Experiential learning emphasizes gaining knowledge through direct experience, allowing you to engage actively with real-world tasks instead of passively absorbing information. This hands-on approach enhances retention, critical thinking, and the ability to apply concepts in practical situations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
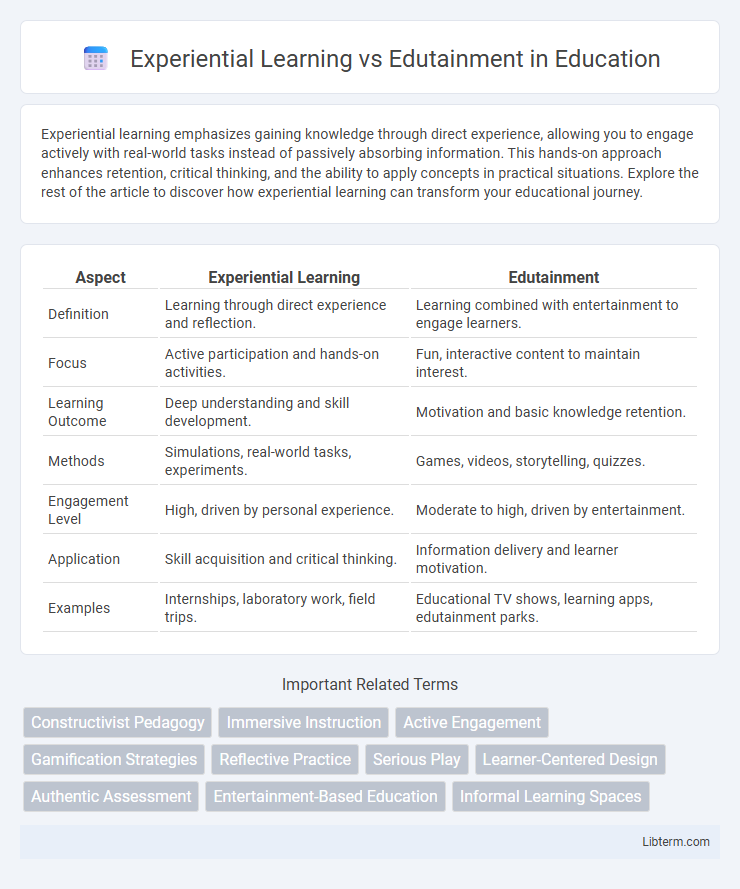
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Edutainment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Learning combined with entertainment to engage learners. |
| Focus | Active participation and hands-on activities. | Fun, interactive content to maintain interest. |
| Learning Outcome | Deep understanding and skill development. | Motivation and basic knowledge retention. |
| Methods | Simulations, real-world tasks, experiments. | Games, videos, storytelling, quizzes. |
| Engagement Level | High, driven by personal experience. | Moderate to high, driven by entertainment. |
| Application | Skill acquisition and critical thinking. | Information delivery and learner motivation. |
| Examples | Internships, laboratory work, field trips. | Educational TV shows, learning apps, edutainment parks. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and real-world experience to deepen knowledge retention and skill development, distinguishing it from edutainment, which blends entertainment with education primarily to engage audiences. This approach involves concrete experiences followed by reflection, conceptualization, and experimentation, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. By immersing learners in authentic tasks, experiential learning enhances cognitive connections and practical understanding more effectively than passive entertainment-based methods.
Defining Edutainment
Edutainment integrates educational content with entertaining elements to enhance engagement and retention, often using multimedia tools, games, or storytelling. Unlike experiential learning, which focuses on hands-on, real-world experiences for skill development, edutainment emphasizes making learning enjoyable through interactive and immersive formats. This method leverages entertainment to motivate learners while embedding instructional objectives seamlessly within the experience.
Key Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation, reflection, and real-world application, enabling learners to engage deeply with the material through hands-on experiences. Key principles include learning by doing, critical thinking, and feedback-driven improvement, fostering long-term retention and skills development. This approach contrasts with edutainment, which blends education and entertainment but often prioritizes engagement over immersive, practical learning processes.
Core Elements of Edutainment
Edutainment combines education and entertainment to engage learners through interactive multimedia, games, storytelling, and simulations, making information more memorable and enjoyable. Core elements include interactivity, immersive narratives, and multimedia content that foster active participation and emotional connection. Unlike experiential learning, which emphasizes hands-on real-world experiences, edutainment focuses on delivering knowledge in engaging formats that balance fun with learning outcomes.
Differences in Learning Outcomes
Experiential learning fosters deep understanding through active participation and real-world problem solving, enhancing critical thinking and long-term retention. Edutainment primarily aims to engage and entertain learners, often resulting in increased motivation but less emphasis on applying knowledge in practical contexts. The key difference lies in experiential learning's focus on skill development and meaningful experience versus edutainment's focus on engagement and enjoyment.
Engagement Strategies Compared
Experiential learning immerses participants through hands-on activities and real-world problem-solving, fostering deep cognitive engagement and skill retention. Edutainment leverages entertainment elements like storytelling, gamification, and multimedia to capture attention and motivate learners emotionally. Both strategies boost engagement, but experiential learning emphasizes active participation, while edutainment focuses on creating enjoyable educational experiences.
Real-World Applications of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world applications, enabling learners to engage directly with practical scenarios that mirror workplace challenges, thereby fostering deeper understanding and skill development. This method contrasts with edutainment, which prioritizes entertainment to capture attention but may lack the immersive, problem-solving elements critical for tangible skill acquisition. By integrating real-life tasks, experiential learning cultivates critical thinking, adaptability, and professional competence essential for career success.
Popular Edutainment Formats
Popular edutainment formats blend entertainment with education through interactive games, virtual reality experiences, and multimedia storytelling, enhancing knowledge retention by engaging multiple senses. These formats often utilize gamification techniques, such as leaderboards and rewards, to motivate learners while delivering curriculum-aligned content. Virtual field trips and augmented reality simulations also provide immersive environments that promote active learning and real-world application of skills.
Assessing Educational Effectiveness
Assessing educational effectiveness in experiential learning involves evaluating hands-on engagement, critical thinking application, and real-world problem-solving outcomes, which foster deeper retention and skill mastery. In contrast, edutainment emphasizes learner motivation and enjoyment, often measured through engagement metrics and short-term knowledge acquisition rather than long-term competency development. Research indicates experiential learning produces higher educational gains by prioritizing active participation and reflective assessment over passive consumption typical in edutainment formats.
Choosing the Right Approach for Learners
Experiential learning engages learners through active participation and real-world problem-solving, making it ideal for developing practical skills and deep understanding. Edutainment combines education and entertainment to capture attention and simplify complex concepts, which works well for young audiences or beginners. Selecting the right approach depends on the learners' age, goals, and learning preferences to maximize engagement and retention.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com