Inquiry-Based Learning enhances critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics deeply. This method fosters active engagement and promotes a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Discover how Inquiry-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
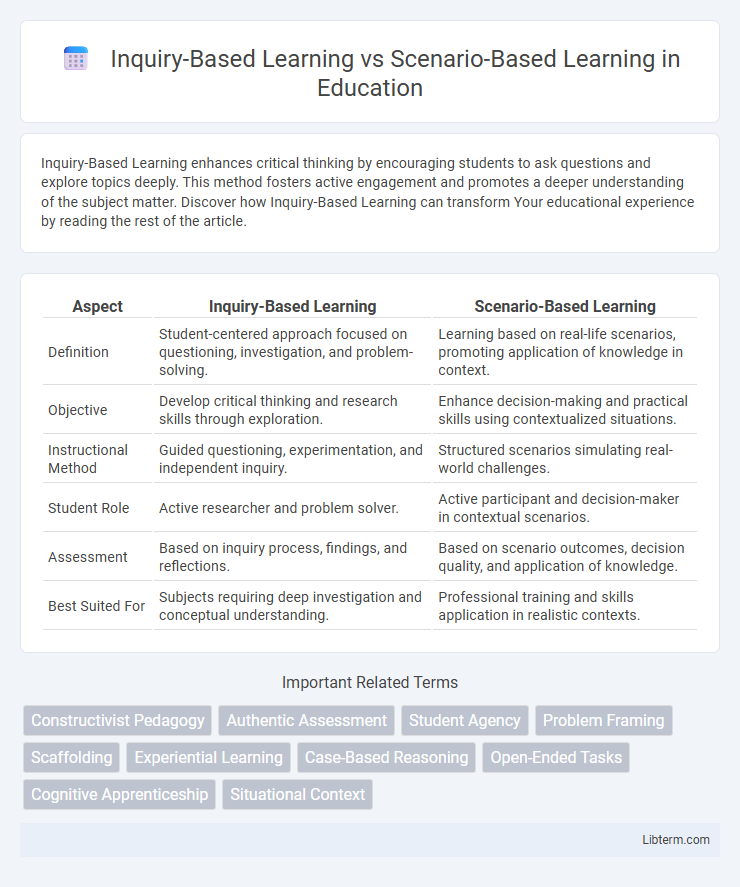
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Scenario-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focused on questioning, investigation, and problem-solving. | Learning based on real-life scenarios, promoting application of knowledge in context. |
| Objective | Develop critical thinking and research skills through exploration. | Enhance decision-making and practical skills using contextualized situations. |
| Instructional Method | Guided questioning, experimentation, and independent inquiry. | Structured scenarios simulating real-world challenges. |
| Student Role | Active researcher and problem solver. | Active participant and decision-maker in contextual scenarios. |
| Assessment | Based on inquiry process, findings, and reflections. | Based on scenario outcomes, decision quality, and application of knowledge. |
| Best Suited For | Subjects requiring deep investigation and conceptual understanding. | Professional training and skills application in realistic contexts. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based and Scenario-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration, encouraging critical thinking by prompting learners to investigate questions and problems independently or collaboratively. Scenario-Based Learning employs realistic, contextualized situations that immerse students in decision-making processes to apply knowledge and develop practical skills. Both approaches prioritize active engagement but differ in structure: Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes open-ended questioning, while Scenario-Based Learning focuses on guided, scenario-driven experiences.
Defining Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning is an educational approach where students actively explore questions, problems, or scenarios to develop deeper understanding through investigation and critical thinking. It emphasizes student-driven inquiry, fostering skills such as research, analysis, and reflection by encouraging learners to formulate hypotheses and seek evidence. This method contrasts with more structured learning models by prioritizing exploration and discovery as key components of knowledge acquisition.
Defining Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-Based Learning (SBL) is an instructional strategy that uses real-world scenarios to engage learners in problem-solving and decision-making activities, promoting practical application of knowledge. This approach enhances critical thinking and situational analysis by immersing students in context-rich environments where they must navigate challenges like professionals in the field. SBL contrasts with Inquiry-Based Learning by emphasizing applied scenarios over open-ended questions to drive learning objectives and skill mastery.
Core Principles and Philosophies
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on fostering curiosity and critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions, investigate, and construct knowledge through active exploration. Scenario-Based Learning emphasizes applying knowledge in realistic, context-driven situations to develop problem-solving skills and decision-making abilities. Both methodologies prioritize student engagement and experiential learning but differ in their approach: Inquiry-Based Learning leans towards open-ended investigation, while Scenario-Based Learning focuses on guided, practical simulation.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven questioning and exploration to construct knowledge through investigation and critical thinking. Scenario-Based Learning centers on applying knowledge to realistic, context-rich situations to develop problem-solving skills and practical understanding. While Inquiry-Based Learning fosters open-ended inquiry and discovery, Scenario-Based Learning provides structured scenarios that simulate real-world challenges for targeted skill development.
Advantages of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to ask questions, investigate, and construct knowledge independently. It promotes active engagement and curiosity, leading to improved problem-solving skills and retention of information. This learner-centered approach enhances adaptability and motivation by allowing exploration tailored to individual interests and real-world complexities.
Advantages of Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-Based Learning enhances critical thinking by immersing learners in real-world contexts, promoting practical problem-solving skills. It increases engagement through interactive, story-driven scenarios that simulate authentic challenges across disciplines. The approach supports knowledge retention by contextualizing information within meaningful situations, making concepts easier to apply in professional environments.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Inquiry-Based Learning often faces challenges such as students' difficulty in formulating research questions and limited prior knowledge, which can hinder effective exploration and result in unfocused learning outcomes. Scenario-Based Learning may encounter limitations including unrealistic scenarios that fail to engage learners deeply or lack of adaptability to diverse learning styles, reducing its overall effectiveness. Both methods require significant instructor expertise to guide learners appropriately and ensure alignment with learning objectives, posing a challenge in implementation.
Application Contexts: When to Use Each Approach
Inquiry-Based Learning excels in educational settings that require deep exploration and the development of critical thinking skills, such as science labs or research projects where students generate questions and investigate answers independently. Scenario-Based Learning is highly effective in professional training and simulations, especially in fields like healthcare, aviation, or customer service, where learners must apply knowledge in realistic, context-driven situations to enhance decision-making and practical skills. Choosing between these approaches depends on whether the goal is to foster autonomous inquiry and conceptual understanding (Inquiry-Based) or to build applied problem-solving abilities through immersive, situational practice (Scenario-Based).
Integrating Inquiry and Scenario Methods for Enhanced Learning
Integrating inquiry-based learning and scenario-based learning combines the strengths of student-driven exploration with realistic, context-rich problem-solving to deepen comprehension and retention. This hybrid approach fosters critical thinking by prompting learners to investigate open-ended questions within authentic scenarios, enhancing engagement and practical application of knowledge. Research indicates that blending these methods increases motivation and develops adaptive expertise, preparing students for complex real-world challenges.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com