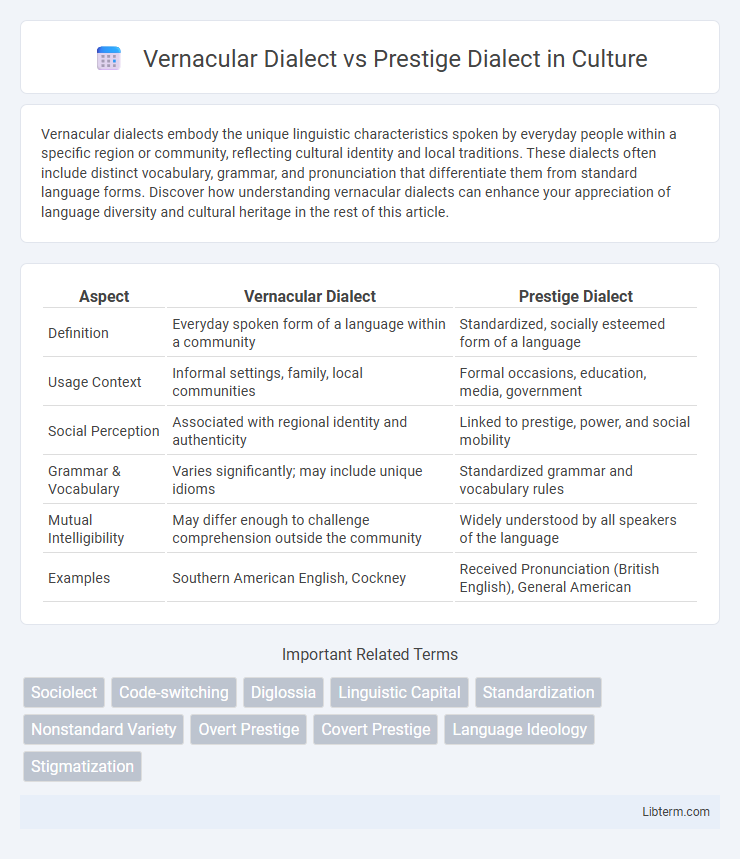
| Aspect | Vernacular Dialect | Prestige Dialect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Everyday spoken form of a language within a community | Standardized, socially esteemed form of a language |
| Usage Context | Informal settings, family, local communities | Formal occasions, education, media, government |
| Social Perception | Associated with regional identity and authenticity | Linked to prestige, power, and social mobility |
| Grammar & Vocabulary | Varies significantly; may include unique idioms | Standardized grammar and vocabulary rules |
| Mutual Intelligibility | May differ enough to challenge comprehension outside the community | Widely understood by all speakers of the language |
| Examples | Southern American English, Cockney | Received Pronunciation (British English), General American |
Introduction to Vernacular and Prestige Dialects
Vernacular dialects represent the everyday language spoken by ordinary people within a specific region or social group, often characterized by informal grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Prestige dialects, however, are associated with social status, education, and power, often used in formal settings and considered the standard or "correct" form of language. Understanding the distinction between vernacular and prestige dialects reveals the social dynamics and cultural identity embedded in language use.
Defining Vernacular Dialect
Vernacular dialect refers to the everyday language spoken by ordinary people in a particular region or social group, characterized by informal vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation distinct from standardized forms. It often reflects the cultural identity and social background of its speakers, serving as a marker of local or community affiliation. Unlike prestige dialects, vernacular dialects lack widespread social recognition or institutional support but hold significant linguistic authenticity.
Understanding Prestige Dialect
Prestige dialect refers to the variety of a language associated with social power, education, and upward mobility, often used in formal settings and media. It is considered the standard form, influencing perceptions of correctness and intelligence, and typically taught in schools to promote social cohesion. Understanding prestige dialect involves recognizing its role in social stratification and how it impacts language attitudes and identity.
Historical Evolution of Dialects
Vernacular dialects historically developed as localized speech varieties shaped by social, geographic, and cultural factors, preserving unique linguistic features within communities. Prestige dialects emerged through processes of social stratification and institutional influence, often linked to centers of political power, education, and economic dominance. Over time, the interaction between vernacular and prestige dialects influenced language standardization, identity, and social mobility across different regions.
Social Factors Influencing Dialect Status
Social factors such as socioeconomic status, education level, and occupation significantly influence the status of vernacular and prestige dialects. Prestige dialects are typically associated with higher social classes, formal education, and professional environments, conferring social mobility and acceptance. Vernacular dialects are often linked to local identity, community solidarity, and lower social prestige, reflecting historical, cultural, and regional backgrounds.
Linguistic Features: Vernacular vs Prestige
Vernacular dialects often exhibit unique phonological, morphological, and syntactic features that differ from standardized norms, reflecting local identity and natural language evolution. Prestige dialects typically adhere to codified grammar rules, standardized vocabulary, and pronunciation, serving as markers of social status and education. The divergence in linguistic features between vernacular and prestige dialects highlights the interplay between language variation and social hierarchy.
Educational Impacts of Dialect Differences
Vernacular dialects often present challenges in educational settings where prestige dialects dominate, leading to potential misunderstandings and biased assessments of student abilities. Students speaking vernacular dialects may face difficulties in standardized testing and classroom communication, which can affect academic performance and self-esteem. Incorporating dialect awareness and inclusive teaching strategies fosters equitable learning opportunities and respects linguistic diversity.
Media Representation of Dialects
Media representation often favors prestige dialects, reinforcing social hierarchies and marginalizing vernacular dialects despite their cultural richness. Television, film, and news outlets predominantly showcase standardized language, shaping public perceptions that associate prestige dialects with intelligence and professionalism. This portrayal limits the visibility and legitimacy of vernacular dialects, affecting speakers' social identity and access to opportunities.
Dialect and Identity: Cultural Implications
Dialect serves as a powerful marker of cultural identity, with vernacular dialects often embodying local traditions, histories, and community values that reinforce social cohesion. Prestige dialects, typically associated with social power and educational institutions, can influence perceptions of credibility and status but may also contribute to stigmatization or marginalization of speakers of non-prestige varieties. The interplay between vernacular and prestige dialects shapes individual and group identities, reflecting cultural pride or social aspiration within multicultural societies.
Conclusion: Bridging Dialectal Divides
Bridging the divide between vernacular and prestige dialects involves recognizing the equal linguistic value and cultural significance of each. Promoting inclusive education and media representation fosters mutual respect and reduces social stigmas associated with vernacular speech. Emphasizing communication across dialects enhances social cohesion and preserves linguistic diversity.
Vernacular Dialect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com