Proprietary courseware offers customized learning solutions designed to meet specific educational needs, enhancing the effectiveness of training programs. These materials often include exclusive content and features that are not available in standard resources, ensuring a tailored experience for your learners. Explore the full article to discover how proprietary courseware can transform your educational strategy.
Table of Comparison
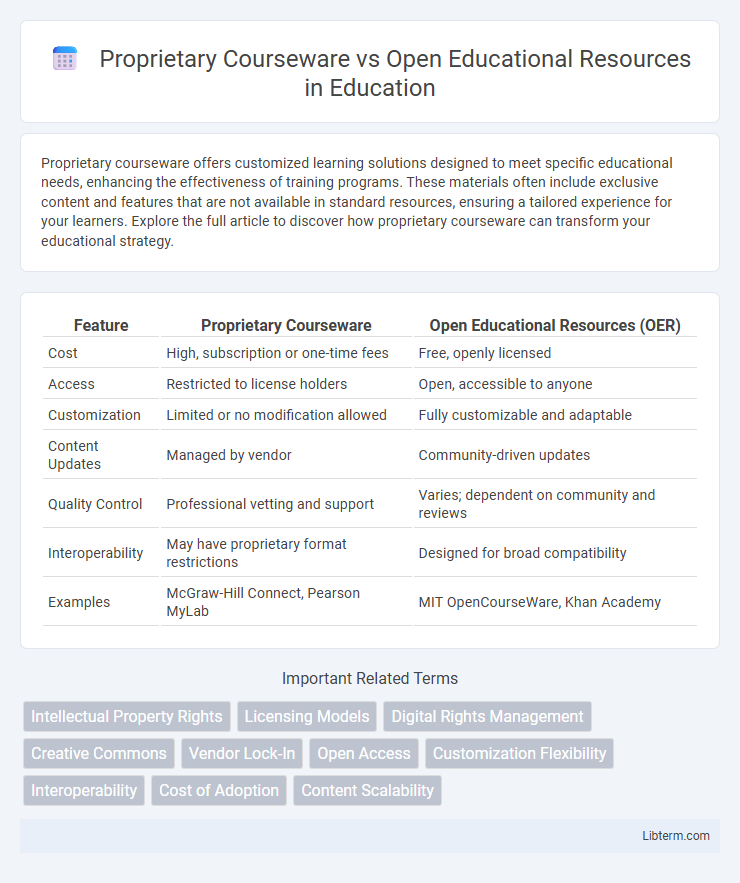
| Feature | Proprietary Courseware | Open Educational Resources (OER) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High, subscription or one-time fees | Free, openly licensed |
| Access | Restricted to license holders | Open, accessible to anyone |
| Customization | Limited or no modification allowed | Fully customizable and adaptable |
| Content Updates | Managed by vendor | Community-driven updates |
| Quality Control | Professional vetting and support | Varies; dependent on community and reviews |
| Interoperability | May have proprietary format restrictions | Designed for broad compatibility |
| Examples | McGraw-Hill Connect, Pearson MyLab | MIT OpenCourseWare, Khan Academy |
Introduction to Proprietary Courseware and Open Educational Resources
Proprietary courseware consists of educational materials developed and controlled by specific companies or institutions, often requiring purchase or subscription for access. Open Educational Resources (OER) are freely accessible, openly licensed materials that educators and learners can use, modify, and share without cost. Both serve distinct roles in education, with proprietary courseware offering standardized, curated content and OER promoting flexibility and widespread accessibility.
Key Differences Between Proprietary and Open Educational Content
Proprietary courseware is typically developed by commercial entities that restrict access and usage through licenses, often requiring purchase or subscription fees, while Open Educational Resources (OER) are freely accessible and licensed for modification and redistribution under open licenses like Creative Commons. Proprietary content often offers polished, cohesive curricula with dedicated support but limits customization, whereas OER provides greater flexibility and collaboration opportunities, enabling educators to adapt materials to specific learning needs. The key difference lies in access control and cost, with proprietary courses prioritizing intellectual property protection and monetization, whereas OER prioritizes educational equity and open sharing.
