Multidisciplinary approaches integrate expertise from various fields to solve complex problems more effectively. This method encourages collaboration and diverse perspectives, enhancing innovation and outcomes. Discover how adopting a multidisciplinary strategy can transform your projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
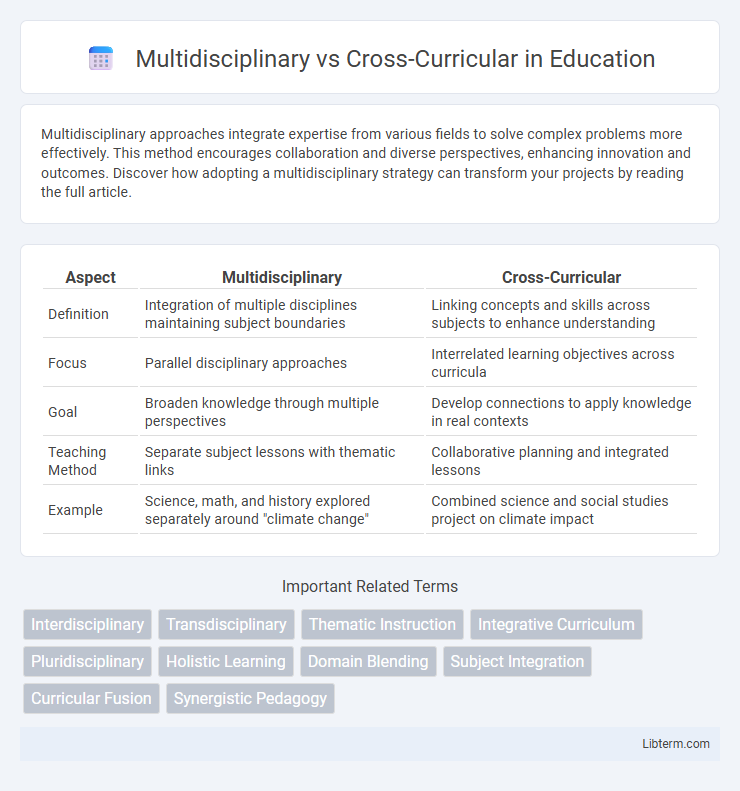
| Aspect | Multidisciplinary | Cross-Curricular |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of multiple disciplines maintaining subject boundaries | Linking concepts and skills across subjects to enhance understanding |
| Focus | Parallel disciplinary approaches | Interrelated learning objectives across curricula |
| Goal | Broaden knowledge through multiple perspectives | Develop connections to apply knowledge in real contexts |
| Teaching Method | Separate subject lessons with thematic links | Collaborative planning and integrated lessons |
| Example | Science, math, and history explored separately around "climate change" | Combined science and social studies project on climate impact |
Introduction to Multidisciplinary and Cross-Curricular Approaches
Multidisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines without necessarily blending them, allowing students to explore topics through distinct academic perspectives. Cross-curricular approaches, on the other hand, intertwine concepts and skills across different subjects to create cohesive learning experiences that emphasize interconnectedness. Both methods aim to enhance critical thinking and problem-solving by fostering comprehensive understanding beyond isolated disciplines.
Defining Multidisciplinary Learning
Multidisciplinary learning involves integrating knowledge and skills from multiple disciplines to explore a common topic, allowing students to examine different perspectives while maintaining the boundaries of each subject. This approach encourages collaboration across subject areas without fully merging their frameworks, fostering a comprehensive understanding of complex issues. Emphasizing distinct disciplinary methods, multidisciplinary learning enhances critical thinking by highlighting contrasts and connections among fields like science, history, and literature.
Understanding Cross-Curricular Integration
Cross-curricular integration involves blending knowledge and skills from multiple subjects to create cohesive learning experiences that reflect real-world applications. Unlike multidisciplinary approaches that keep subjects separate but related, cross-curricular strategies emphasize interconnectedness, encouraging students to draw connections and apply concepts across disciplines. This integration enhances critical thinking and fosters deeper comprehension by situating learning within broader, meaningful contexts.
Key Differences Between Multidisciplinary and Cross-Curricular Strategies
Multidisciplinary strategies involve integrating multiple disciplines to address a common theme while maintaining distinct subject boundaries, allowing students to explore diverse perspectives within their specific fields. Cross-curricular approaches blend skills and content from different subjects to create interconnected learning experiences focused on real-world applications and problem-solving. The key difference lies in the level of integration, where multidisciplinary learning keeps disciplines separate but related, whereas cross-curricular learning fuses content and skills across subjects for holistic understanding.
Benefits of Multidisciplinary Education
Multidisciplinary education integrates multiple disciplines to provide students with a cohesive understanding of complex concepts, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach fosters creativity by encouraging connections across varied knowledge areas, preparing students for real-world challenges that require diverse expertise. Exposure to different perspectives within multidisciplinary frameworks cultivates adaptability and a deeper appreciation of subject interrelations, contributing to holistic cognitive development.
Advantages of Cross-Curricular Teaching
Cross-curricular teaching integrates multiple subject areas to create cohesive learning experiences that enhance critical thinking and real-world application. It fosters deeper understanding by connecting concepts across disciplines, promoting student engagement and retention. This approach develops essential skills such as collaboration, problem-solving, and adaptability, preparing learners for complex challenges beyond the classroom.
Challenges in Implementing Multidisciplinary Approaches
Implementing multidisciplinary approaches in education faces challenges such as aligning diverse disciplinary standards and coordinating collaborative planning among educators with varying expertise. Resource allocation and effective communication often become complex when integrating subjects to create cohesive learning experiences. Resistance to change in traditional teaching methods further complicates the adoption of multidisciplinary frameworks in academic institutions.
Obstacles to Effective Cross-Curricular Integration
Obstacles to effective cross-curricular integration include rigid curriculum structures that limit collaboration between disciplines and insufficient teacher training in interdisciplinary methods. Time constraints and conflicting assessment standards further hinder the seamless blending of subject content. Overcoming these challenges requires systemic reforms and professional development focused on curriculum flexibility and integrative instructional strategies.
Real-World Examples in Education
Multidisciplinary education integrates concepts from multiple disciplines to explore a central theme, such as combining history, literature, and art to study the Renaissance, while cross-curricular learning links skills across subjects, like applying mathematical data analysis in science experiments. Real-world examples include a project where students design sustainable cities, using geography, environmental science, and economics in a multidisciplinary approach versus a cross-curricular activity where English and social studies classes collaborate to improve students' argumentative writing through current events. These methods enhance critical thinking and application by providing diverse perspectives and relevant skill development in education.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Multidisciplinary approaches integrate multiple disciplines to explore a central theme, fostering comprehensive understanding through varied perspectives, ideal for engaging diverse learners by connecting content areas meaningfully. Cross-curricular strategies link skills and knowledge across subjects, promoting transferable learning and real-world application, beneficial for students who thrive on practical, interconnected knowledge. Selecting the right approach depends on learners' needs, with multidisciplinary methods supporting depth and complexity, while cross-curricular approaches enhance adaptability and holistic skill development.
Multidisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com