Islamic knowledge encompasses the study of the Quran, Hadith, Fiqh, and various aspects of Islamic theology and history, providing a comprehensive understanding of the religion's principles and practices. Mastery of this knowledge allows you to deepen your faith, make informed decisions, and connect with the rich cultural and spiritual heritage of Islam. Explore the rest of the article to enhance your understanding and application of Islamic teachings in daily life.
Table of Comparison
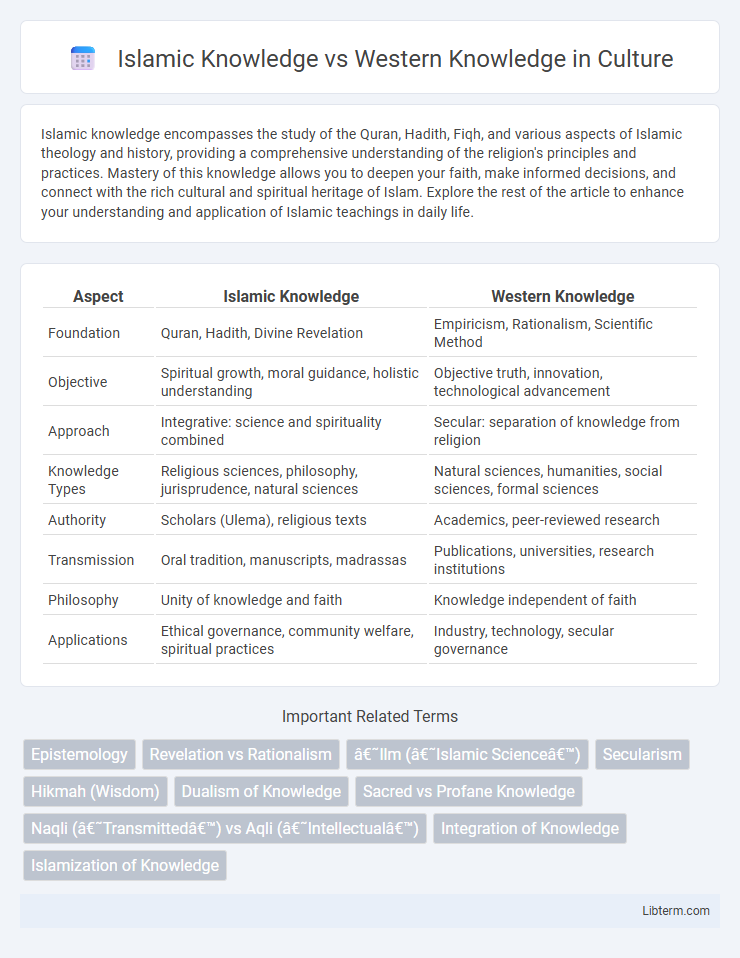
| Aspect | Islamic Knowledge | Western Knowledge |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Quran, Hadith, Divine Revelation | Empiricism, Rationalism, Scientific Method |
| Objective | Spiritual growth, moral guidance, holistic understanding | Objective truth, innovation, technological advancement |
| Approach | Integrative: science and spirituality combined | Secular: separation of knowledge from religion |
| Knowledge Types | Religious sciences, philosophy, jurisprudence, natural sciences | Natural sciences, humanities, social sciences, formal sciences |
| Authority | Scholars (Ulema), religious texts | Academics, peer-reviewed research |
| Transmission | Oral tradition, manuscripts, madrassas | Publications, universities, research institutions |
| Philosophy | Unity of knowledge and faith | Knowledge independent of faith |
| Applications | Ethical governance, community welfare, spiritual practices | Industry, technology, secular governance |
Defining Islamic Knowledge
Islamic knowledge centers on the Quran, Hadith, and Shariah, emphasizing spiritual, moral, and legal guidance derived from divine revelation. It integrates theology, jurisprudence, and ethics to foster a holistic understanding of human purpose and the universe. Unlike Western knowledge, which often relies on empirical science and secular philosophy, Islamic knowledge prioritizes harmony between faith and reason.
