Charter schools offer a unique educational alternative by providing publicly funded but independently operated institutions that focus on specialized curricula and innovative teaching methods. These schools aim to enhance student outcomes through increased flexibility and accountability compared to traditional public schools. Discover how charter schools could impact Your child's learning experience and education options in the full article.
Table of Comparison
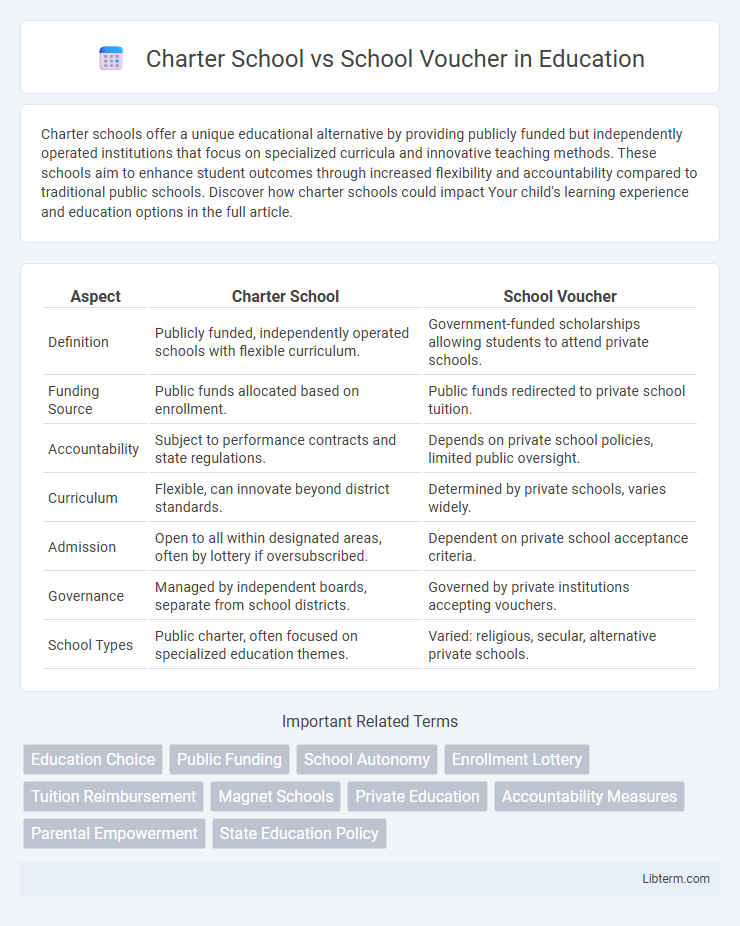
| Aspect | Charter School | School Voucher |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Publicly funded, independently operated schools with flexible curriculum. | Government-funded scholarships allowing students to attend private schools. |
| Funding Source | Public funds allocated based on enrollment. | Public funds redirected to private school tuition. |
| Accountability | Subject to performance contracts and state regulations. | Depends on private school policies, limited public oversight. |
| Curriculum | Flexible, can innovate beyond district standards. | Determined by private schools, varies widely. |
| Admission | Open to all within designated areas, often by lottery if oversubscribed. | Dependent on private school acceptance criteria. |
| Governance | Managed by independent boards, separate from school districts. | Governed by private institutions accepting vouchers. |
| School Types | Public charter, often focused on specialized education themes. | Varied: religious, secular, alternative private schools. |
Overview of Charter Schools and School Vouchers
Charter schools are publicly funded independent schools operating under a charter, allowing them more flexibility in curriculum and management compared to traditional public schools. School vouchers provide parents with public funds to enroll their children in private or charter schools, giving families more school choice options. The debate centers on accountability, educational outcomes, and the impact on public school funding.
Key Differences Between Charter Schools and Voucher Programs
Charter schools are publicly funded but operate independently from traditional public school systems, offering specialized curricula and greater flexibility in teaching methods, whereas school voucher programs provide public funding directly to parents to apply toward tuition at private schools, including religious institutions. Charter schools are held accountable to performance contracts and must meet specific academic standards, while voucher-funded private schools are generally subject to less stringent state oversight. Enrollment in charter schools is open to all students within a designated area, contrasting with voucher programs that depend on family choice and availability of participating private schools.
Admission Processes: Who Gets Access?
Charter schools typically use a lottery system for admissions when applications exceed available spots, ensuring a random selection process open to all students within the designated area. In contrast, school vouchers allow families to choose private or public schools that accept the voucher, often without strict admission criteria, but access depends on the availability of participating schools and their own enrollment policies. Both approaches aim to increase educational choice, yet they differ significantly in how access is determined and regulated.
Funding Structure and Financial Implications
Charter schools receive public funding based on enrollment but operate independently from traditional public school districts, allowing for flexible budgeting and allocation of resources. In contrast, school vouchers provide parents with public funds to pay for tuition at private schools, effectively shifting public education dollars away from public school systems. Both funding structures impact financial transparency and accountability, with charter schools required to adhere to public reporting standards, while voucher programs often face criticism for reduced oversight and potential diversion of funds from public education.
Impact on Student Performance and Outcomes
Charter schools, independently operated public schools, often showcase improved student performance by implementing innovative curricula and personalized learning approaches, particularly in underserved communities. School vouchers provide families with public funding to attend private schools, increasing school choice but yielding mixed results on student outcomes due to variable private school quality. Research indicates that while charter schools sometimes boost standardized test scores and graduation rates, voucher programs have inconsistent effects on academic achievement and long-term educational benefits.
Parental Choice and Community Involvement
Charter schools provide parents with the ability to choose specialized educational programs within public education while maintaining accountability to state standards. School vouchers offer families financial assistance to enroll their children in private schools, expanding parental choice beyond the public system. Both models encourage active community involvement by fostering partnerships between families, educators, and local organizations to support student success.
Accountability and Oversight Mechanisms
Charter schools operate under specific accountability frameworks, often required to meet performance goals outlined in their charters, with oversight conducted by authorizing bodies such as school districts or independent charter boards. In contrast, school voucher programs provide families with public funds to attend private schools, where oversight and accountability vary widely by state and often lack stringent performance reporting requirements. The effectiveness of accountability mechanisms in both systems critically impacts educational outcomes and the equitable use of public funds.
Equity Concerns: Serving Diverse Populations
Charter schools aim to serve diverse populations by offering specialized programs and flexible admissions, but concerns remain about equitable access for low-income and minority students due to uneven funding and location disparities. School vouchers provide families with the choice to attend private schools, yet critics argue they may exacerbate segregation and reduce resources for public schools serving the most disadvantaged communities. Both models face challenges in ensuring fair access and promoting inclusivity for historically underserved student groups.
Controversies and Common Criticisms
Charter schools face criticism for lack of accountability, inconsistent academic performance, and potential to drain resources from traditional public schools, raising equity concerns. School voucher programs are controversial due to the diversion of public funds to private and sometimes religious schools, undermining public education and lacking oversight on educational outcomes. Both policies ignite debates over public funding priorities, educational equity, and the overall impact on the quality of education for underserved communities.
Future Trends in School Choice Policies
Future trends in school choice policies indicate a growing emphasis on expanding both charter schools and school voucher programs to increase educational options for families. Policymakers are exploring hybrid models that combine the flexibility of charter schools with the funding mechanisms of vouchers to enhance accessibility and personalized learning experiences. Data-driven outcomes and equity considerations are expected to play a critical role in shaping more inclusive and accountable school choice frameworks.
Charter School Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com