Accessibility and Affordability: A Comparative Analysis
Proprietary courseware often presents accessibility challenges due to licensing restrictions and digital rights management, limiting usage across diverse platforms and user groups. Open Educational Resources (OER) enhance accessibility by offering freely available materials adaptable to various learning environments without cost barriers. In terms of affordability, proprietary courseware incurs significant expenses through licensing fees, whereas OER drastically reduce financial burdens, promoting equitable educational opportunities for a broader audience.
Content Quality and Academic Standards
Proprietary courseware often undergoes rigorous quality assurance processes ensuring alignment with institutional academic standards, typically developed by subject matter experts and regularly updated to reflect current curriculum requirements. Open Educational Resources (OER) provide flexible, freely accessible content, but quality and academic rigor can vary significantly depending on the source and peer review mechanisms employed. Institutions adopting OER frequently implement review protocols to maintain comparability to proprietary materials, aiming to uphold consistent academic standards across diverse educational environments.
Customization and Adaptability for Educators
Proprietary courseware often offers limited customization, restricting educators to preset content and tools dictated by the vendor, which can impede alignment with specific curriculum needs. In contrast, open educational resources (OER) provide educators with extensive adaptability, allowing them to modify, remix, and personalize materials to better suit diverse student learning styles and institutional goals. This flexibility in OER supports dynamic teaching practices and enhances the ability to update content quickly in response to evolving educational standards.
Licensing and Intellectual Property Considerations
Proprietary courseware typically involves strict licensing agreements that restrict redistribution and modification, ensuring the content remains under the control of the creator or publisher. In contrast, Open Educational Resources (OER) are released under licenses like Creative Commons, allowing users to freely access, adapt, and share materials while attributing the original authors. Intellectual property considerations for proprietary courseware often prioritize revenue protection, whereas OER emphasizes collaborative improvement and broad dissemination of knowledge.
Technological Integration and Platform Compatibility
Proprietary courseware often offers advanced technological integration with seamless compatibility across multiple platforms, including dedicated apps and LMS systems, ensuring a consistent user experience. Open Educational Resources (OER) typically rely on open standards and web-based platforms, providing greater flexibility but sometimes facing challenges in uniform performance across devices. Both models leverage technology differently; proprietary solutions prioritize optimized, controlled environments, while OER emphasizes accessibility and adaptability across diverse technological ecosystems.
Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Proprietary courseware offers structured content with interactive features designed to enhance student engagement through adaptive learning technologies and detailed analytics, often leading to improved learning outcomes. Open Educational Resources (OER) provide flexible, freely accessible materials that encourage collaborative learning and allow instructors to tailor content, fostering diverse engagement strategies that can boost student motivation. Studies indicate that while proprietary courseware may offer more consistent performance gains, OER's customization potential supports deeper, personalized learning experiences benefiting different student groups.
Institutional Adoption: Benefits and Challenges
Institutional adoption of proprietary courseware offers structured, high-quality content with dedicated support and regular updates, ensuring alignment with curriculum standards, yet often entails significant licensing costs and limited customization. Open Educational Resources (OER) provide flexibility, cost savings, and the ability to tailor materials to specific institutional needs, but may require additional faculty time for adaptation and raise concerns about content quality and consistency. Balancing these benefits and challenges is critical for institutions aiming to optimize educational effectiveness and budgetary constraints.
Future Trends in Educational Resource Development
Future trends in educational resource development emphasize increased integration of adaptive learning technologies within both proprietary courseware and open educational resources (OER). Artificial intelligence-driven personalization and data analytics will enhance student engagement and learning outcomes, driving demand for customizable content. Growth in collaborative platforms and interoperability standards will further blur the lines between proprietary and open resources, fostering hybrid models that maximize accessibility and quality.
Proprietary Courseware Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com