Paralanguage refers to the non-verbal elements of communication used to convey emotion and meaning, such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate. Understanding these vocal cues can significantly enhance Your ability to interpret messages beyond the spoken words and improve interpersonal interactions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how paralanguage influences communication in everyday life and professional settings.
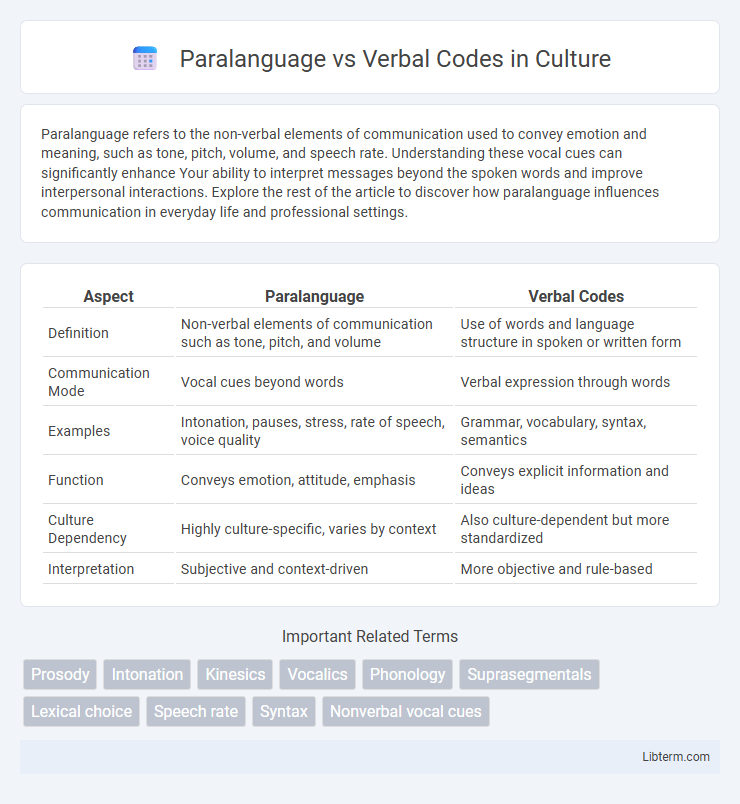
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Paralanguage | Verbal Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-verbal elements of communication such as tone, pitch, and volume | Use of words and language structure in spoken or written form |
| Communication Mode | Vocal cues beyond words | Verbal expression through words |
| Examples | Intonation, pauses, stress, rate of speech, voice quality | Grammar, vocabulary, syntax, semantics |
| Function | Conveys emotion, attitude, emphasis | Conveys explicit information and ideas |
| Culture Dependency | Highly culture-specific, varies by context | Also culture-dependent but more standardized |
| Interpretation | Subjective and context-driven | More objective and rule-based |
Introduction to Paralanguage and Verbal Codes
Paralanguage refers to the nonverbal elements of communication used to convey emotion and meaning, such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate. Verbal codes encompass spoken or written language structures, including vocabulary and grammar, that convey explicit information. Understanding the interplay between paralanguage and verbal codes is essential for interpreting the full context and intent behind a message.
Defining Paralanguage: Beyond Words
Paralanguage encompasses the non-verbal elements of communication such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate that convey meaning beyond the literal words spoken. These vocal cues reveal emotions, attitudes, and intentions, playing a crucial role in face-to-face interactions and enhancing the interpretation of verbal messages. Understanding paralanguage is essential for decoding the full context of communication, as it provides insight into the speaker's true feelings and social signals that verbal codes alone cannot convey.
Understanding Verbal Codes: The Structure of Language
Verbal codes refer to the structured system of language, encompassing syntax, grammar, and vocabulary that enable clear communication and meaning construction. Understanding verbal codes involves recognizing how words form phrases and sentences through rules that govern word order and sentence structure. This linguistic framework allows individuals to encode and decode messages accurately, facilitating effective verbal interactions.
Key Differences Between Paralanguage and Verbal Codes
Paralanguage involves non-verbal vocal cues such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate that convey emotions and attitudes beyond the spoken words. Verbal codes consist of the actual words and language structure used to communicate explicit information and meaning. Key differences lie in paralanguage shaping how a message is interpreted emotionally, while verbal codes carry the direct semantic content of the communication.
Functions of Paralanguage in Communication
Paralanguage enhances communication by conveying emotions, attitudes, and intentions through vocal cues such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate. These non-verbal vocal signals regulate conversational flow, emphasize spoken words, and provide feedback to the listener, complementing the verbal code's literal meaning. Effective use of paralanguage improves interpersonal understanding and helps detect underlying feelings that verbal language alone may not express.
Importance of Verbal Codes in Meaning-Making
Verbal codes are essential in meaning-making as they provide the structured linguistic framework through which ideas, emotions, and information are precisely conveyed. Unlike paralanguage, which includes tone, pitch, and non-verbal cues, verbal codes rely on vocabulary, grammar, and syntax to create clear, unambiguous communication. Effective use of verbal codes ensures the accurate transmission of messages, enabling shared understanding and cognitive processing in interpersonal and mass communication contexts.
Examples of Paralanguage in Everyday Interaction
Paralanguage includes vocal elements such as tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate that convey meaning alongside spoken words. Examples of paralanguage in everyday interactions consist of a raised voice indicating anger, a soft tone expressing empathy, or a hesitant pause signaling uncertainty. These vocal cues enhance communication by providing emotional context often absent from verbal codes alone.
Cultural Variations in Paralanguage and Verbal Codes
Cultural variations in paralanguage significantly influence communication styles, as tone, pitch, and vocal intensity convey different meanings across societies, such as the high pitch signaling respect in Japanese versus assertiveness in Western cultures. Verbal codes vary through language structures, idiomatic expressions, and contextual usage shaped by cultural norms, impacting interpretation and interaction patterns within diverse communities. Understanding these cultural distinctions aids in improving cross-cultural communication by respecting nuanced vocal cues and language conventions unique to each cultural group.
The Role of Paralanguage and Verbal Codes in Miscommunication
Paralanguage, including tone, pitch, and volume, significantly influences the interpretation of verbal codes, with mismatched signals often causing miscommunication. Verbal codes rely on words and grammar, whereas paralanguage conveys emotion and intent, creating ambiguity when these elements conflict. Understanding the interplay between paralanguage and verbal codes is crucial for accurate message decoding and reducing misunderstandings in communication.
Conclusion: Integrating Paralanguage and Verbal Codes for Effective Communication
Integrating paralanguage and verbal codes enhances communication by conveying emotions, intentions, and nuances beyond spoken words. Effective communicators synchronize tone, pitch, and body language with verbal content to create a coherent and impactful message. This holistic approach reduces misunderstandings and fosters deeper connections in personal and professional interactions.
Paralanguage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com