Thematic units organize curriculum content around central themes, enhancing connections between concepts for deeper understanding and retention. These units integrate various subjects and skills, fostering meaningful learning experiences that relate to real-world contexts. Explore how thematic units can transform your teaching approach and improve student engagement throughout the article.
Table of Comparison
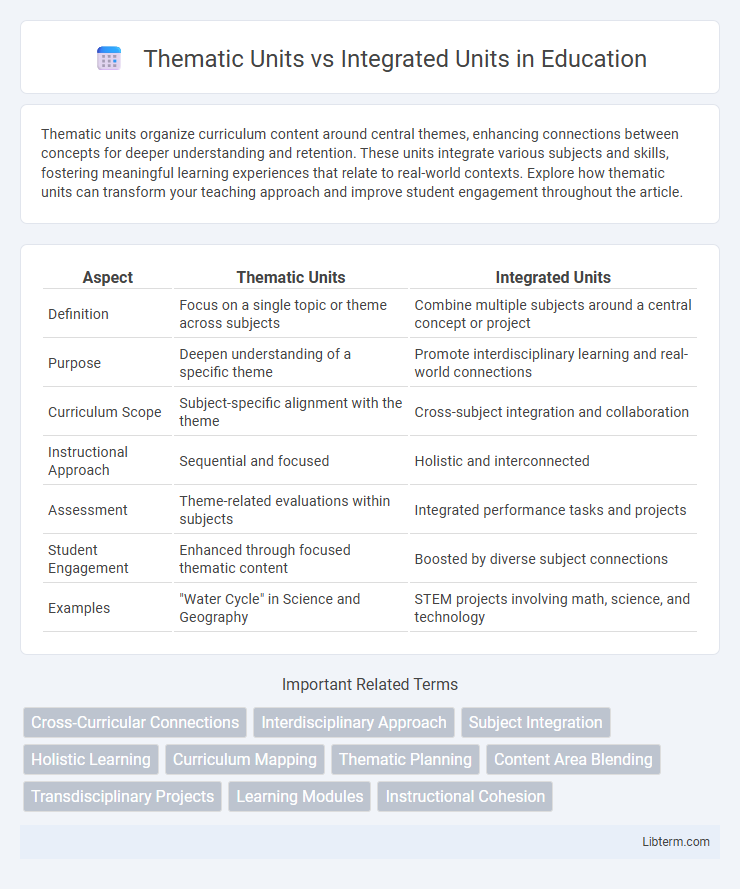
| Aspect | Thematic Units | Integrated Units |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on a single topic or theme across subjects | Combine multiple subjects around a central concept or project |
| Purpose | Deepen understanding of a specific theme | Promote interdisciplinary learning and real-world connections |
| Curriculum Scope | Subject-specific alignment with the theme | Cross-subject integration and collaboration |
| Instructional Approach | Sequential and focused | Holistic and interconnected |
| Assessment | Theme-related evaluations within subjects | Integrated performance tasks and projects |
| Student Engagement | Enhanced through focused thematic content | Boosted by diverse subject connections |
| Examples | "Water Cycle" in Science and Geography | STEM projects involving math, science, and technology |
Understanding Thematic Units
Thematic units organize curriculum around a central theme, allowing students to explore various subjects through interconnected concepts, enhancing deeper understanding and retention. This approach supports cognitive development by linking knowledge across disciplines such as science, language arts, and social studies, fostering critical thinking. Understanding thematic units enables educators to create coherent learning experiences that promote meaningful engagement and student-centered inquiry.
What Are Integrated Units?
Integrated units combine multiple subject areas into a cohesive learning experience, promoting connections across disciplines such as reading, science, and social studies. These units focus on real-world themes or problems, encouraging critical thinking and deeper understanding by linking concepts and skills from various subjects. Integrated units enhance student engagement through interdisciplinary content, fostering comprehensive knowledge and application.
Key Differences Between Thematic and Integrated Units
Thematic units center on a single, overarching theme that connects all lesson components, fostering deep exploration within a specific subject area. Integrated units combine multiple subjects, creating interdisciplinary lessons that link concepts across different fields for a broader learning experience. Key differences include thematic units' focus on in-depth content mastery versus integrated units' emphasis on cross-curricular connections and real-world application.
Benefits of Thematic Units
Thematic units enhance learning by providing focused content that connects concepts within a specific topic, promoting deeper understanding and retention. These units encourage critical thinking and make it easier for students to grasp complex ideas through curated, context-rich lessons. Thematic units also support differentiated instruction by allowing educators to tailor activities around a central theme, addressing diverse learning styles effectively.
Advantages of Integrated Units
Integrated units combine multiple subject areas into cohesive lessons, enhancing student engagement by connecting learning to real-world contexts. This approach promotes deeper understanding through the application of knowledge across disciplines, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Teachers benefit from streamlined planning and the ability to address diverse learning styles within a unified framework.
Curriculum Planning for Thematic Units
Thematic units in curriculum planning concentrate on exploring a central theme across multiple subjects, fostering deeper student engagement and meaningful connections between concepts. This approach enhances coherence and relevance by aligning learning objectives around a core idea, improving retention and critical thinking skills. Unlike integrated units, which blend disciplines more loosely, thematic units provide a structured framework that promotes interdisciplinary understanding while maintaining clear educational goals.
Designing Effective Integrated Units
Designing effective Integrated Units involves blending multiple subject areas into cohesive learning experiences that promote deeper understanding and real-world application. Key strategies include aligning objectives across disciplines, incorporating thematic concepts that are relevant and engaging, and using authentic assessment methods to evaluate student learning holistically. This approach enhances critical thinking and helps students make connections between knowledge domains, fostering comprehensive educational development.
Challenges in Implementing Thematic and Integrated Units
Challenges in implementing thematic units include difficulties in aligning diverse content areas with distinct learning objectives and managing time efficiently to cover all topics comprehensively. Integrated units face obstacles such as balancing depth and breadth across subjects, ensuring cohesive instructional planning, and overcoming resistance from educators accustomed to traditional, subject-specific teaching methods. Both approaches require extensive collaboration among teachers, ongoing professional development, and access to appropriate resources to support effective interdisciplinary learning.
Best Practices for Combining Thematic and Integrated Approaches
Effective best practices for combining thematic and integrated units emphasize aligning content around core themes while incorporating multiple subject areas to enhance interdisciplinary learning. Educators prioritize creating cohesive lesson plans that connect concepts across disciplines, fostering deeper understanding and relevance. Utilizing project-based activities and authentic assessments ensures meaningful engagement and application of both thematic and integrated instructional strategies.
Choosing the Right Unit Type for Your Classroom
Thematic units focus on a single topic across multiple subjects, promoting depth and coherence, while integrated units combine content from different disciplines to foster connections and relevance. Choose thematic units when aiming for in-depth exploration of a central theme that builds subject-specific skills, and select integrated units to encourage interdisciplinary understanding and real-world application. Matching unit type to your students' learning goals, curriculum standards, and engagement preferences ensures effective instruction and meaningful learning outcomes.
Thematic Units Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com