Common Core State Standards provide a clear, consistent framework to prepare students for college and career readiness by outlining what they should know and be able to do at each grade level in math and English language arts. These standards promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills to ensure students are equipped for success in a global economy. Explore the rest of this article to learn how Common Core can impact Your child's education and ways to support their academic growth.
Table of Comparison
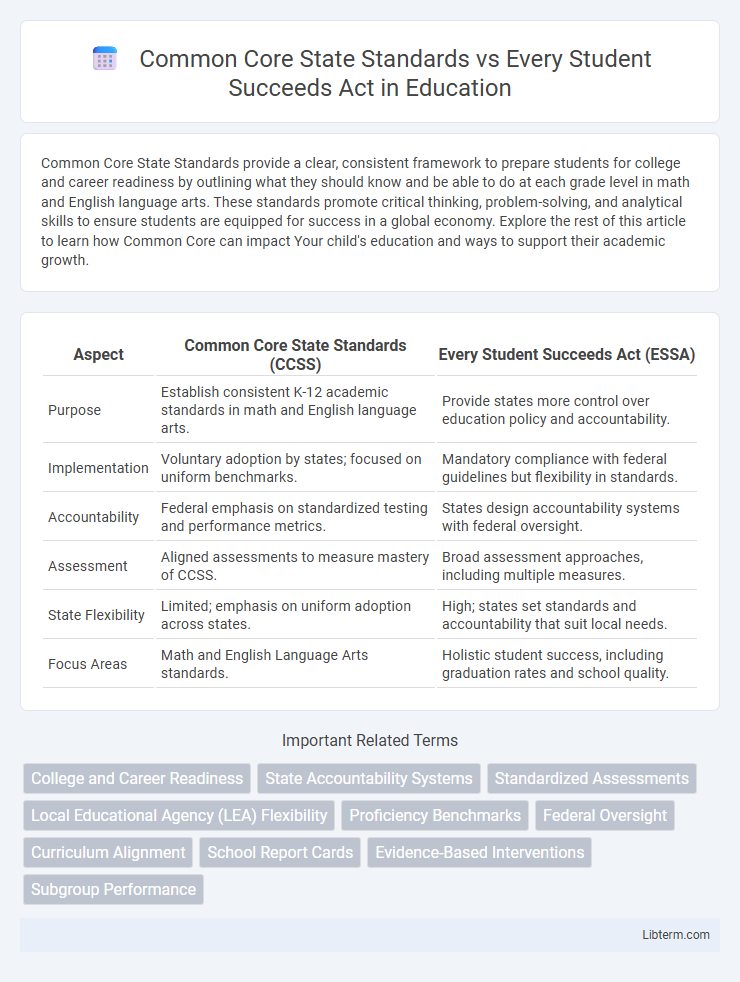
| Aspect | Common Core State Standards (CCSS) | Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Establish consistent K-12 academic standards in math and English language arts. | Provide states more control over education policy and accountability. |
| Implementation | Voluntary adoption by states; focused on uniform benchmarks. | Mandatory compliance with federal guidelines but flexibility in standards. |
| Accountability | Federal emphasis on standardized testing and performance metrics. | States design accountability systems with federal oversight. |
| Assessment | Aligned assessments to measure mastery of CCSS. | Broad assessment approaches, including multiple measures. |
| State Flexibility | Limited; emphasis on uniform adoption across states. | High; states set standards and accountability that suit local needs. |
| Focus Areas | Math and English Language Arts standards. | Holistic student success, including graduation rates and school quality. |
Introduction: Understanding Educational Reforms
The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) emphasize standardized academic benchmarks aimed at ensuring consistent learning goals across states, primarily focusing on math and English language arts. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) shifts responsibility to states, allowing more flexibility in designing accountability systems and educational programs while maintaining federal funding and support. Both reforms target improving student outcomes but differ in governance, accountability, and implementation strategies, reflecting evolving approaches to national education policy.
