High dropout rates negatively impact educational success and long-term career opportunities. Understanding the key factors contributing to student attrition can help implement effective strategies to keep learners engaged and motivated. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical ways to reduce dropout rates and support your educational goals.
Table of Comparison
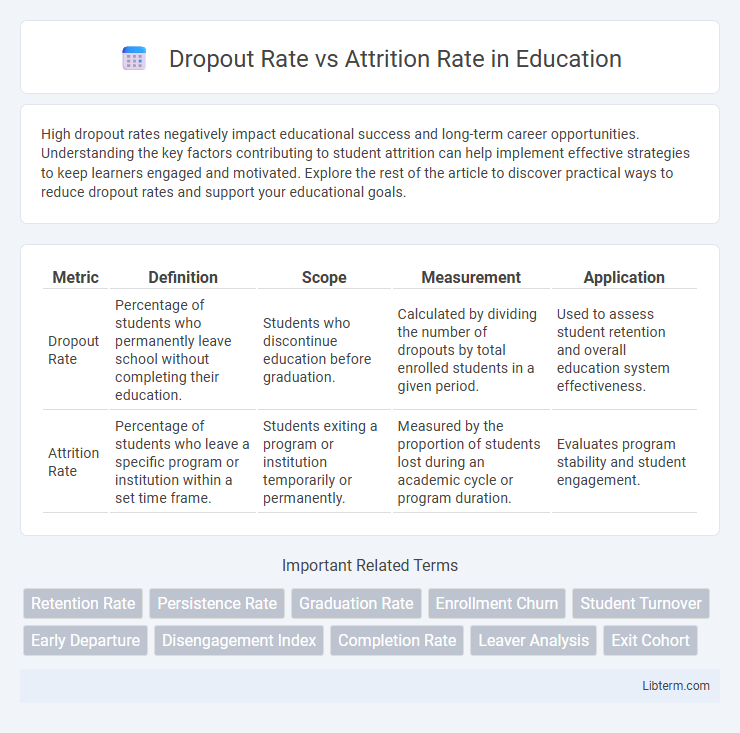
| Metric | Definition | Scope | Measurement | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dropout Rate | Percentage of students who permanently leave school without completing their education. | Students who discontinue education before graduation. | Calculated by dividing the number of dropouts by total enrolled students in a given period. | Used to assess student retention and overall education system effectiveness. |
| Attrition Rate | Percentage of students who leave a specific program or institution within a set time frame. | Students exiting a program or institution temporarily or permanently. | Measured by the proportion of students lost during an academic cycle or program duration. | Evaluates program stability and student engagement. |
Understanding Dropout Rate: Definition and Context
Dropout rate measures the percentage of individuals who discontinue participation in a program or institution before completion, often reflecting academic or engagement challenges. Attrition rate, while related, encompasses a broader scope including voluntary or involuntary exits from any process or study. Understanding dropout rate requires analyzing enrollment data, reasons for withdrawal, and demographic factors to identify patterns and improve retention strategies.
What is Attrition Rate? Key Concepts
Attrition rate measures the percentage of participants who leave a study, job, or organization over a specific period, reflecting overall loss without distinction of the cause. Key concepts include voluntary versus involuntary attrition, churn, and retention, which help analyze workforce stability, customer loyalty, or student engagement. Understanding attrition rate is crucial for identifying trends in performance, satisfaction, and long-term viability across industries and research contexts.
Dropout Rate vs Attrition Rate: Core Differences
Dropout rate measures the percentage of individuals who leave a program or institution before completion, often focusing on students failing to finish their studies. Attrition rate encompasses a broader scope, including all types of loss such as employees leaving a company or participants discontinuing a project. The core difference lies in dropout rate's specific application to education settings, whereas attrition rate applies to various fields involving participant or member loss.
Calculating Dropout Rate: Methods and Metrics
Calculating dropout rate involves dividing the number of students who leave a program before completion by the total number of enrolled students, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. Common metrics include cohort analysis, where dropout rates are tracked over specific groups within a defined timeframe, and survival rate techniques that examine the duration students remain engaged. Accurate data collection on enrollment status changes and exit reasons enhances the precision of dropout rate calculations, distinguishing it from attrition rate metrics that may encompass broader participant losses.
Measuring Attrition Rate: Tools and Techniques
Measuring attrition rate involves tracking employee departures over a specified period using tools like human resource information systems (HRIS), exit interviews, and employee surveys to identify patterns and causes. Techniques such as cohort analysis and turnover analytics enable organizations to pinpoint high-risk groups and evaluate retention strategies effectively. Leveraging predictive analytics and real-time dashboards further enhances accuracy in forecasting attrition trends and informs proactive workforce planning.
Causes of High Dropout Rates in Institutions
High dropout rates in institutions often stem from factors such as inadequate academic support, financial difficulties, and lack of student engagement. Poor learning environments and insufficient counseling services contribute significantly to students' decisions to leave. Addressing these causes requires targeted interventions to improve retention and reduce attrition rates effectively.
Factors Contributing to Attrition Rates
High attrition rates in organizations are primarily driven by factors such as job dissatisfaction, inadequate compensation, lack of career advancement opportunities, and poor work-life balance. Employee disengagement and ineffective management practices further exacerbate turnover. Economic conditions and competitive job markets also play significant roles in influencing attrition levels.
Impact of Dropout and Attrition on Organizational Performance
High dropout rates disrupt workforce stability by increasing recruitment and training costs, which reduces overall productivity. Attrition rate, reflecting employee turnover due to retirement, resignation, or termination, leads to knowledge loss and skill gaps, impairing team performance and operational continuity. Both dropout and attrition negatively impact organizational performance by diminishing employee morale and increasing operational expenses.
Strategies to Reduce Dropout and Attrition Rates
Implementing personalized learning plans and offering robust student support services significantly reduce dropout and attrition rates by addressing individual challenges and promoting engagement. Early identification systems using predictive analytics help institutions intervene timely to prevent student withdrawals. Enhancing academic advising and providing flexible course schedules also improve retention by accommodating diverse student needs and commitments.
Dropout Rate vs Attrition Rate: Which Metric Matters Most?
Dropout rate measures the percentage of students who leave an educational program before completion, reflecting academic disengagement and systemic issues. Attrition rate encompasses all forms of participant loss, including transfers or withdrawals, providing a broader view of retention challenges across industries. Understanding which metric matters most depends on organizational goals, with dropout rate critical for academic success evaluation and attrition rate essential for overall workforce or membership stability analysis.
Dropout Rate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com