Transculture explores the blending and interaction of different cultural identities, creating dynamic and hybrid social experiences. This process influences communication, art, and societal norms, reflecting the evolving nature of global connectivity. Discover how transculture shapes your world and the importance it holds in today's interconnected society by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
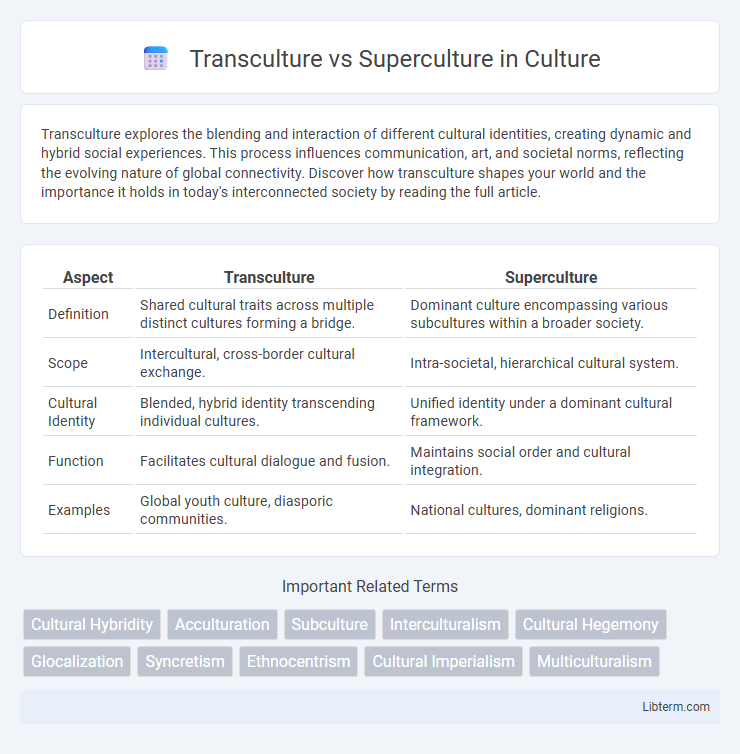
| Aspect | Transculture | Superculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared cultural traits across multiple distinct cultures forming a bridge. | Dominant culture encompassing various subcultures within a broader society. |
| Scope | Intercultural, cross-border cultural exchange. | Intra-societal, hierarchical cultural system. |
| Cultural Identity | Blended, hybrid identity transcending individual cultures. | Unified identity under a dominant cultural framework. |
| Function | Facilitates cultural dialogue and fusion. | Maintains social order and cultural integration. |
| Examples | Global youth culture, diasporic communities. | National cultures, dominant religions. |
Understanding Transculture: Definition and Key Concepts
Transculture refers to the dynamic process through which individuals and groups integrate and navigate multiple cultural identities, creating hybrid cultural experiences that transcend traditional boundaries. It involves the blending and interaction of cultural elements, fostering intercultural dialogue and mutual understanding within diverse societies. Key concepts include cultural fluidity, identity negotiation, and the coexistence of multiple cultural frameworks within a single social context.
Exploring Superculture: Origins and Characteristics
Superculture emerges as a dominant cultural framework that transcends individual cultures by integrating shared values, symbols, and practices, often rooted in globalization and technological advancements. Its characteristics include widespread cultural homogenization, the prominence of universal language elements like English, and the diffusion of mass media influencing global social norms. The origins of superculture trace back to intensified intercultural exchanges and economic interdependencies that foster common cultural experiences across diverse populations.
Historical Evolution: Transculture vs Superculture
Transculture evolves through the continuous interaction and exchange between distinct cultures, generating hybrid identities and shared meanings that transcend original cultural boundaries. Superculture emerges as an overarching cultural system dominated by a powerful or majority culture imposing norms and values on subordinate groups, often resulting from colonialism or globalization processes. Historically, transculturation facilitated mutual adaptation among indigenous and colonial societies in Latin America, while superculture predominates in modern nation-states where centralized ideologies unify diverse ethnic groups under a singular cultural identity.
Cultural Adaptation: How Transcultures Emerge
Transcultures emerge through dynamic cultural adaptation processes where individuals and groups blend elements from multiple cultures, creating hybrid identities beyond traditional boundaries. This intercultural exchange fosters mutual influence, allowing for the simultaneous coexistence and transformation of cultural traits rather than dominance by one culture. Unlike supercultures that impose a unified cultural framework, transcultures evolve organically from reciprocal interactions and shared experiences across diverse societies.
Superculture Dominance: Mechanisms and Impacts
Superculture dominance manifests through mechanisms such as cultural imperialism, economic globalization, and media homogenization, which facilitate the spread and reinforcement of dominant cultural values over others. These processes lead to significant impacts including the erosion of local traditions, language loss, and reduced cultural diversity, often marginalizing transcultural identities. The overwhelming influence of superculture reshapes social norms and power structures, creating a homogenized global culture that prioritizes dominant ideologies and practices.
Identity Formation: Navigating Between Transculture and Superculture
Identity formation involves navigating the fluid exchanges of transculture, where individuals integrate and adapt elements from multiple cultural frameworks, creating hybrid identities. Superculture operates as an overarching cultural system imposing dominant values and norms, often shaping collective identity through homogenization processes. Understanding the tension between transculture's dynamic hybridity and superculture's normative pressures is essential for grasping contemporary identity construction in globalized contexts.
Globalization’s Role in Shaping Transculture and Superculture
Globalization accelerates the blending of diverse cultural elements into transcultures, creating dynamic hybrid identities that transcend traditional cultural boundaries. Superculture emerges as a dominant, overarching cultural framework shaped by global interconnectedness, influencing local customs and social norms worldwide. The continuous exchange of ideas, technology, and trade sustains the evolution of both transcultures and superculture, highlighting globalization's pivotal role in cultural convergence and transformation.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Transculture vs Superculture
Case studies illustrating Transculture vs Superculture highlight how global brands like McDonald's adapt menus to local tastes, exemplifying transculture by blending global and local cultural elements. In contrast, the Superculture model is evident in international institutions such as the United Nations, where common cultural frameworks unify diverse national identities under overarching protocols and values. These examples reveal transculture's fluid cultural exchanges versus superculture's structured cultural integration in real-world contexts.
Challenges and Conflicts: When Transculture Meets Superculture
When transculture intersects with superculture, challenges arise from conflicting values, communication barriers, and power dynamics that complicate cultural integration. Misunderstandings often stem from differing worldviews and social norms, leading to identity struggles and resistance within both cultural groups. Navigating these tensions requires adaptive strategies to promote mutual respect and inclusive dialogue while addressing inherent inequalities.
Future Trends: The Interplay of Transculture and Superculture in a Connected World
Future trends in globalization highlight the dynamic interplay between transculture and superculture, where transculture facilitates the blending of diverse cultural identities through cross-cultural interaction, and superculture represents an overarching, dominant cultural framework shaping collective values. Digital connectivity accelerates transcultural exchanges by enabling real-time communication and cultural adaptation, while superculture influences global norms via media, technology, and economic power centers. This interaction drives increased cultural hybridity, fostering innovation and reshaping social structures in an interconnected world.
Transculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com