Remediation involves identifying and addressing environmental contamination to restore affected areas to safe conditions. Effective remediation techniques include soil excavation, groundwater treatment, and bioremediation, each tailored to specific pollutants and site characteristics. Explore the rest of the article to understand how remediation can protect your health and the environment.
Table of Comparison
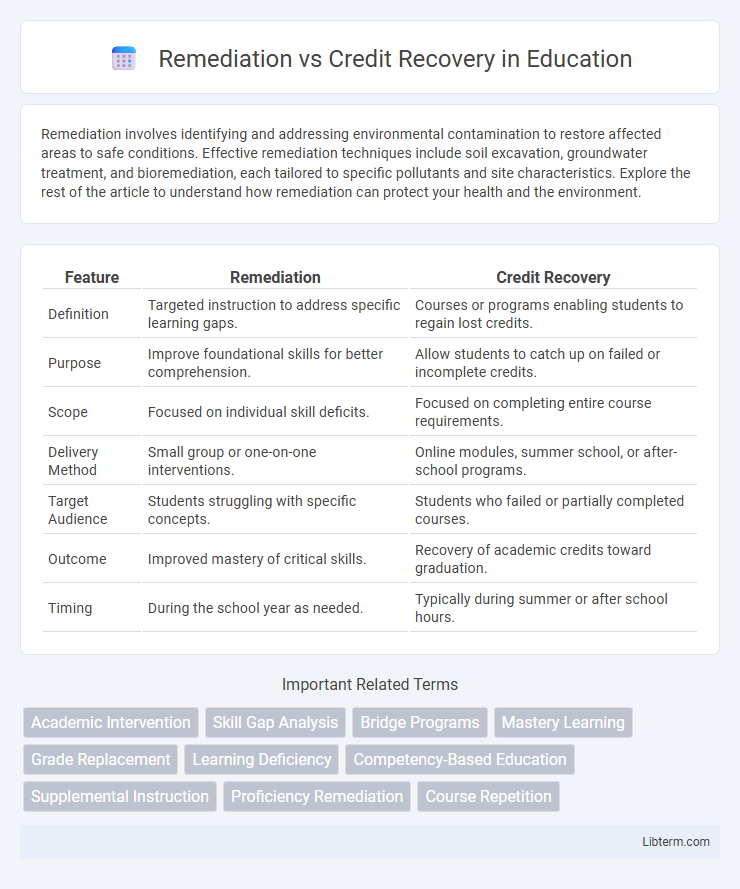
| Feature | Remediation | Credit Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Targeted instruction to address specific learning gaps. | Courses or programs enabling students to regain lost credits. |
| Purpose | Improve foundational skills for better comprehension. | Allow students to catch up on failed or incomplete credits. |
| Scope | Focused on individual skill deficits. | Focused on completing entire course requirements. |
| Delivery Method | Small group or one-on-one interventions. | Online modules, summer school, or after-school programs. |
| Target Audience | Students struggling with specific concepts. | Students who failed or partially completed courses. |
| Outcome | Improved mastery of critical skills. | Recovery of academic credits toward graduation. |
| Timing | During the school year as needed. | Typically during summer or after school hours. |
Understanding Remediation and Credit Recovery
Remediation involves targeted instruction designed to address specific skill gaps and foundational knowledge deficiencies in students, ensuring they meet grade-level standards. Credit recovery allows students who have previously failed a course to retake and earn the necessary credits for graduation, typically through accelerated or alternative learning formats. Both strategies aim to improve academic outcomes but differ in their approach and scope of content coverage.
Key Differences Between Remediation and Credit Recovery
Remediation focuses on strengthening foundational skills students struggle with through targeted instruction, while credit recovery allows students to retake or complete courses to earn academic credits required for graduation. Remediation targets skill deficits without necessarily granting course credit, whereas credit recovery is structured to fulfill specific credit requirements and accelerate progress towards graduation. Academic institutions often use remediation for long-term skill development and credit recovery for immediate course completion.
Goals and Objectives of Remediation Programs
Remediation programs primarily aim to address students' foundational knowledge gaps to ensure mastery of essential skills and concepts before advancing. They focus on personalized learning interventions targeting specific weaknesses to improve academic performance and support long-term achievement. The core objective is to build competence and confidence, enabling students to meet grade-level standards and reduce future learning difficulties.
Purpose and Outcomes of Credit Recovery
Credit recovery programs aim to help students regain lost academic credits efficiently to stay on track for graduation, focusing on mastering core content through flexible and personalized learning paths. Unlike remediation, which emphasizes foundational skill-building to address knowledge gaps, credit recovery often utilizes targeted interventions and assessments to demonstrate competency quickly. The primary outcome of credit recovery is facilitating timely progression through educational milestones without compromising academic standards.
Eligibility Criteria for Remediation vs Credit Recovery
Eligibility criteria for remediation typically target students who have not met the foundational skills or minimum competency levels in core subjects, requiring tailored instruction to bridge learning gaps. Credit recovery programs are designed for students who have previously failed a course and need to regain academic credit to progress, often necessitating prior enrollment and course failure documentation. Both approaches require verification of academic records, but remediation focuses on skill deficiency diagnosis while credit recovery mandates proof of course incompletion.
Instructional Approaches and Methods
Remediation emphasizes targeted instruction to address specific learning gaps through one-on-one tutoring, scaffolded lessons, and repetitive practice to build foundational skills. Credit recovery focuses on flexible, competency-based learning models, often utilizing online modules and project-based assessments to help students regain lost credits efficiently. Instructional methods in remediation prioritize mastery of content before progression, whereas credit recovery integrates paced interventions and technology to accommodate diverse learner needs.
Role of Teachers and Support Staff
Teachers play a critical role in remediation by diagnosing learning gaps and providing targeted instruction tailored to individual student needs, while support staff assist by offering specialized interventions and monitoring progress. In credit recovery, educators focus on helping students meet specific course requirements to earn credits, often through alternative methods like online courses or accelerated programs, with support staff facilitating access to resources and technology. Collaboration between teachers and support staff ensures personalized learning plans and timely support, maximizing student success in both remediation and credit recovery contexts.
Impact on Student Achievement and Graduation Rates
Remediation programs often target foundational skill gaps to improve student proficiency, but can slow progression and delay graduation, negatively affecting overall achievement metrics. Credit recovery enables students to retake failed courses quickly, supporting on-time graduation and maintaining academic momentum, which enhances graduation rates in at-risk populations. Schools that balance remediation to address learning deficits with credit recovery opportunities tend to see more positive impacts on both student achievement and timely graduation outcomes.
Challenges and Controversies in Implementation
Remediation programs often face criticism for potentially lowering academic standards by providing excessive support that may not fully prepare students for future coursework, while credit recovery initiatives struggle with ensuring the authenticity and rigor of completed credits. Both approaches encounter challenges in balancing student engagement with maintaining educational quality, as well as in addressing equity concerns, particularly for underserved populations. Controversies also arise around resource allocation, with debates on whether funding should prioritize intensive remediation or more flexible credit recovery options.
Best Practices for Schools and Educators
Effective remediation targets specific skill gaps through personalized instruction and ongoing assessment to ensure mastery of foundational concepts. Credit recovery programs prioritize pacing and flexibility, allowing students to regain lost credits through competency-based learning and targeted support. Schools and educators should implement data-driven interventions, leverage technology for adaptive learning, and foster collaboration between teachers, counselors, and families to optimize student outcomes.
Remediation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com