A standardized curriculum ensures consistent educational content and learning outcomes across different schools and regions, promoting fairness and equal opportunity for all students. It establishes clear benchmarks that guide teachers and help measure student progress effectively. Discover how a standardized curriculum can impact Your education and why it remains a pivotal topic in educational reform.
Table of Comparison
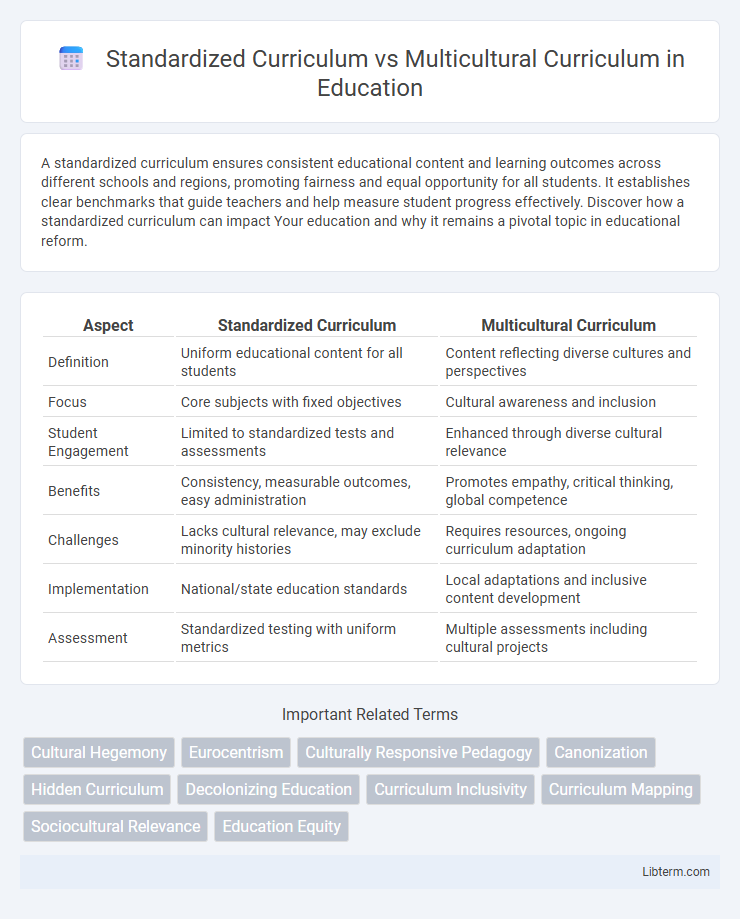
| Aspect | Standardized Curriculum | Multicultural Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform educational content for all students | Content reflecting diverse cultures and perspectives |
| Focus | Core subjects with fixed objectives | Cultural awareness and inclusion |
| Student Engagement | Limited to standardized tests and assessments | Enhanced through diverse cultural relevance |
| Benefits | Consistency, measurable outcomes, easy administration | Promotes empathy, critical thinking, global competence |
| Challenges | Lacks cultural relevance, may exclude minority histories | Requires resources, ongoing curriculum adaptation |
| Implementation | National/state education standards | Local adaptations and inclusive content development |
| Assessment | Standardized testing with uniform metrics | Multiple assessments including cultural projects |
Introduction to Curriculum Approaches
Standardized curriculum emphasizes uniform content and assessment practices designed to ensure consistency and comparability across educational settings. Multicultural curriculum integrates diverse cultural perspectives and experiences to promote inclusivity and critical awareness among students. Both approaches address curriculum design but differ in their goals of standardization versus cultural representation.
Defining Standardized Curriculum
Standardized curriculum refers to a uniform educational framework designed to ensure consistent teaching content, objectives, and assessment methods across different schools and regions. It emphasizes predefined learning outcomes, promoting equity by providing all students with the same academic standards regardless of background. This approach often prioritizes core subjects like math, science, and language arts, aiming for measurable achievement through standardized testing.
Understanding Multicultural Curriculum
Understanding multicultural curriculum involves recognizing diverse cultural perspectives, histories, and values integrated into educational content, promoting inclusivity and equity among students. Unlike standardized curriculum, which adheres to uniform content and assessment criteria, multicultural curriculum adapts to the unique cultural backgrounds of learners, fostering critical thinking and cross-cultural awareness. This approach enhances student engagement and prepares learners for global citizenship by validating multiple identities and experiences within the learning environment.
Goals and Objectives of Each Approach
A standardized curriculum emphasizes uniform goals and objectives aimed at achieving consistent academic outcomes, ensuring all students meet predetermined benchmarks in core subjects. In contrast, a multicultural curriculum prioritizes inclusive goals that reflect cultural diversity, fostering critical thinking, cultural awareness, and respect for multiple perspectives. The standardized approach seeks measurable proficiency and knowledge retention, while the multicultural approach targets social equity, cultural competence, and preparing students for global citizenship.
Benefits of a Standardized Curriculum
A standardized curriculum ensures consistent learning outcomes by providing uniform content and assessment methods across different schools, facilitating equitable education. It streamlines teacher training and resource allocation, leading to improved instructional quality and efficiency. Standardization also simplifies benchmarking and accountability, enabling clear measurement of student performance at regional and national levels.
Advantages of a Multicultural Curriculum
A multicultural curriculum promotes inclusivity by representing diverse cultures, perspectives, and histories, which enhances students' cultural awareness and empathy. It fosters critical thinking and adaptability by encouraging learners to analyze issues from multiple viewpoints and prepares them for global citizenship in an interconnected world. Research shows students engaged with multicultural content perform better academically and develop stronger social skills compared to those in standardized curriculums.
Challenges and Criticisms of Standardization
Standardized curriculum often faces criticism for imposing a uniform educational framework that may neglect cultural diversity and fail to address the unique needs of diverse student populations. This approach can limit the inclusion of multicultural perspectives, resulting in reduced cultural relevance and engagement among students from varied backgrounds. Challenges include the marginalization of minority voices and the potential reinforcement of systemic biases within educational content and assessment methods.
Potential Drawbacks of Multicultural Curricula
Multicultural curricula often face challenges such as the risk of cultural stereotyping and oversimplification, which can lead to misrepresentation of diverse groups. Teachers may struggle with inadequate training and resources to effectively deliver content that authentically represents multiple cultures. These drawbacks can result in a fragmented or superficial understanding of cultural diversity, potentially undermining the educational goals of inclusion and equity.
Impact on Student Learning and Inclusion
A standardized curriculum provides consistent content and assessment, promoting uniform academic benchmarks but may limit cultural relevance and student engagement. A multicultural curriculum enhances inclusion by incorporating diverse perspectives, fostering critical thinking, and validating students' cultural identities, which can improve motivation and learning outcomes. Balancing both approaches optimizes equitable education, supporting academic success while embracing cultural diversity.
Finding a Balance: Integrating Diverse Curriculum Models
Finding a balance between standardized and multicultural curricula requires blending consistent educational benchmarks with inclusive content that reflects diverse cultural perspectives. Integrating multicultural elements into a standardized framework promotes both academic rigor and cultural competence, fostering a learning environment where all students feel represented and valued. Effective curriculum design leverages data on student demographics and learning outcomes to adapt materials that support equity and prepare learners for a globalized society.
Standardized Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com