Constructivist teaching emphasizes active learning where students build new knowledge based on their experiences and prior understanding, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach encourages collaboration, exploration, and reflection to help learners construct meaningful connections. Discover how this method transforms education and supports your student's growth by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
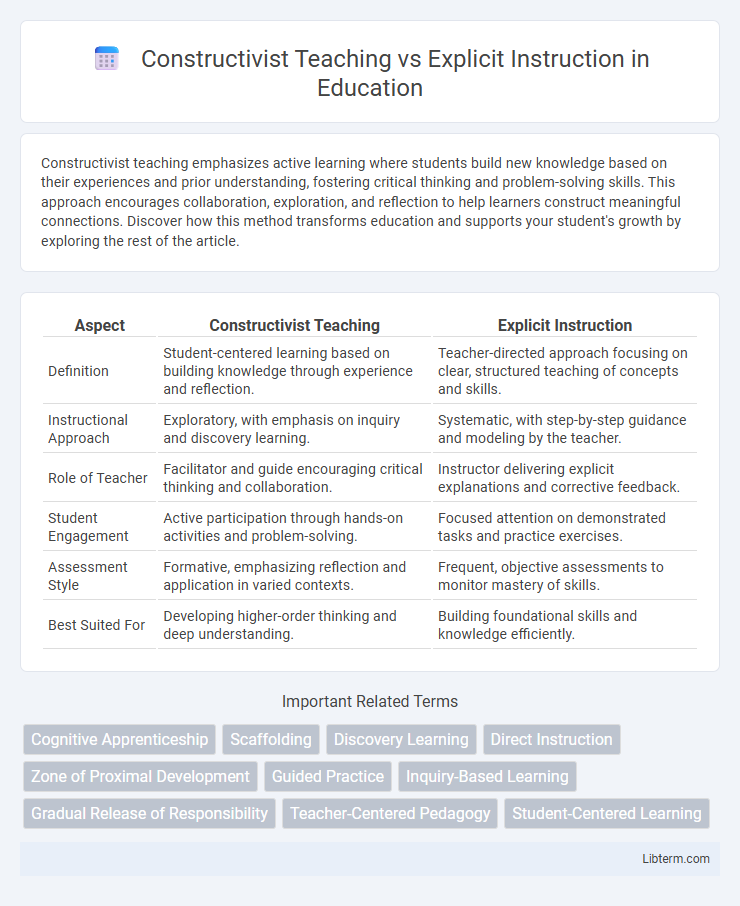
| Aspect | Constructivist Teaching | Explicit Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered learning based on building knowledge through experience and reflection. | Teacher-directed approach focusing on clear, structured teaching of concepts and skills. |
| Instructional Approach | Exploratory, with emphasis on inquiry and discovery learning. | Systematic, with step-by-step guidance and modeling by the teacher. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide encouraging critical thinking and collaboration. | Instructor delivering explicit explanations and corrective feedback. |
| Student Engagement | Active participation through hands-on activities and problem-solving. | Focused attention on demonstrated tasks and practice exercises. |
| Assessment Style | Formative, emphasizing reflection and application in varied contexts. | Frequent, objective assessments to monitor mastery of skills. |
| Best Suited For | Developing higher-order thinking and deep understanding. | Building foundational skills and knowledge efficiently. |
Defining Constructivist Teaching
Constructivist teaching emphasizes student-centered learning where learners actively construct knowledge through experiences and reflection, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It contrasts with explicit instruction, which relies on direct, systematic teaching of specific skills or concepts by the teacher. In constructivist classrooms, knowledge is seen as dynamic and personalized, encouraging collaboration and inquiry-based activities to deepen understanding.
What Is Explicit Instruction?
Explicit instruction involves structured, clear, and direct teaching where educators provide step-by-step guidance, clear explanations, and modeling of new concepts or skills. This method emphasizes teacher-led demonstrations, corrective feedback, and frequent student practice to ensure mastery and understanding. Unlike constructivist teaching, explicit instruction minimizes ambiguity by delivering precise learning objectives and measurable outcomes.
Key Principles of Constructivist Approaches
Constructivist teaching emphasizes learner-centered approaches where students actively construct knowledge through exploration, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving. Key principles include promoting inquiry-based learning, encouraging prior knowledge integration, and fostering metacognitive skills that enable learners to reflect on their understanding. This approach contrasts with explicit instruction's direct teaching methods, prioritizing conceptual understanding and meaningful learning experiences over rote memorization.
Core Components of Explicit Instruction
Explicit instruction centers on clear, systematic teaching with core components including clear learning objectives, teacher modeling, guided practice, and immediate feedback. This approach emphasizes step-by-step explanation and active teacher involvement to ensure student understanding. Contrasting with constructivist teaching, explicit instruction provides structured guidance to build foundational skills effectively.
Comparing Teaching Philosophies
Constructivist teaching prioritizes student-centered learning by encouraging exploration, critical thinking, and knowledge construction through hands-on experiences and social interaction. Explicit instruction follows a teacher-centered approach, emphasizing clear, structured, and systematic teaching with direct explanations and guided practice to ensure mastery of specific skills and concepts. While constructivism fosters deep understanding and learner autonomy, explicit instruction targets efficiency and skill acquisition, highlighting contrasting philosophies in classroom dynamics and cognitive engagement.
Student Engagement in Each Method
Constructivist teaching fosters student engagement by encouraging learners to actively construct knowledge through exploration, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, which enhances critical thinking and intrinsic motivation. Explicit instruction maximizes engagement by delivering clear, structured guidance with immediate feedback, helping students quickly grasp and practice specific skills or concepts. Both methods promote student involvement, but constructivism emphasizes discovery and self-directed learning, whereas explicit instruction prioritizes clarity and direct teacher support.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Constructivist teaching enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to actively construct knowledge through exploration and collaboration. Explicit instruction provides clear, structured guidance that improves mastery of foundational concepts and reduces cognitive load, leading to higher immediate retention and performance. Research indicates that combining explicit instruction with constructivist strategies optimizes learning outcomes by balancing skill acquisition with deeper understanding.
Suitable Contexts for Each Approach
Constructivist teaching thrives in inquiry-based and exploratory learning environments where students build knowledge through hands-on activities and social interaction, making it ideal for subjects like science and social studies that benefit from critical thinking and problem-solving. Explicit instruction is best suited for subjects requiring foundational skill mastery and clear, systematic teaching, such as mathematics and reading, where step-by-step guidance and immediate feedback enhance learning efficiency. Both approaches can be integrated effectively by aligning constructivist methods with higher-order thinking tasks and explicit instruction with skill acquisition and practice.
Challenges and Critiques
Constructivist teaching faces challenges such as students struggling with open-ended tasks without structured guidance, leading to cognitive overload and slower mastery of foundational skills. Critics argue explicit instruction provides clearer, systematic teaching that enhances knowledge retention and skill acquisition, especially for novices and struggling learners. However, explicit instruction may limit critical thinking and creativity by emphasizing rote learning and reducing student autonomy.
Blending Constructivism and Explicit Instruction
Blending constructivism and explicit instruction creates a balanced learning environment where students actively construct knowledge through hands-on experiences while receiving clear, structured guidance from educators. This approach leverages scaffolding techniques to support learners in developing critical thinking skills and deep conceptual understanding without sacrificing the clarity and efficiency of direct teaching methods. Research indicates that combining these methods enhances student engagement and improves long-term retention of complex subjects across diverse educational settings.
Constructivist Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com