Project-Based Learning immerses students in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on experience. This approach promotes collaboration, creativity, and deeper understanding by engaging learners in meaningful projects connected to actual contexts. Discover how Project-Based Learning can transform your educational journey by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
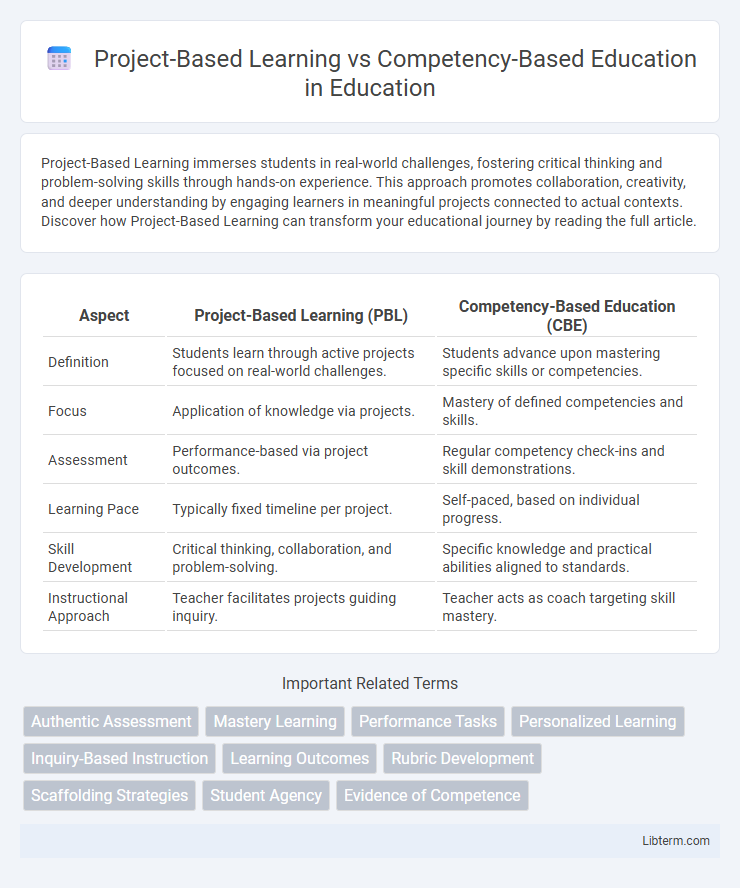
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Competency-Based Education (CBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students learn through active projects focused on real-world challenges. | Students advance upon mastering specific skills or competencies. |
| Focus | Application of knowledge via projects. | Mastery of defined competencies and skills. |
| Assessment | Performance-based via project outcomes. | Regular competency check-ins and skill demonstrations. |
| Learning Pace | Typically fixed timeline per project. | Self-paced, based on individual progress. |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving. | Specific knowledge and practical abilities aligned to standards. |
| Instructional Approach | Teacher facilitates projects guiding inquiry. | Teacher acts as coach targeting skill mastery. |
Defining Project-Based Learning (PBL)
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional methodology where students acquire knowledge and skills through engaging in real-world and meaningful projects. This approach emphasizes active exploration, collaboration, and practical problem-solving, enabling learners to apply concepts in authentic contexts. PBL fosters critical thinking, creativity, and deeper understanding by integrating interdisciplinary content within hands-on project experiences.
Understanding Competency-Based Education (CBE)
Competency-Based Education (CBE) centers on mastery of specific skills and knowledge rather than time spent in class, allowing students to progress at their own pace upon demonstrating proficiency. Unlike Project-Based Learning, which emphasizes applying knowledge through hands-on projects, CBE provides clear, measurable learning outcomes aligned with real-world competencies. This approach ensures personalized learning pathways and prepares students for workforce demands by focusing on relevant abilities and practical application.
Core Principles of PBL and CBE
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on student-driven projects that promote active exploration and real-world problem-solving, emphasizing collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity. Competency-Based Education (CBE) focuses on mastering specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to progress at their own pace once they demonstrate proficiency. Both approaches prioritize personalized learning, but PBL emphasizes experiential engagement through complex tasks, while CBE ensures measurable competency acquisition aligned with clearly defined outcomes.
Instructional Approaches: PBL vs CBE
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes experiential, student-driven projects that integrate real-world problems, fostering collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity throughout the learning process. Competency-Based Education (CBE) centers on mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to progress at their own pace once defined competencies are demonstrated. Instructionally, PBL engages students through iterative problem-solving and teamwork, while CBE utilizes personalized assessments and targeted feedback to ensure proficiency in discrete competencies.
Assessment Strategies: Competency vs Project Outcomes
Assessment strategies in Project-Based Learning prioritize evaluating project outcomes through real-world applications and collaborative problem-solving, emphasizing creativity and critical thinking skills. Competency-Based Education focuses on measuring specific skills and knowledge mastery through standardized assessments and performance tasks aligned with clearly defined competencies. Both approaches require tailored evaluation methods to effectively capture student progress, with project outcomes highlighting applied learning and competency assessments ensuring skill proficiency.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances student engagement by involving learners in real-world, meaningful projects that foster deep understanding and active participation. Competency-Based Education (CBE) motivates students through personalized pacing and mastery of specific skills, allowing learners to progress upon demonstrating proficiency. Both approaches promote intrinsic motivation but differ in structure: PBL emphasizes collaborative problem-solving, while CBE centers on skill acquisition and assessment-driven advancement.
Real-World Application and Skill Development
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on real-world problem solving, fostering critical thinking and collaboration through extended projects that simulate authentic work scenarios. Competency-Based Education prioritizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to progress upon demonstrating proficiency critical for career readiness. Both approaches enhance skill development, with Project-Based Learning driving applied experience and Competency-Based Education ensuring targeted, measurable learning outcomes.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementation challenges of Project-Based Learning include time management, resource allocation, and ensuring alignment with standardized curricula, while Competency-Based Education struggles with clearly defining competencies and assessing mastery consistently. Solutions for Project-Based Learning involve integrating interdisciplinary projects and leveraging technology for collaboration and feedback, whereas Competency-Based Education benefits from developing detailed rubrics, adaptive learning platforms, and continuous instructor training. Both approaches require institutional commitment, professional development, and robust assessment systems to effectively address their unique challenges.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Model
Project-Based Learning (PBL) fosters critical thinking and real-world problem-solving by engaging students in hands-on projects, promoting collaboration and creativity while sometimes lacking standardized assessment metrics. Competency-Based Education (CBE) ensures mastery of specific skills through personalized pacing and clear benchmarks, offering flexibility but potentially limiting opportunities for interdisciplinary exploration. Both models enhance learner engagement but require careful implementation to balance depth of knowledge with measurable outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Learning Environment
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world projects that foster critical thinking and collaboration, making it ideal for environments focused on practical skill application and teamwork. Competency-Based Education prioritizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge at an individualized pace, suited for settings where learners require flexibility and targeted skill development. Selecting the right approach depends on your educational goals, learner needs, and available resources to balance engagement with measurable outcomes.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com