Formative assessment provides continuous feedback during the learning process, allowing educators to identify students' strengths and areas for improvement. This approach helps tailor instruction to meet Your unique needs, enhancing overall academic growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective formative assessment strategies and their benefits.
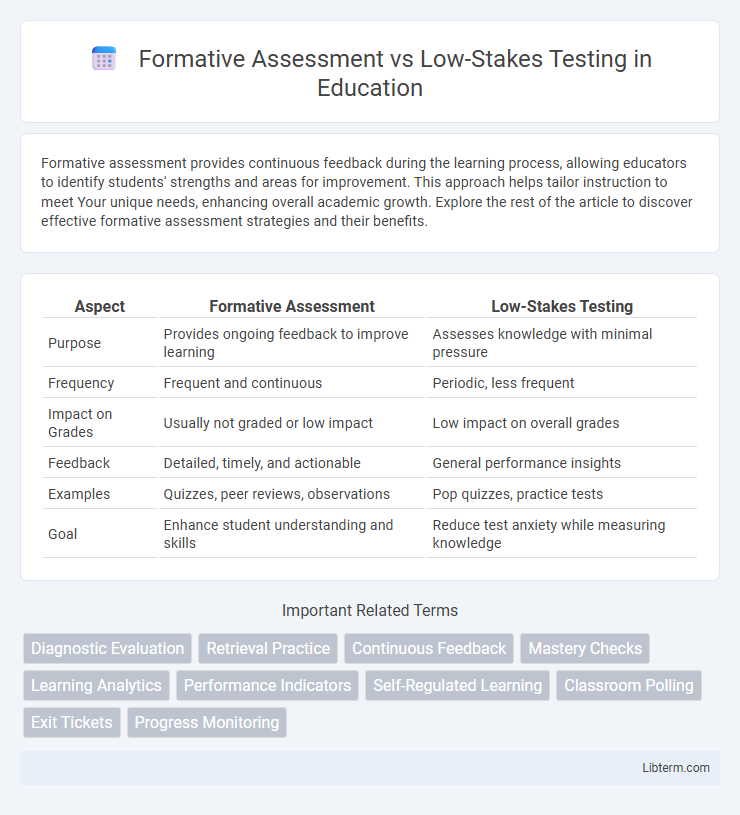
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formative Assessment | Low-Stakes Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides ongoing feedback to improve learning | Assesses knowledge with minimal pressure |
| Frequency | Frequent and continuous | Periodic, less frequent |
| Impact on Grades | Usually not graded or low impact | Low impact on overall grades |
| Feedback | Detailed, timely, and actionable | General performance insights |
| Examples | Quizzes, peer reviews, observations | Pop quizzes, practice tests |
| Goal | Enhance student understanding and skills | Reduce test anxiety while measuring knowledge |
Understanding Formative Assessment
Formative assessment involves continuous evaluation techniques that provide real-time feedback to enhance student learning and instructional methods. It emphasizes identifying students' strengths and weaknesses through informal, low-pressure activities like quizzes, discussions, and peer reviews, promoting active engagement and self-regulation. Unlike low-stakes testing, formative assessment aims to support learning progression rather than merely measuring performance outcomes.
What Is Low-Stakes Testing?
Low-stakes testing refers to assessments that carry minimal consequences for students' grades or academic progression, primarily designed to monitor learning without the pressure of high-stakes outcomes. These tests provide real-time feedback to both educators and learners, fostering a supportive environment that encourages risk-taking and concept mastery. Unlike formative assessments that guide instructional adjustments, low-stakes tests emphasize reducing anxiety and promoting continuous engagement through frequent, informal evaluation opportunities.
Core Differences Between the Two Approaches
Formative assessment continuously monitors student learning to provide real-time feedback that guides instructional adjustments and promotes skill development. Low-stakes testing involves assessments with minimal impact on final grades, aiming to reduce anxiety while identifying knowledge gaps. The core difference lies in formative assessment's dynamic, feedback-driven nature versus low-stakes testing's focus on assessment outcomes with reduced pressure.
Purposes and Goals of Each Method
Formative assessment aims to monitor student learning continuously, providing immediate feedback to improve instruction and support mastery of content. Low-stakes testing serves to gauge understanding without significant pressure, encouraging consistent practice and reducing test anxiety. Both methods prioritize enhancing student engagement and promoting deeper comprehension through regular, non-punitive evaluation.
Key Benefits of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment fosters continuous feedback, enabling educators to identify student learning gaps and adjust instruction in real time. It enhances student engagement and motivation by promoting active learning and self-reflection, which supports long-term academic growth. Compared to low-stakes testing, formative assessment provides more personalized insights, helping to tailor teaching strategies to individual learning needs.
Advantages of Low-Stakes Testing
Low-stakes testing offers unique advantages by reducing student anxiety and promoting a growth mindset, which encourages learning through error correction. It provides frequent opportunities for feedback without the pressure of high consequences, enhancing motivation and engagement. This approach supports retention and skill mastery by allowing repeated practice and self-assessment in a low-risk environment.
Impact on Student Learning and Engagement
Formative assessment enhances student learning by providing continuous, actionable feedback that helps identify strengths and areas for improvement, fostering deeper understanding and skill development. Low-stakes testing reduces anxiety and encourages consistent effort without the pressure of high-stakes consequences, promoting a more positive and engaging learning environment. Both approaches increase student engagement by emphasizing progress and mastery over grades, ultimately leading to better academic outcomes.
Practical Classroom Strategies for Both
Formative assessment strategies include frequent quizzes, interactive discussions, and real-time feedback to monitor student learning and guide instruction effectively. Low-stakes testing reduces anxiety by emphasizing learning over grades, using practices like ungraded practice tests or collaborative group assessments to boost engagement. Combining both approaches enhances student motivation and provides actionable insights to tailor teaching methods in diverse classroom settings.
Challenges and Limitations
Formative assessment faces challenges such as time constraints for educators and difficulties in providing immediate, individualized feedback that effectively guides student learning. Low-stakes testing can suffer from limitations including reduced student motivation and engagement due to the minimal consequences of test outcomes. Both methods require careful implementation to balance assessment accuracy with meaningful learning insights and classroom practicality.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Formative assessment offers ongoing feedback that informs instruction and supports student learning growth, whereas low-stakes testing provides less pressure and helps identify knowledge gaps without heavily impacting grades. Selecting the right approach depends on the classroom goals, student needs, and curriculum demands, emphasizing a balance between meaningful feedback and anxiety reduction. Integrating both methods strategically enhances student engagement and promotes a deeper understanding of subject matter.
Formative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com