Subsurface culture encompasses the hidden and often intangible aspects of society, including beliefs, values, and norms that influence behavior beneath the surface. Understanding these deeper cultural layers can reveal why certain actions or traditions persist within communities. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how subsurface culture shapes your everyday interactions and societal dynamics.
Table of Comparison
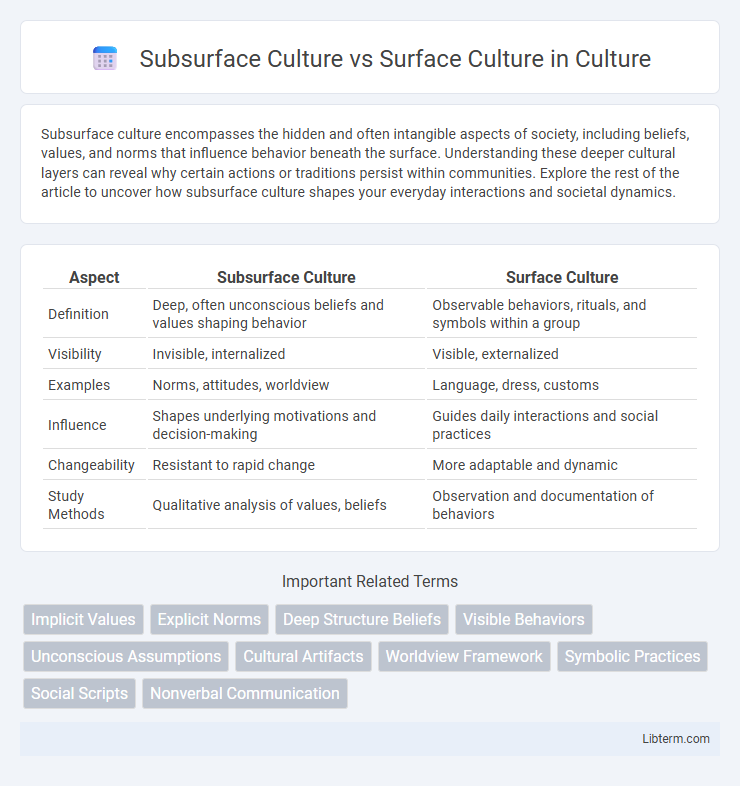
| Aspect | Subsurface Culture | Surface Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deep, often unconscious beliefs and values shaping behavior | Observable behaviors, rituals, and symbols within a group |
| Visibility | Invisible, internalized | Visible, externalized |
| Examples | Norms, attitudes, worldview | Language, dress, customs |
| Influence | Shapes underlying motivations and decision-making | Guides daily interactions and social practices |
| Changeability | Resistant to rapid change | More adaptable and dynamic |
| Study Methods | Qualitative analysis of values, beliefs | Observation and documentation of behaviors |
Introduction to Subsurface and Surface Cultures
Subsurface culture refers to the deeper, often unconscious values, beliefs, and thought patterns that subtly influence behavior within a group, while surface culture includes visible elements like language, dress, customs, and rituals easily observed by outsiders. Understanding subsurface culture requires examining implicit assumptions and worldviews that shape communication and social interactions beneath the observable cultural expressions. Surface culture is accessible through direct observation, but subsurface culture provides critical context for interpreting behaviors and avoiding misunderstandings in cross-cultural exchanges.
Defining Subsurface Culture: Key Characteristics
Subsurface culture is characterized by implicit values, deep-rooted beliefs, and unspoken social norms that govern behavior beneath the visible surface of a society. It includes rituals, thought patterns, and emotional expressions that remain concealed from outsiders but profoundly influence interpersonal interactions and decision-making. Unlike surface culture, which is observable through language, dress, and customs, subsurface culture shapes identity and worldview through ingrained cognitive frameworks and subconscious traditions.
Surface Culture: What It Encompasses
Surface culture encompasses observable behaviors and customs such as language, clothing, food, rituals, and social etiquette easily seen and experienced by outsiders. It includes material artifacts, traditions, and public celebrations that represent a society's visible identity. Understanding surface culture provides initial insight but requires deeper exploration of underlying beliefs and values found in subsurface culture for comprehensive cultural awareness.
Historical Context of Cultural Layers
Subsurface culture encompasses the underlying values, beliefs, and norms that shape a society's identity over time, often remaining hidden from immediate awareness, while surface culture includes visible expressions such as language, rituals, and customs. Historically, surface culture reflects tangible elements like art, dress, and social behaviors prominent in a given era, whereas subsurface culture represents the deep-rooted ideologies and worldviews formed through centuries of historical development. Understanding the historical context of cultural layers reveals how societies evolve, with surface culture adapting visibly while subsurface culture maintains continuity beneath societal transformations.
Importance of Understanding Subsurface Values
Understanding subsurface culture is essential for effective cross-cultural communication, as it encompasses deeply held values, beliefs, and norms that are not immediately visible but drive behavior and decision-making. Surface culture includes observable elements like language, dress, and customs, but without recognizing subsurface culture, misunderstandings and conflicts are likely to arise. Organizations and individuals who grasp subsurface values can foster trust, collaboration, and inclusive environments by addressing underlying cultural motivations rather than just external behaviors.
Visible Expressions in Surface Culture
Visible expressions in surface culture include language, dress, customs, rituals, and behaviors that are easily observable in everyday interactions and social settings. These tangible elements serve as symbols of a culture's identity, making it accessible for outsiders to recognize and interpret cultural norms. Surface culture reflects explicit cultural values, while subsurface culture encompasses underlying beliefs, values, and thought patterns that require deeper understanding.
Interplay Between Subsurface and Surface Culture
Subsurface culture refers to the underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions that shape a society, while surface culture encompasses observable behaviors, customs, and artifacts. The interplay between subsurface and surface culture is dynamic, as surface expressions are continually influenced by deeper cultural structures and, conversely, visible practices can reinforce or challenge underlying norms. Understanding this interaction is crucial for effective cross-cultural communication, as misinterpretations often arise when surface behaviors are divorced from their subsurface cultural meanings.
Impact on Cross-Cultural Communication
Subsurface culture refers to underlying beliefs, values, and thought patterns that are not immediately visible but profoundly influence behavior and communication styles. Surface culture includes visible elements such as language, dress, and customs, which are often easier to identify and adapt to in cross-cultural interactions. Ignoring subsurface cultural factors can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations, undermining effective communication and collaboration across cultures.
Challenges in Navigating Cultural Dimensions
Navigating the challenges between subsurface culture and surface culture requires understanding deeply embedded values that are often invisible yet shape behavior and decision-making. Surface culture includes visible elements such as language, customs, and dress, while subsurface culture involves unconscious beliefs, attitudes, and thought patterns that can cause misunderstandings and conflicts in cross-cultural interactions. Addressing these challenges demands sensitivity to implicit cultural cues and a commitment to ongoing cultural competence development in diverse environments.
Strategies for Bridging Subsurface and Surface Culture
Effective strategies for bridging subsurface and surface culture include fostering open communication channels that encourage sharing hidden values and beliefs within the organization. Implementing cross-cultural training programs enhances awareness of underlying assumptions and promotes mutual understanding between visible practices and deeper cultural elements. Leveraging storytelling and immersive experiences helps surface tacit knowledge, enabling alignment between surface behaviors and subsurface cultural drivers essential for cohesive organizational change.
Subsurface Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com