Isolation can significantly impact mental health, leading to feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Creating meaningful social connections and engaging in regular activities are essential strategies to combat isolation. Discover effective ways to overcome isolation and improve your well-being in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
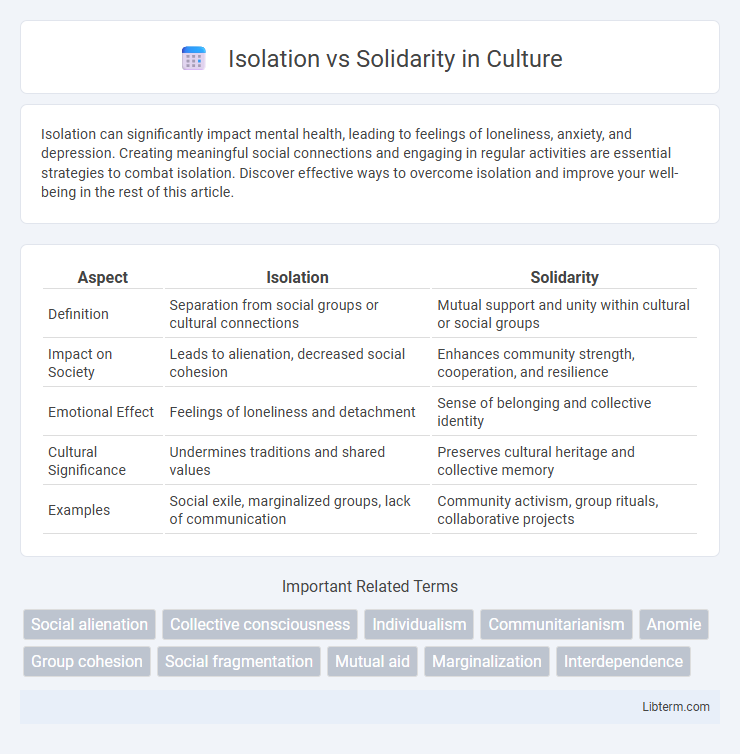
| Aspect | Isolation | Solidarity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separation from social groups or cultural connections | Mutual support and unity within cultural or social groups |
| Impact on Society | Leads to alienation, decreased social cohesion | Enhances community strength, cooperation, and resilience |
| Emotional Effect | Feelings of loneliness and detachment | Sense of belonging and collective identity |
| Cultural Significance | Undermines traditions and shared values | Preserves cultural heritage and collective memory |
| Examples | Social exile, marginalized groups, lack of communication | Community activism, group rituals, collaborative projects |
Understanding Isolation: Definition and Impacts
Isolation refers to the state of being separated from others, often leading to feelings of loneliness and emotional distress. Prolonged isolation can significantly impact mental health, increasing risks of anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline. Understanding isolation involves recognizing both its psychological effects and the social factors contributing to physical or emotional detachment.
The Psychology Behind Solidarity
Solidarity fosters a deep psychological sense of belonging, essential for mental well-being and resilience during adversity. It activates brain regions associated with empathy, trust, and social bonding, releasing oxytocin which enhances cooperation and reduces stress. Understanding the neuroscience behind solidarity highlights its role in combating feelings of isolation and promoting collective emotional strength.
Causes of Social Isolation
Social isolation often stems from factors such as mental health issues, chronic illness, and significant life changes, including bereavement or relocation. Economic hardships and lack of social support networks contribute significantly to an individual's withdrawal from community interactions. Modern societal trends like increased digital communication also reduce face-to-face connections, intensifying feelings of isolation despite virtual connectivity.
Benefits of Community Solidarity
Community solidarity enhances emotional resilience by fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support, which reduces feelings of isolation and stress. Shared resources and collective problem-solving improve overall wellbeing, enabling individuals to access assistance and opportunities more efficiently. Social cohesion within communities promotes trust and cooperation, creating safer and more inclusive environments for all members.
Mental Health: Isolation vs. Solidarity
Isolation intensifies feelings of loneliness and exacerbates mental health issues such as depression and anxiety due to the lack of social support and meaningful connections. Solidarity promotes emotional resilience by fostering a sense of belonging, mutual support, and shared purpose, which significantly improves psychological well-being. Studies indicate that social integration and community participation reduce stress hormones and enhance cognitive function, underscoring the importance of solidarity in mental health recovery.
Social Media’s Role: Separating or Uniting Us?
Social media platforms create both isolation and solidarity by shaping online communities and personal interactions. Algorithms often promote echo chambers, intensifying social isolation by limiting exposure to diverse perspectives while also enabling marginalized groups to find solidarity and mobilize support globally. The dual nature of social media influences societal cohesion, highlighting the need for intentional digital engagement to foster genuine connection over fragmentation.
Strategies to Overcome Isolation
Effective strategies to overcome isolation include fostering social connections through community groups and virtual platforms that encourage meaningful interaction. Promoting mental health awareness and providing access to counseling services help individuals develop coping skills and resilience. Encouraging participation in collaborative projects and volunteer work strengthens solidarity by creating shared purpose and mutual support networks.
Building and Sustaining Solidarity
Building and sustaining solidarity requires intentional communication, shared goals, and mutual support among individuals or groups facing common challenges. Establishing trust and fostering empathy help transform isolation into a collective strength that promotes resilience and social cohesion. Collaborative efforts, such as community organizing and inclusive decision-making, enhance the durability of solidarity in diverse social contexts.
Real-World Cases: Isolation and Solidarity in Action
Real-world examples illustrate isolation through the quarantine measures during the COVID-19 pandemic, where social distancing prevented virus spread but increased feelings of loneliness. In contrast, solidarity emerged as communities organized mutual aid networks, providing food and emotional support to vulnerable populations, demonstrating collective resilience. These cases highlight how isolation can challenge mental health, whereas solidarity fosters social cohesion and shared responsibility.
Choosing Connection: Pathways to Solidarity
Choosing connection over isolation fosters collective resilience by encouraging empathy, shared goals, and mutual support. Pathways to solidarity include community engagement, active listening, and inclusive dialogue that bridge differences and build trust. These practices enhance social cohesion and empower individuals to address common challenges collaboratively.
Isolation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com