Curriculum integration enhances student learning by connecting different subjects around common themes, promoting critical thinking and real-world application. This approach helps You see the relevance of knowledge across various disciplines, making education more engaging and meaningful. Discover how curriculum integration can transform your teaching and learning experience in the full article.
Table of Comparison
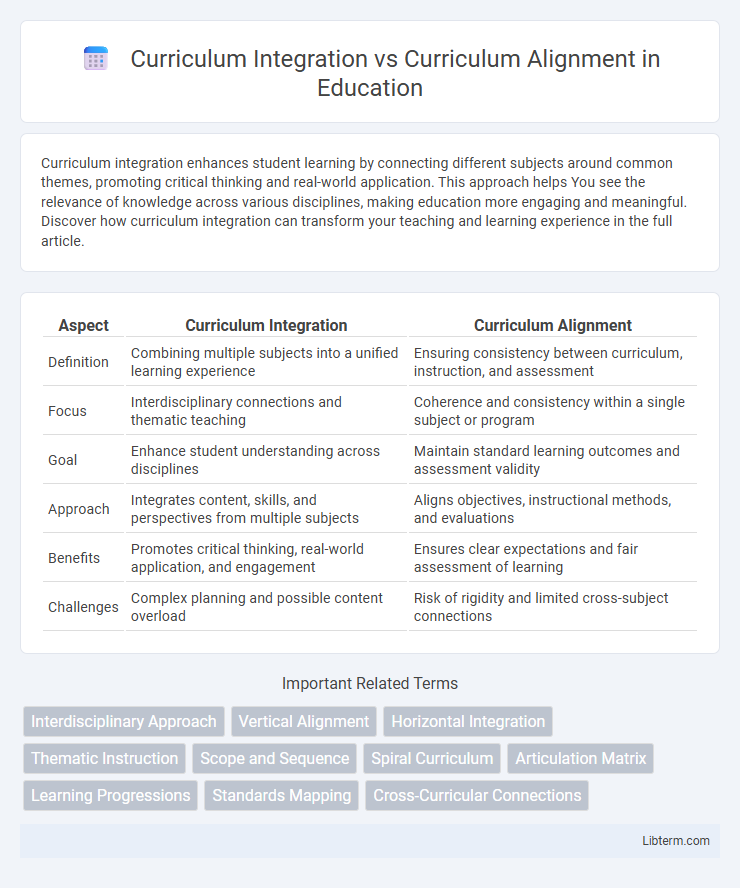
| Aspect | Curriculum Integration | Curriculum Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple subjects into a unified learning experience | Ensuring consistency between curriculum, instruction, and assessment |
| Focus | Interdisciplinary connections and thematic teaching | Coherence and consistency within a single subject or program |
| Goal | Enhance student understanding across disciplines | Maintain standard learning outcomes and assessment validity |
| Approach | Integrates content, skills, and perspectives from multiple subjects | Aligns objectives, instructional methods, and evaluations |
| Benefits | Promotes critical thinking, real-world application, and engagement | Ensures clear expectations and fair assessment of learning |
| Challenges | Complex planning and possible content overload | Risk of rigidity and limited cross-subject connections |
Introduction to Curriculum Integration and Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum Integration involves blending multiple subject areas into a unified learning experience, enhancing interdisciplinary understanding and real-world application. Curriculum Alignment ensures that learning objectives, instructional methods, and assessments are consistently matched across grade levels and subject areas to maintain coherence and reinforce educational goals. Both strategies aim to improve student learning outcomes by fostering connections between content and ensuring instructional effectiveness.
Defining Curriculum Integration
Curriculum integration involves combining multiple subject areas into cohesive learning experiences that connect knowledge and skills across disciplines, fostering deeper understanding and real-world application. It emphasizes interdisciplinary themes, projects, or problem-solving tasks that engage students in holistic learning. This approach contrasts with curriculum alignment, which systematically ensures that instructional content, standards, assessments, and objectives are consistently matched within a single subject area.
Understanding Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum alignment ensures coherence between learning objectives, instructional methods, and assessment strategies to promote consistent educational outcomes. It involves mapping standards and benchmarks directly to classroom activities and evaluation tools, ensuring students achieve targeted competencies. Understanding curriculum alignment enables educators to systematically connect all aspects of the educational process, enhancing student learning and performance tracking.
Key Differences Between Integration and Alignment
Curriculum integration combines multiple subject areas into cohesive learning experiences that promote interdisciplinary understanding, while curriculum alignment ensures that instructional content, assessments, and standards are consistently connected within and across grade levels. Integration emphasizes blending concepts and skills from different disciplines, fostering deeper critical thinking, whereas alignment focuses on coherence and progression, guaranteeing that learning objectives and evaluations match curriculum standards. The key difference lies in integration's holistic approach to interconnected knowledge versus alignment's structured synchronization of curriculum components.
Benefits of Curriculum Integration
Curriculum Integration enhances student learning by connecting concepts across multiple subjects, fostering critical thinking and real-world application skills. It promotes interdisciplinary collaboration among teachers, resulting in a cohesive educational experience that aligns with diverse learner needs. This approach improves engagement and retention by making learning more relevant and meaningful, ultimately supporting deeper understanding and skill transfer.
Advantages of Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum alignment ensures that learning objectives, instructional materials, and assessments are consistently linked, promoting a cohesive and focused educational experience. This alignment enhances student understanding and retention by reinforcing key concepts across lessons and assessments. It also facilitates more accurate measurement of student progress, enabling educators to identify gaps and adjust instruction effectively.
Challenges in Implementing Curriculum Integration
Challenges in implementing curriculum integration include difficulty in coordinating interdisciplinary content among diverse subject teachers and aligning learning objectives with standardized testing requirements. Integrating curricula demands extensive collaboration, professional development, and flexible scheduling, often constrained by rigid school structures and limited resources. Resistance to change from educators accustomed to traditional disciplinary teaching further complicates effective curriculum integration.
Obstacles to Effective Curriculum Alignment
Obstacles to effective curriculum alignment often include inconsistent standards across grade levels, insufficient teacher collaboration, and lack of access to aligned instructional resources. Variability in teacher understanding and implementation of curriculum goals further hinders coherence between content, instruction, and assessment. Addressing these challenges requires targeted professional development and systemic support to ensure continuity and rigor throughout the educational program.
Best Practices for Merging Integration and Alignment
Successful merging of curriculum integration and curriculum alignment hinges on designing interdisciplinary units that align learning objectives with standardized benchmarks across subjects, ensuring coherence and relevance in instruction. Emphasizing collaborative planning among educators enhances alignment with state standards while fostering thematic connections between disciplines, promoting deeper student engagement and skill transfer. Utilizing data-driven assessments helps monitor both integrated content mastery and adherence to aligned goals, enabling targeted instructional adjustments for optimal learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Context
Curriculum integration merges subjects to create interdisciplinary learning experiences, enhancing student engagement and real-world application, while curriculum alignment ensures consistency and coherence between standards, instruction, and assessments to meet specific educational goals. Choosing the right approach depends on your educational context, including school goals, student needs, and available resources, where integration suits contexts emphasizing creativity and problem-solving, and alignment fits settings prioritizing standardized outcomes and accountability. Understanding the strengths of both approaches helps educators design effective curricula that address diverse learning objectives and improve overall student achievement.
Curriculum Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com