Lecture-based learning remains a widely used educational approach where instructors deliver information directly to students, focusing on content mastery and structured knowledge acquisition. This method can help streamline complex topics and enhance understanding through expert guidance, but it may limit active student engagement and critical thinking opportunities. Discover how you can maximize the effectiveness of lecture-based learning and explore its benefits and challenges in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
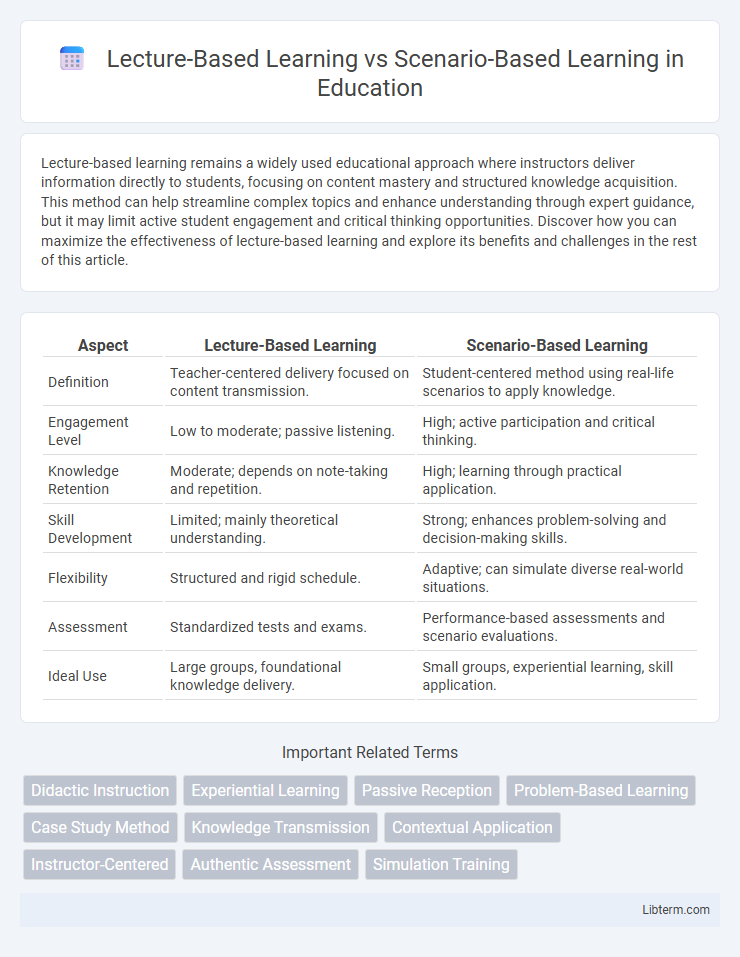
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Learning | Scenario-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered delivery focused on content transmission. | Student-centered method using real-life scenarios to apply knowledge. |
| Engagement Level | Low to moderate; passive listening. | High; active participation and critical thinking. |
| Knowledge Retention | Moderate; depends on note-taking and repetition. | High; learning through practical application. |
| Skill Development | Limited; mainly theoretical understanding. | Strong; enhances problem-solving and decision-making skills. |
| Flexibility | Structured and rigid schedule. | Adaptive; can simulate diverse real-world situations. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and exams. | Performance-based assessments and scenario evaluations. |
| Ideal Use | Large groups, foundational knowledge delivery. | Small groups, experiential learning, skill application. |
Introduction to Learning Approaches
Lecture-based learning emphasizes structured content delivery by instructors, facilitating knowledge acquisition through direct teaching methods. Scenario-based learning engages students with real-world situations, promoting critical thinking and application of concepts in context. Both approaches serve distinct educational purposes, with lecture-based learning ideal for foundational knowledge and scenario-based learning enhancing problem-solving skills.
Defining Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-Based Learning is a traditional instructional method where an expert delivers content through speeches or presentations, focusing on the clear transmission of theoretical knowledge. This approach emphasizes passive reception, with learners absorbing information primarily through listening and note-taking. It is effective for conveying foundational concepts and large volumes of information to large groups efficiently.
Understanding Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-Based Learning (SBL) enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by immersing learners in real-world situations that require active decision-making. This instructional approach prioritizes experiential engagement, enabling deeper comprehension compared to traditional Lecture-Based Learning (LBL), which primarily involves passive knowledge reception. SBL's effectiveness lies in its ability to simulate authentic contexts, fostering practical application and retention of concepts within diverse educational and professional settings.
Core Principles of Each Method
Lecture-based learning centers on the structured delivery of information from an instructor to students, emphasizing clear presentation of facts and theories to facilitate foundational knowledge acquisition. Scenario-based learning engages learners through immersive, real-world situations that require critical thinking, decision-making, and application of skills in context, promoting active problem-solving and experiential understanding. Core principles of lecture-based learning include authoritative content transmission and passive absorption, while scenario-based learning prioritizes interaction, contextual relevance, and learner autonomy.
Advantages of Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-based learning offers structured delivery of comprehensive content, ensuring consistent knowledge transfer across diverse audiences. It efficiently covers foundational theories and complex concepts, allowing learners to absorb information through expert explanations. This method supports scalability in education, making it ideal for large groups and standardized curriculum implementation.
Benefits of Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-based learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by immersing students in realistic contexts that promote active engagement and deeper understanding. It fosters collaboration and communication through interactive group activities, making knowledge retention more effective compared to traditional lecture-based methods. This approach also adapts to diverse learning styles, increasing motivation and practical application in real-world scenarios across disciplines like healthcare, business, and engineering.
Comparing Engagement and Retention Rates
Lecture-Based Learning often results in lower engagement and retention rates due to passive information delivery, where students primarily listen and take notes. Scenario-Based Learning enhances engagement by immersing learners in realistic contexts, promoting active problem-solving and critical thinking. Studies show retention rates can improve by up to 60% with scenario-based methods compared to traditional lectures.
Suitability for Different Learner Types
Lecture-based learning suits analytical learners who thrive on structured, information-dense content and absorb material through listening and note-taking. Scenario-based learning benefits experiential and kinesthetic learners by immersing them in realistic situations that enhance problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Adapting teaching methods to learner preferences improves engagement and knowledge retention across diverse educational settings.
Challenges and Limitations
Lecture-based learning often faces challenges such as passive knowledge absorption, limited student engagement, and difficulty in catering to diverse learning styles, which can hinder deep comprehension. Scenario-based learning, while promoting active problem-solving and critical thinking, may encounter limitations including the high resource demands for scenario development, potential learner frustration with complex situations, and variable effectiveness depending on scenario relevance. Both methods require strategic integration and adaptation to overcome these inherent challenges and maximize educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Educational Success
Lecture-based learning delivers structured content efficiently to large groups, ideal for foundational knowledge acquisition in subjects like history or science. Scenario-based learning enhances critical thinking and practical skills by immersing students in real-world situations, making it effective for fields such as medicine, law, and business. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on educational goals: use lectures for information transfer and scenarios to foster problem-solving and application of knowledge.
Lecture-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com