Graduation rates measure the percentage of students who successfully complete their academic programs within a given time frame, reflecting the effectiveness of educational institutions. High graduation rates often indicate strong student support services and quality instruction, which can enhance your academic and career prospects. Explore the rest of the article to understand the factors influencing graduation rates and how they impact your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
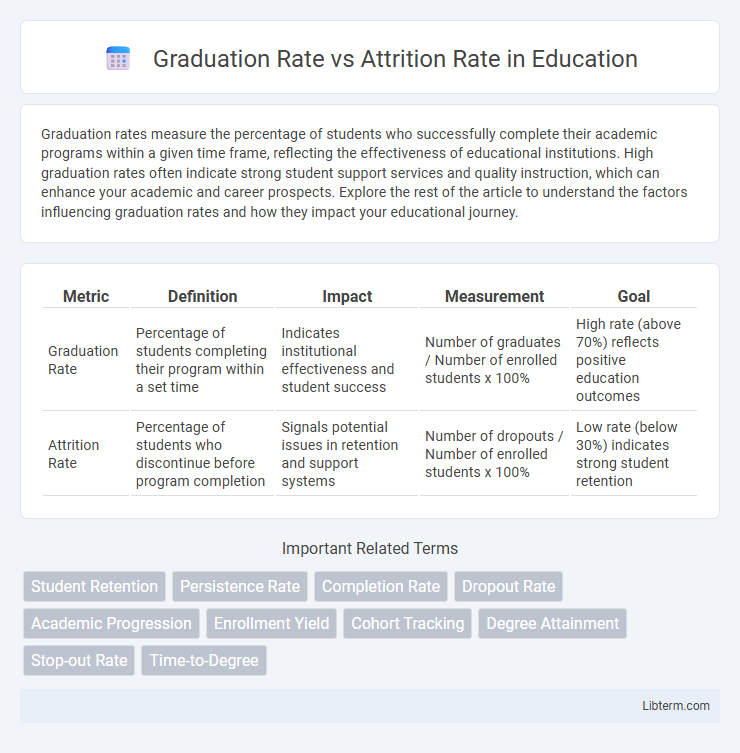
| Metric | Definition | Impact | Measurement | Goal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graduation Rate | Percentage of students completing their program within a set time | Indicates institutional effectiveness and student success | Number of graduates / Number of enrolled students x 100% | High rate (above 70%) reflects positive education outcomes |
| Attrition Rate | Percentage of students who discontinue before program completion | Signals potential issues in retention and support systems | Number of dropouts / Number of enrolled students x 100% | Low rate (below 30%) indicates strong student retention |
Understanding Graduation Rate: Definition and Importance
Graduation rate measures the percentage of students who complete their academic program within a specified time frame, serving as a key indicator of institutional effectiveness and student success. High graduation rates often reflect strong academic support, student engagement, and resource availability, which contribute to positive educational outcomes. Understanding graduation rate is crucial for policymakers and educators aiming to improve retention strategies and allocate resources efficiently.
What Is Attrition Rate? Key Concepts Explained
Attrition rate refers to the percentage of students who leave an educational institution before completing their program, serving as a critical indicator of student retention and institutional effectiveness. It measures the dropout or withdrawal numbers relative to the total enrolled population over a specific period, often annually. High attrition rates can signal challenges such as academic difficulties, financial constraints, or lack of engagement, contrasting with graduation rates that reflect successful program completion.
Graduation Rate vs Attrition Rate: Core Differences
Graduation rate measures the percentage of students who successfully complete their program within a specified time, reflecting academic achievement and institutional effectiveness. Attrition rate indicates the proportion of students who discontinue their studies before completion, highlighting challenges in student retention and satisfaction. Understanding these core differences helps institutions develop targeted strategies to improve student success and reduce dropout rates.
Factors Influencing Graduation Rates in Schools
Graduation rates in schools are significantly influenced by factors such as student engagement, quality of instruction, and availability of support services like counseling and tutoring. Socioeconomic status and family involvement also play critical roles, impacting students' access to resources and motivation to complete their education. Furthermore, school climate and effective intervention strategies contribute to reducing dropout rates and improving overall student retention.
Common Causes of High Attrition Rates
High attrition rates in educational institutions often stem from factors such as financial difficulties, lack of academic support, and personal challenges faced by students. Inadequate engagement with the curriculum and poor campus environment also contribute significantly to student dropout. Addressing these core issues is essential for improving graduation rates and reducing attrition.
The Impact of Graduation and Attrition Rates on Institutional Reputation
High graduation rates enhance institutional reputation by signaling academic success and student satisfaction, attracting prospective students and funding opportunities. Conversely, elevated attrition rates can damage reputation by indicating potential issues with curriculum quality, student support, or campus environment. Balancing these metrics is crucial for maintaining credibility and competitive positioning in higher education.
Strategies to Improve Graduation Rates
Effective strategies to improve graduation rates include implementing comprehensive academic support programs, such as tutoring and mentoring, which address individual student needs and enhance retention. Institutions increase graduation rates by fostering engaging learning environments and providing early alert systems to identify at-risk students for timely intervention. Streamlining credit requirements and offering flexible scheduling options also play critical roles in reducing attrition and supporting on-time degree completion.
How to Reduce Attrition Rates Effectively
Improving student engagement through personalized support programs and early intervention systems significantly reduces attrition rates by addressing academic and emotional challenges promptly. Implementing comprehensive advising and mentorship enhances retention by fostering a strong connection between students and the institution. Data-driven strategies that monitor at-risk student behavior enable targeted resources, leading to higher graduation rates and improved overall institutional performance.
Analyzing Graduation and Attrition Trends by Demographics
Analyzing graduation and attrition trends by demographics reveals significant disparities across different student groups, with graduation rates often higher among certain ethnicities and socioeconomic statuses while attrition rates remain elevated in underrepresented populations. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) indicates that students from low-income backgrounds experience attrition rates up to 30% higher than their affluent peers, impacting overall institutional performance metrics. Gender differences also emerge, as female students typically achieve higher graduation rates, emphasizing the need for targeted retention strategies that address diverse demographic challenges.
Measuring Success: Using Graduation and Attrition Rates for Institutional Improvement
Graduation rates reflect the percentage of students completing their programs within a specified time, serving as a key indicator of institutional effectiveness and student success. Attrition rates measure the proportion of students who leave before completing their studies, highlighting areas needing targeted support and intervention. Comparing these metrics allows institutions to identify gaps, implement strategic improvements, and enhance overall educational outcomes.
Graduation Rate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com