Overview of Common Core State Standards
The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) establish clear, consistent academic benchmarks in English language arts and mathematics designed to ensure students across states are college- and career-ready. Developed through state-led initiatives, CCSS emphasizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills across grade levels K-12. These standards contrast with the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), which grants states greater flexibility in setting educational goals and accountability systems while maintaining a commitment to student achievement.
Key Goals of the Every Student Succeeds Act
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) prioritizes equitable access to high-quality education by promoting state-driven accountability systems and emphasizing support for underserved and disadvantaged student groups. ESSA aims to enhance academic achievement, improve school quality, and increase transparency through evidence-based interventions and comprehensive assessments. This federal legislation empowers states to set tailored goals while maintaining a focus on closing achievement gaps and preparing all students for college and career readiness.
Historical Background and Implementation
The Common Core State Standards (CCSS), introduced in 2009, were developed to establish consistent educational benchmarks across states, emphasizing college and career readiness in Math and English Language Arts. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), enacted in 2015, replaced the No Child Left Behind Act and shifted greater authority to states for setting educational goals, accountability, and interventions while maintaining federal oversight. Implementation of CCSS faced varied adoption levels, whereas ESSA grants states flexibility in designing accountability systems, promoting tailored approaches for student success.
Curriculum Content and Academic Expectations
The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) emphasize consistent, clear academic expectations in English Language Arts and Mathematics across states, focusing on developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills through specific grade-level benchmarks. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) provides states greater flexibility to design curriculum content that aligns with local priorities while maintaining rigorous academic standards, expanding the scope beyond CCSS to include broader subjects and measures of school performance. Both initiatives aim to improve educational outcomes but differ in their approach to curriculum control and the specificity of academic expectations.
Assessment and Accountability Measures
The Common Core State Standards emphasize uniform academic benchmarks and standardized assessments designed to measure student proficiency consistently across states. The Every Student Succeeds Act shifts accountability to state and local levels, allowing for diverse assessment methods while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity and school performance. Both frameworks prioritize data-driven decision-making but differ in their balance of federal control versus state flexibility in assessment and accountability systems.
State vs. Federal Control in Education Policy
The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) emphasize a state-led approach where states voluntarily adopt uniform academic benchmarks to ensure consistency across the nation. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) shifts more control back to states, granting them greater authority over setting education standards, accountability systems, and intervention strategies while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity and compliance. ESSA's design reflects a balance between federal accountability requirements and increased state flexibility in tailoring education policies to local needs.
Teacher Evaluation and Professional Development
The Common Core State Standards emphasize rigorous academic benchmarks, often linking teacher evaluations directly to student performance data to ensure accountability and instructional quality. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) provides states greater flexibility to design teacher evaluation systems that include multiple measures beyond standardized test scores, promoting comprehensive assessment practices. ESSA also allocates federal funding for professional development programs focused on improving instructional strategies and supporting ongoing teacher growth aligned with state-specific educational goals.
Impact on Students and Learning Outcomes
Common Core State Standards (CCSS) provide a consistent, clear framework aiming to ensure all students attain essential skills in math and English language arts, fostering college and career readiness across states. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) shifts accountability to states, allowing tailored interventions and standards while maintaining federal oversight to improve learning outcomes and reduce achievement gaps. ESSA's flexibility enables diverse educational approaches, which can impact students differently based on state implementation compared to the uniformity emphasized by CCSS.
Future Directions and Ongoing Debates
Future directions of Common Core State Standards (CCSS) emphasize enhancing college and career readiness through updated benchmarks and increased state-led customization, whereas the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) focuses on granting states greater flexibility in accountability and intervention strategies. Ongoing debates center on the balance between federal oversight and local control, with critics questioning the effectiveness of standardized testing under CCSS and advocating for ESSA's diverse assessment approaches. Policymakers continue to negotiate the integration of equity-driven goals with measurable outcomes to improve educational quality and student achievement nationwide.
Common Core State Standards Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com