Optional features in products or services enhance user experience by allowing customization to meet individual needs and preferences. These choices can improve functionality, convenience, and satisfaction without increasing the core cost. Explore the rest of this article to discover how optional features can benefit your specific situation.
Table of Comparison
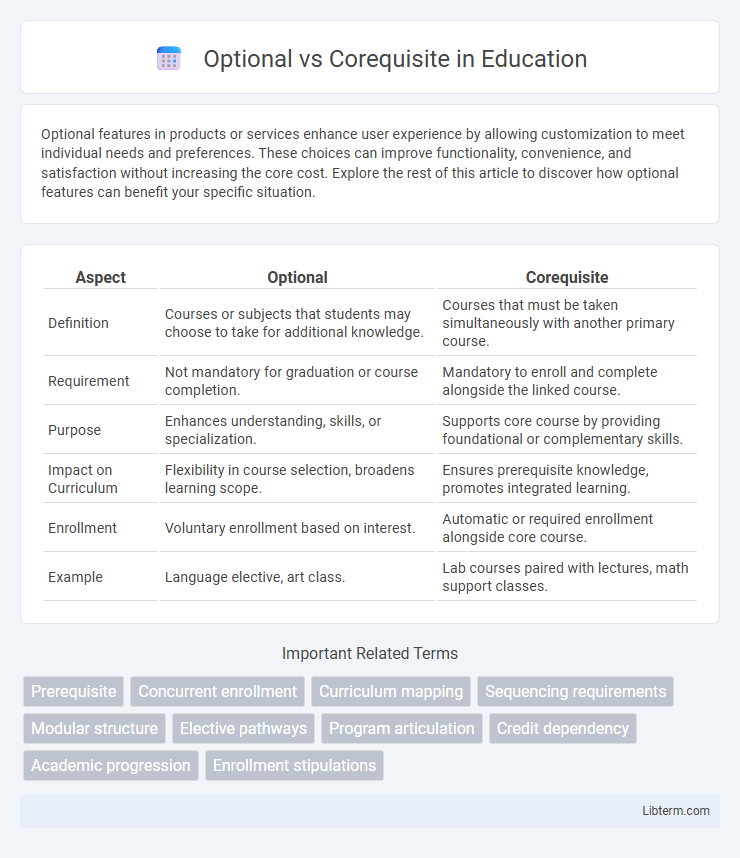
| Aspect | Optional | Corequisite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Courses or subjects that students may choose to take for additional knowledge. | Courses that must be taken simultaneously with another primary course. |
| Requirement | Not mandatory for graduation or course completion. | Mandatory to enroll and complete alongside the linked course. |
| Purpose | Enhances understanding, skills, or specialization. | Supports core course by providing foundational or complementary skills. |
| Impact on Curriculum | Flexibility in course selection, broadens learning scope. | Ensures prerequisite knowledge, promotes integrated learning. |
| Enrollment | Voluntary enrollment based on interest. | Automatic or required enrollment alongside core course. |
| Example | Language elective, art class. | Lab courses paired with lectures, math support classes. |
Understanding Optional vs Corequisite Courses
Optional courses provide students with the flexibility to enhance their knowledge without being mandatory for program completion, allowing them to tailor their education to personal interests or career goals. Corequisite courses must be taken simultaneously or within the same term as a related course to ensure students acquire essential knowledge and skills concurrently. Understanding the distinction between optional and corequisite courses is crucial for academic planning and meeting program requirements effectively.
Defining Optional Courses
Optional courses provide students with the flexibility to choose subjects based on their interests or career goals, without being mandatory for program completion. These courses allow learners to enrich their academic experience by exploring diverse topics beyond the core curriculum. Unlike corequisites, optional courses do not require simultaneous enrollment with specific classes, enabling greater customization of the study plan.
What Are Corequisite Courses?
Corequisite courses are classes that must be taken simultaneously with another related course to ensure students gain the necessary knowledge and skills for academic success. These courses often include foundational subjects that support the content of the primary class, like a lab required alongside a lecture. Institutions utilize corequisites to improve student outcomes by providing immediate academic support and reinforcing key concepts in real-time.
Key Differences Between Optional and Corequisite Classes
Optional classes provide supplementary learning opportunities that students can choose based on interest or academic goals, without being mandatory for course progression. Corequisite classes require simultaneous enrollment alongside a primary course to ensure foundational understanding and academic success. The key difference lies in the necessity for enrollment: optional classes enhance learning but are not required, whereas corequisite classes are essential and must be taken concurrently.
Benefits of Optional Courses
Optional courses offer students the flexibility to tailor their education according to personal interests and career goals, enhancing overall engagement and motivation. They provide opportunities to develop diverse skills and explore interdisciplinary knowledge without the pressure of mandatory completion. This flexibility supports individualized learning paths and can improve academic performance by allowing students to focus on areas they find most relevant or stimulating.
Advantages of Corequisite Courses
Corequisite courses enhance student learning outcomes by allowing simultaneous enrollment in foundational and advanced classes, ensuring immediate application of concepts. This integrated approach reduces time to degree completion and improves retention rates by providing targeted academic support alongside challenging coursework. Corequisites also address skill gaps promptly, preventing delays that often occur with prerequisite requirements.
Challenges with Optional and Corequisite Enrollment
Challenges with optional enrollment include students underestimating the value of supplementary courses, leading to lower participation and inconsistent skill development. Corequisite enrollment often struggles with resource allocation, as institutions must simultaneously provide remedial and credit-bearing instruction, increasing demand for qualified instructors and classroom space. Both models face difficulties in accurately assessing student readiness and ensuring timely intervention to prevent course failure.
How Institutions Decide Course Requirements
Institutions determine course requirements based on program goals, accreditation standards, and student learning outcomes, deciding whether a course is optional or a corequisite to ensure foundational knowledge and skill progression. Corequisites are mandated when simultaneous completion enhances comprehension or practical application, while optional courses offer flexibility for specialization or enrichment without affecting core competency. Data-driven curriculum reviews and feedback from faculty and industry experts guide these decisions to balance academic rigor and student workload.
Student Strategies for Choosing Courses
Students evaluating optional versus corequisite courses should prioritize understanding course requirements and academic goals to optimize their workload and learning outcomes. Corequisite courses often provide necessary skills that support mastery in primary subjects, making them essential for timely graduation and knowledge progression. Analyzing personal strengths and consulting academic advisors helps students strategically select optional courses that enhance expertise without overextending their resources.
Impact of Optional vs Corequisite Choices on Academic Success
Choosing corequisites over optional courses significantly enhances academic success by ensuring students master foundational content necessary for advanced topics, which reduces failure rates and improves overall GPA. Optional courses, while flexible, often lead to gaps in essential knowledge that may hinder comprehension and performance in subsequent coursework. Research indicates that mandatory corequisite enrollment increases retention and timely graduation compared to relying solely on optional study pathways.
Optional Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com