Habit formation shapes daily routines and influences long-term success by reinforcing behaviors through repetition. Understanding the psychological mechanisms behind habits can empower you to build positive patterns and eliminate negative ones effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for mastering your habits and transforming your life.
Table of Comparison
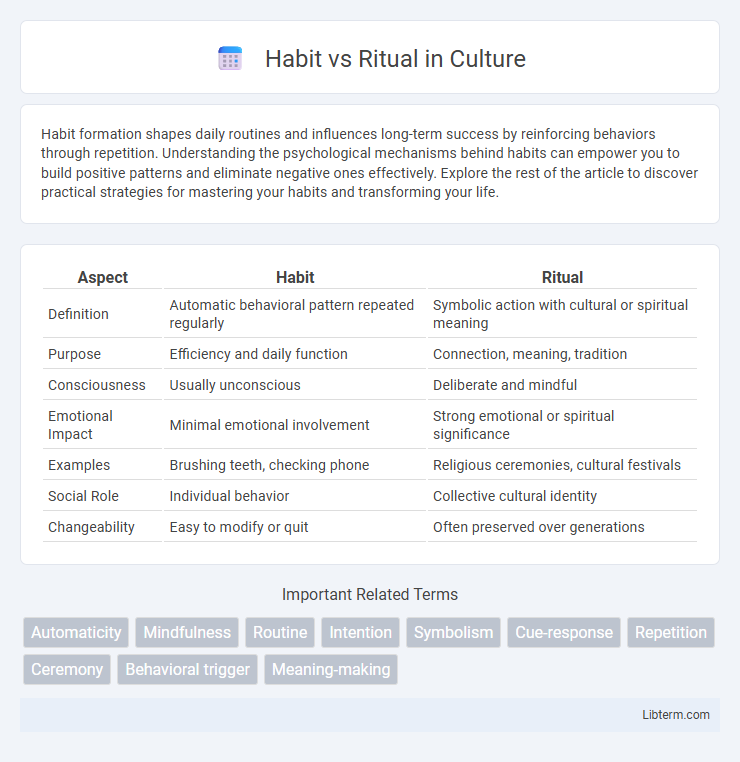
| Aspect | Habit | Ritual |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatic behavioral pattern repeated regularly | Symbolic action with cultural or spiritual meaning |
| Purpose | Efficiency and daily function | Connection, meaning, tradition |
| Consciousness | Usually unconscious | Deliberate and mindful |
| Emotional Impact | Minimal emotional involvement | Strong emotional or spiritual significance |
| Examples | Brushing teeth, checking phone | Religious ceremonies, cultural festivals |
| Social Role | Individual behavior | Collective cultural identity |
| Changeability | Easy to modify or quit | Often preserved over generations |
Understanding the Basics: What Are Habits and Rituals?
Habits are automatic, repetitive behaviors triggered by specific cues, often performed unconsciously to achieve efficiency in daily life. Rituals involve deliberate, meaningful actions imbued with symbolic value, typically practiced with intention to create a sense of purpose or connection. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize personal growth by identifying when routine behaviors can be transformed into purposeful, mindful practices.
Key Differences Between Habits and Rituals
Habits are automatic behaviors triggered by specific cues and performed unconsciously, while rituals are deliberate actions infused with meaning and intention. Habits often serve practical purposes such as brushing teeth or checking notifications, whereas rituals create emotional or symbolic significance, like morning meditation or wedding ceremonies. The key difference lies in consciousness and purpose: habits run on autopilot to streamline daily tasks, rituals consciously reinforce values or beliefs.
The Psychology Behind Habits
Habits are automatic behaviors triggered by contextual cues, formed through repetition and reinforcement, engaging the brain's basal ganglia to streamline routine actions. Rituals, in contrast, involve deliberate, meaningful sequences often tied to emotions and social identity, activating broader brain networks associated with intention and significance. Understanding the psychology behind habits reveals how neural pathways solidify behavior patterns, enabling efficient energy use while rituals provide cognitive and emotional anchors beyond mere automaticity.
Rituals: Meaning, Purpose, and Impact
Rituals are structured, intentional actions performed with symbolic meaning, often reinforcing social bonds and cultural identity. Unlike habits, rituals carry a deeper psychological purpose, promoting mindfulness, emotional regulation, and a sense of belonging. Research shows that engaging in rituals can enhance mental well-being, reduce anxiety, and increase focus by creating consistent moments of meaning in daily life.
Formation: How Habits and Rituals Develop
Habits form through repetitive actions triggered by specific cues, creating automatic behavior patterns reinforced by rewards, often emerging unconsciously over time. Rituals develop intentionally with symbolic meaning, structured sequences performed purposefully to convey significance, often cultivated within cultural or personal contexts. Habit formation relies on neural pathways strengthening through repetition, while rituals engage cognitive and emotional processes to establish meaningful routines.
The Role of Intention in Habits vs Rituals
Habits operate through automatic behavior triggered by environmental cues with minimal conscious intention, reinforcing routine efficiency and mental economy. Rituals require deliberate intention and mindfulness, serving as meaningful practices that promote emotional well-being and personal significance. The intentionality in rituals distinguishes them from habits, embedding purpose and symbolic value into repetitive actions.
Benefits of Habits for Productivity and Health
Habits enhance productivity by automating routine tasks, reducing decision fatigue, and freeing mental energy for complex problem-solving. Consistent healthy habits, such as regular exercise and balanced nutrition, improve physical wellness and boost cognitive function. Building positive habits fosters discipline and long-term success through incremental progress and sustained motivation.
The Power of Rituals in Daily Life
Rituals harness the power of intentionality and mindfulness, transforming simple routines into meaningful practices that reinforce identity and emotional well-being. Unlike habits, which often operate on autopilot, rituals engage the senses and create a purposeful structure that enhances focus, reduces stress, and fosters connection. Neuroscientific studies show that rituals activate the brain's reward system, strengthening motivation and resilience in daily life.
Breaking Bad Habits and Creating Positive Rituals
Breaking bad habits requires consistent self-awareness and deliberate changes in behavior patterns often triggered by specific cues. Creating positive rituals involves embedding intentional actions into daily routines that promote well-being and productivity, reinforcing desired outcomes through repetition. Replacing negative behaviors with meaningful rituals enhances habit formation by leveraging psychological cues and reward mechanisms, leading to sustainable personal growth.
Choosing Between Habit and Ritual for Personal Growth
Selecting between habit and ritual for personal growth depends on the intention behind the action and its emotional impact. Habits are automatic behaviors that conserve mental energy, while rituals are purposeful activities imbued with meaning that foster mindfulness and self-awareness. Emphasizing rituals over habits can enhance motivation and deepen the transformational experience during personal development.
Habit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com