Disciplinary actions are essential for maintaining order and upholding standards within organizations, ensuring fairness and accountability among all members. Effective disciplinary measures can address misconduct promptly while encouraging positive behavior changes. Discover how implementing the right disciplinary strategies benefits your workplace by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
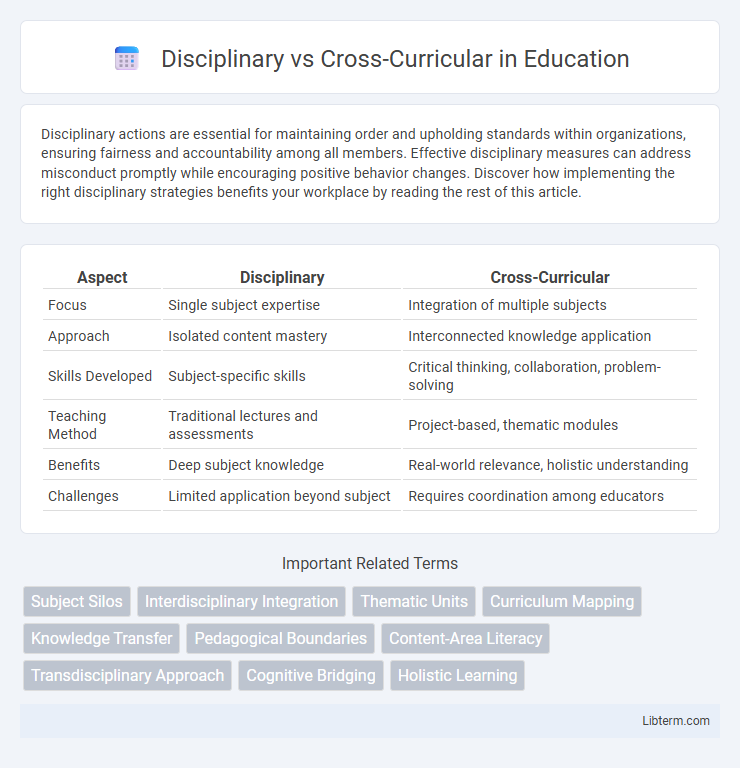
| Aspect | Disciplinary | Cross-Curricular |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Single subject expertise | Integration of multiple subjects |
| Approach | Isolated content mastery | Interconnected knowledge application |
| Skills Developed | Subject-specific skills | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving |
| Teaching Method | Traditional lectures and assessments | Project-based, thematic modules |
| Benefits | Deep subject knowledge | Real-world relevance, holistic understanding |
| Challenges | Limited application beyond subject | Requires coordination among educators |
Understanding Disciplinary Learning
Disciplinary learning emphasizes deep expertise within a specific subject area, fostering specialized knowledge and critical thinking skills unique to that discipline. Understanding disciplinary learning involves recognizing how subject-specific methodologies and terminologies shape cognitive processes and problem-solving approaches. This focused mastery contrasts with cross-curricular strategies, which integrate multiple disciplines to enhance connections and real-world application.
Key Characteristics of Cross-Curricular Approaches
Cross-curricular approaches integrate concepts, skills, and knowledge from multiple subject areas to create cohesive learning experiences that mirror real-world applications. These methods emphasize interconnected thinking, collaborative problem-solving, and the application of diverse perspectives, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking. Unlike disciplinary teaching, cross-curricular strategies prioritize thematic units, student-centered inquiry, and authentic tasks that transcend traditional subject boundaries.
Benefits of Disciplinary Instruction
Disciplinary instruction deepens subject-specific knowledge, fostering expertise in core academic areas such as mathematics, science, or literature. This focused approach enhances critical thinking within a discipline, promoting specialized skills that are essential for advanced study and professional development. Students develop a solid conceptual foundation, enabling precise application of theories and methods unique to each field.
Advantages of Cross-Curricular Learning
Cross-curricular learning enhances critical thinking by integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines, fostering deeper understanding and real-world application. It promotes collaboration and creativity, enabling students to connect concepts across subjects and develop versatile problem-solving skills. This approach supports holistic education, preparing learners for complex challenges by encouraging adaptability and interdisciplinary communication.
Challenges in Implementing Disciplinary Methods
Disciplinary methods face challenges such as rigid curriculum structures limiting integration and teacher specialization requiring advanced subject matter expertise. These methods often struggle with student engagement due to isolated content delivery and insufficient real-world context. Addressing these issues demands targeted professional development and resource allocation to enhance disciplinary teaching efficacy.
Obstacles to Cross-Curricular Integration
Obstacles to cross-curricular integration include entrenched disciplinary silos that limit collaboration between subject areas and rigid curriculum frameworks that prioritize standardized testing over interdisciplinary learning. Teachers often lack sufficient training and resources to effectively design and implement integrated lessons, resulting in fragmented instruction. Institutional resistance and scheduling conflicts further hinder seamless coordination across different academic departments.
Comparing Learning Outcomes: Disciplinary vs Cross-Curricular
Disciplinary learning develops deep expertise and critical thinking within a specific field, enhancing specialized knowledge and technical skills. Cross-curricular approaches foster transferable skills such as problem-solving, collaboration, and adaptability by linking concepts across multiple subjects. Comparative studies indicate cross-curricular methods often improve real-world application and holistic understanding, while disciplinary learning strengthens domain-specific mastery.
Strategies for Effective Disciplinary Teaching
Effective disciplinary teaching strategies include deepening subject-specific knowledge, using targeted language and concepts, and designing assessments that reflect discipline criteria. Teachers enhance learning by integrating inquiry-based approaches and scaffolding complex content to build critical thinking within the discipline. Fostering collaboration among subject experts ensures that instruction remains rigorous and aligned with disciplinary standards.
Best Practices for Cross-Curricular Design
Effective cross-curricular design integrates core concepts and skills from multiple disciplines to create cohesive and relevant learning experiences that mirror real-world applications. Best practices emphasize collaboration among educators, aligning standards across subjects, and employing thematic units that encourage critical thinking and problem-solving. Utilizing project-based learning and authentic assessments enhances student engagement and fosters deeper understanding by connecting knowledge across traditional subject boundaries.
Selecting the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Selecting the right approach between disciplinary and cross-curricular strategies depends on diverse learners' unique needs, cognitive styles, and learning goals. Disciplinary methods emphasize deep expertise in singular subjects, benefiting students who thrive on structured, focused content, while cross-curricular approaches integrate multiple subjects, fostering critical thinking and real-world problem solving for learners who excel in interconnected learning environments. Educators must assess learner profiles, curriculum goals, and skill development priorities to optimize engagement and academic success.
Disciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com