Station rotations enhance learning by allowing students to engage with diverse activities in a structured environment, promoting active participation and deeper understanding. This method supports differentiated instruction, catering to various learning styles and paces. Discover how mastering station rotations can transform your teaching and elevate student outcomes in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
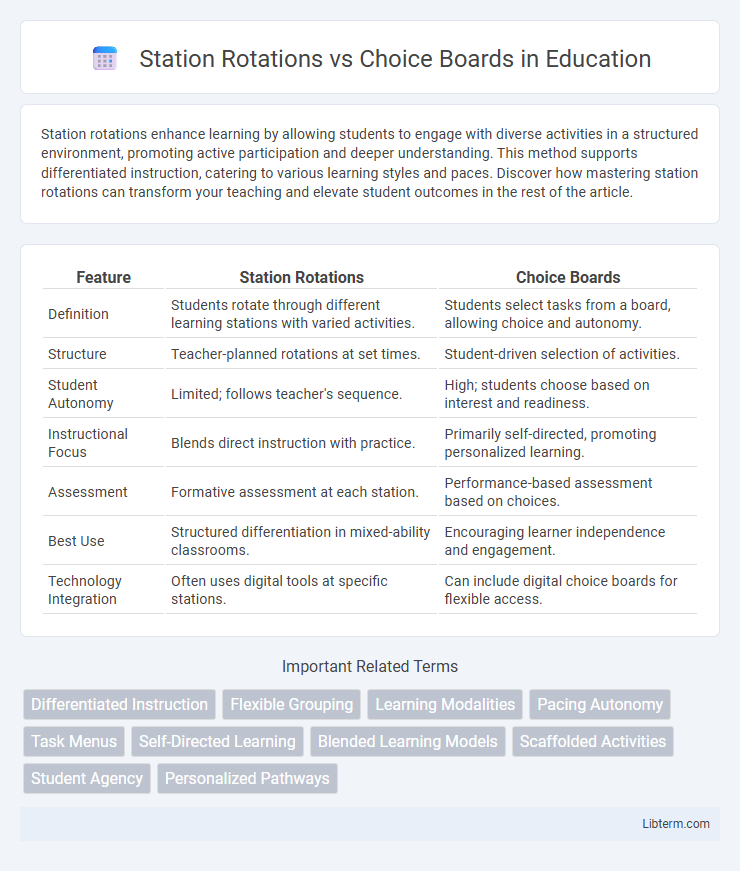
| Feature | Station Rotations | Choice Boards |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students rotate through different learning stations with varied activities. | Students select tasks from a board, allowing choice and autonomy. |
| Structure | Teacher-planned rotations at set times. | Student-driven selection of activities. |
| Student Autonomy | Limited; follows teacher's sequence. | High; students choose based on interest and readiness. |
| Instructional Focus | Blends direct instruction with practice. | Primarily self-directed, promoting personalized learning. |
| Assessment | Formative assessment at each station. | Performance-based assessment based on choices. |
| Best Use | Structured differentiation in mixed-ability classrooms. | Encouraging learner independence and engagement. |
| Technology Integration | Often uses digital tools at specific stations. | Can include digital choice boards for flexible access. |
Introduction to Station Rotations and Choice Boards
Station rotations involve students moving through a series of predefined learning stations, each targeting specific skills or content areas to reinforce understanding and engagement. Choice boards offer students a variety of activity options aligned with learning objectives, allowing personalized, self-directed exploration that caters to diverse learning preferences. Both strategies promote active learning and differentiate instruction effectively in classroom settings.
Defining Station Rotations
Station rotations involve dividing students into small groups that rotate between different learning stations, each designed to target specific skills or content areas. This instructional strategy allows for personalized pacing and active engagement as learners move through varied activities tailored to their needs. Defined by structured movement and clearly assigned tasks, station rotations foster collaborative learning and facilitate differentiated instruction.
Understanding Choice Boards
Choice Boards empower students with autonomy by offering a variety of learning activities tailored to different skill levels and interests, fostering personalized learning experiences. Unlike Station Rotations where students rotate through fixed tasks, Choice Boards enable self-paced progression and encourage decision-making. This flexibility enhances engagement and accommodates diverse learning styles, promoting deeper concept comprehension and skill development.
Key Features of Station Rotations
Station Rotations involve students rotating through a series of distinct learning stations within the classroom, each designed to target specific skills or content areas, promoting active engagement and personalized learning. Key features include structured time management, teacher-led small groups, and independent or collaborative tasks at each station, allowing differentiation and immediate feedback. This model enhances student accountability through rotational checkpoints and supports diverse learning preferences by varying instructional modalities.
Core Elements of Choice Boards
Choice Boards offer a versatile framework that emphasizes student autonomy, differentiated learning paths, and self-paced engagement, making them an essential tool in personalized education. Core elements include a grid layout presenting varied tasks aligned with learning objectives, options that cater to multiple intelligences and learning styles, and opportunities for students to select activities based on interest and readiness levels. This structure contrasts with Station Rotations, which follow a fixed schedule and group movement, focusing more on teacher-directed pacing and collaborative work.
Benefits of Station Rotations
Station rotations promote personalized learning by allowing students to engage with diverse activities at their own pace, enhancing mastery of content. This method facilitates small group instruction and targeted intervention, improving student outcomes through differentiated support. Frequent shifts between stations boost student engagement and collaboration, fostering active participation and reinforcing key concepts.
Advantages of Choice Boards
Choice boards offer personalized learning by allowing students to select tasks that match their interests and skill levels, increasing motivation and engagement. They provide flexibility in pacing and encourage student autonomy, fostering critical thinking and decision-making skills. Educators benefit from differentiated instruction opportunities without the need for extensive pre-planning required by station rotations.
Comparing Student Engagement
Station Rotations foster student engagement by enabling hands-on interaction with diverse tasks in small groups, promoting collaboration and active learning. Choice Boards enhance engagement through personalized learning paths, allowing students to select activities that match their interests and learning styles. Both strategies increase motivation, but Station Rotations emphasize structured peer interaction while Choice Boards prioritize self-directed exploration.
Classroom Management Considerations
Station rotations require clear behavioral expectations and timed transitions to maintain student engagement and minimize disruptions, ensuring smooth circulation between stations. Choice boards demand structured guidelines and monitoring to prevent off-task behavior as students independently select activities, emphasizing accountability and clear instructions. Effective classroom management for both strategies involves proactive routines, consistent enforcement of rules, and strategic grouping to support focused learning environments.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Learners
Selecting between Station Rotations and Choice Boards depends on learner needs and instructional goals; Station Rotations offer structured, teacher-led activities ideal for individualized pacing, while Choice Boards empower learners with autonomy through varied task options. Consider student preferences, classroom dynamics, and content complexity to determine which model promotes engagement and mastery. Integrating data on student performance and learning styles helps tailor the approach to maximize educational outcomes.
Station Rotations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com