Emotion shapes your experiences and influences decision-making by connecting feelings with memories and thoughts. Understanding the science and psychology behind emotions can enhance personal growth and improve relationships. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering emotion regulation benefits your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
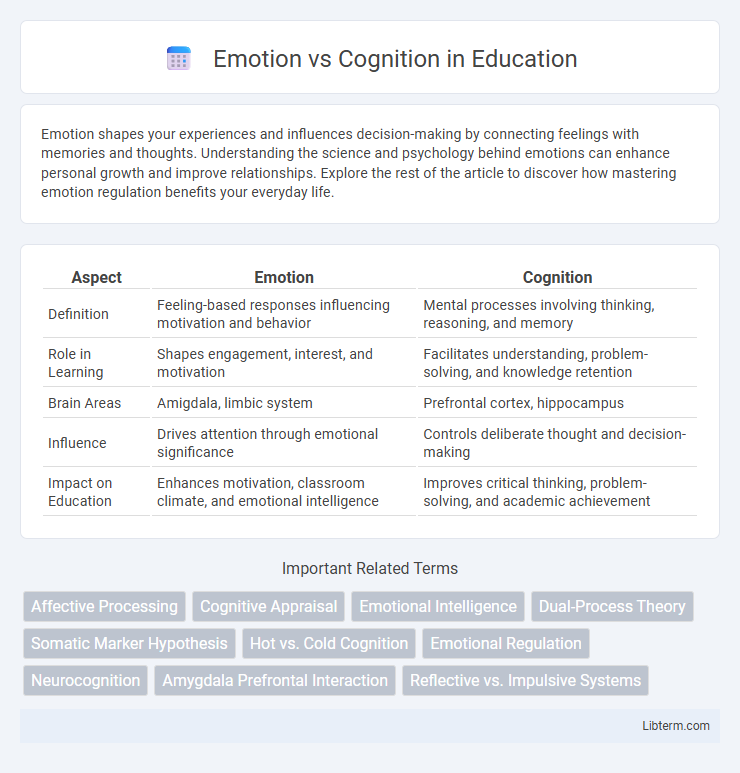
| Aspect | Emotion | Cognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Feeling-based responses influencing motivation and behavior | Mental processes involving thinking, reasoning, and memory |
| Role in Learning | Shapes engagement, interest, and motivation | Facilitates understanding, problem-solving, and knowledge retention |
| Brain Areas | Amigdala, limbic system | Prefrontal cortex, hippocampus |
| Influence | Drives attention through emotional significance | Controls deliberate thought and decision-making |
| Impact on Education | Enhances motivation, classroom climate, and emotional intelligence | Improves critical thinking, problem-solving, and academic achievement |
Introduction to Emotion and Cognition
Emotion and cognition are fundamental aspects of human psychology that interact to influence behavior and decision-making processes. Emotion refers to complex psychological states involving subjective experience, physiological response, and behavioral expression, while cognition encompasses mental processes such as perception, memory, reasoning, and problem-solving. Understanding the interplay between emotion and cognition is essential for insights into how individuals process information, regulate responses, and adapt to their environments.
Defining Emotion and Its Components
Emotion encompasses a complex interplay of physiological arousal, subjective experience, and expressive behavior that together shape human responses. Its components include an affective state, cognitive appraisal, physiological changes like heart rate variation, and behavioral tendencies such as facial expressions or gestures. Understanding these elements is crucial for distinguishing emotion from cognition, which primarily involves mental processes like reasoning, memory, and attention.
Understanding Cognitive Processes
Understanding cognitive processes involves analyzing how the brain interprets, stores, and retrieves information to make decisions and solve problems. Emotion significantly influences cognition by modulating attention, memory encoding, and reasoning, often prioritizing emotionally charged stimuli for faster processing. Research in neuroscience highlights the dynamic interplay between limbic structures and prefrontal cortex regions, which underpins the integration of emotional and cognitive functions.
Key Differences Between Emotion and Cognition
Emotion involves automatic, affective responses triggered by stimuli, primarily processed in the limbic system, especially the amygdala. Cognition engages deliberate, rational thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making functions centered in the prefrontal cortex. Emotions influence cognitive processes by modulating attention and memory, while cognition provides control over emotional reactions through executive functions.
The Interaction Between Emotion and Cognition
Emotion and cognition are deeply interconnected processes that influence decision-making, attention, and memory. Emotional states can enhance or impair cognitive functions, such as reasoning and problem-solving, by modulating neural networks in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Research highlights that effective interaction between emotion and cognition is crucial for adaptive behavior and mental health.
Neurobiological Foundations of Emotion and Cognition
Neurobiological foundations of emotion and cognition reveal distinct yet interconnected brain structures, with the amygdala playing a critical role in emotional processing and the prefrontal cortex governing cognitive functions such as decision-making and executive control. Functional MRI studies show that emotional stimuli activate the limbic system, while cognitive tasks engage frontal and parietal networks, highlighting the dynamic interplay between emotion and cognition. Neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin modulate both emotional regulation and cognitive processes, underscoring their integrated neurobiological mechanisms.
Impact of Emotion on Cognitive Function
Emotions significantly influence cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and decision-making by modulating neural activity in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Positive emotions enhance cognitive flexibility and problem-solving abilities, while negative emotions can impair working memory and increase cognitive biases. Understanding the impact of emotion on cognition is critical for developing interventions in mental health and optimizing learning environments.
Cognitive Regulation of Emotional Responses
Cognitive regulation of emotional responses involves the use of executive functions, such as attention control and reappraisal, to modulate emotional intensity and expression. Neuroimaging studies show prefrontal cortex regions, including the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (VMPFC), play a crucial role in this regulation by influencing amygdala activity. Effective cognitive regulation enhances emotional resilience, reduces maladaptive reactions, and supports adaptive decision-making processes.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Understanding the interplay between emotion and cognition enhances decision-making by balancing logical analysis with emotional insight in daily situations. Emotional intelligence improves communication, conflict resolution, and stress management, while cognitive skills support problem-solving and critical thinking. Integrating both aspects optimizes personal relationships, workplace performance, and overall well-being.
Future Directions in Emotion and Cognition Research
Future directions in emotion and cognition research emphasize integrating neuroimaging and computational modeling to unravel the dynamic interplay between affective processes and executive functions. Advances in machine learning algorithms enable more precise prediction of emotional influences on decision-making and cognitive control. Emerging studies prioritize real-time monitoring and modulation of emotional states to enhance cognitive performance and mental health interventions.
Emotion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com