Understanding Western Knowledge
Understanding Western knowledge involves analyzing its foundations in scientific inquiry, rationalism, and empirical evidence, which contrast with Islamic knowledge's basis in divine revelation and spiritual guidance. Western knowledge emphasizes secular disciplines like philosophy, natural sciences, and social studies, aiming to explain natural phenomena and human behavior through observation and experimentation. This approach complements Islamic knowledge by offering practical tools and methodologies that can be integrated with ethical and spiritual insights for holistic comprehension.
Historical Evolution of Both Traditions
Islamic knowledge has historically evolved through the synthesis of Quranic teachings, classical Greek philosophy, and indigenous scientific inquiry, flourishing during the Golden Age of Islam from the 8th to 14th centuries with advancements in medicine, mathematics, and astronomy. Western knowledge developed through the Greco-Roman tradition, the Scholasticism of the Middle Ages, and the Scientific Revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries, emphasizing empirical observation and rationalism. Both traditions have deeply influenced global intellectual history, with modern scholarship increasingly recognizing the interconnectedness of their historical evolutions.
Foundational Sources and Epistemologies
Islamic knowledge is fundamentally rooted in the Quran and Sunnah, emphasizing divine revelation and prophetic traditions as its epistemic foundation. Western knowledge relies heavily on empirical observation, reason, and the scientific method, privileging human experience and rational inquiry. These distinct epistemologies shape diverse worldviews: Islamic epistemology integrates spiritual and moral dimensions, while Western epistemology often focuses on secular, objective analysis.
Goals and Purposes of Knowledge Acquisition
Islamic knowledge centers on spiritual growth, ethical conduct, and understanding the divine laws as revealed in the Quran and Hadith, aiming to cultivate a harmonious relationship between humans and God. Western knowledge often emphasizes empirical evidence, scientific exploration, and human progress through technology and innovation, prioritizing practical applications and material advancement. Both systems seek truth but diverge in their ultimate objectives: one rooted in spiritual fulfillment and divine obedience, the other in intellectual development and societal improvement.
Methodologies: Revelation vs. Empiricism
Islamic knowledge relies on revelation from the Quran and Hadith as primary sources, emphasizing divine guidance and spiritual insights. Western knowledge prioritizes empiricism, deriving understanding through observation, experimentation, and evidence-based reasoning. This methodological divergence shapes distinct epistemological frameworks within Islamic and Western intellectual traditions.
Integration and Conflict in Knowledge Systems
Islamic knowledge emphasizes a holistic integration of spiritual, ethical, and empirical dimensions, harmonizing revelation and reason within its educational framework. Western knowledge systems often prioritize empirical evidence and secular methodologies, creating epistemological frameworks that can conflict with metaphysical and moral aspects central to Islamic scholarship. Tensions arise where Western paradigms marginalize spiritual insights, yet integrative approaches seek synergies by contextualizing scientific inquiry within ethical and metaphysical principles inherent in Islamic thought.
Impact on Science and Technology
Islamic knowledge, rooted in centuries of scholarly contributions during the Golden Age of Islam, significantly advanced fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and optics, laying foundational principles for modern science and technology. Western knowledge, influenced by the Renaissance and Enlightenment, built upon these early Islamic scientific achievements through empirical methods and industrial innovation, driving rapid technological progress. The exchange between these knowledge systems fostered critical developments, such as algebra and experimental science, which continue to shape contemporary scientific and technological advancements.
Ethical Dimensions in Knowledge Pursuit
Islamic knowledge emphasizes the integration of ethical principles derived from the Quran and Hadith, guiding the pursuit of knowledge toward spiritual and moral development. Western knowledge often prioritizes empirical evidence and rational inquiry, with ethics viewed as a separate or secondary consideration in knowledge acquisition. The ethical dimensions in Islamic knowledge ensure that intellectual endeavors align with social justice, human dignity, and accountability to divine law.
Bridging Islamic and Western Approaches
Bridging Islamic and Western approaches to knowledge involves integrating Quranic principles with empirical scientific methods to foster a holistic understanding of reality. Emphasizing the complementary nature of revelation and reason allows for the development of interdisciplinary frameworks that respect spiritual values while promoting innovation. Collaborative efforts in education and research encourage cross-cultural dialogue and mutual enrichment, enhancing the global pursuit of wisdom.
Islamic Knowledge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com