Effective behavioral management techniques focus on reinforcing positive behavior while addressing negative actions through clear expectations and consistent consequences. Strategies such as setting routines, using motivational rewards, and implementing corrective feedback help create a structured environment that promotes self-discipline and social skills. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips and tools for enhancing your behavioral management approach.
Table of Comparison
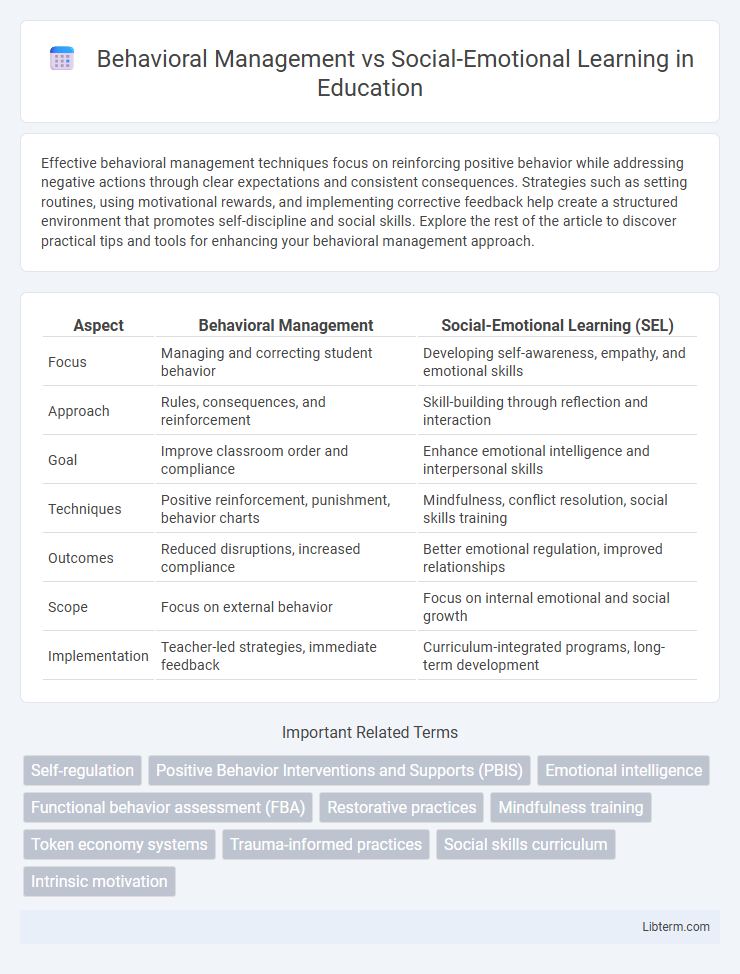
| Aspect | Behavioral Management | Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Managing and correcting student behavior | Developing self-awareness, empathy, and emotional skills |
| Approach | Rules, consequences, and reinforcement | Skill-building through reflection and interaction |
| Goal | Improve classroom order and compliance | Enhance emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills |
| Techniques | Positive reinforcement, punishment, behavior charts | Mindfulness, conflict resolution, social skills training |
| Outcomes | Reduced disruptions, increased compliance | Better emotional regulation, improved relationships |
| Scope | Focus on external behavior | Focus on internal emotional and social growth |
| Implementation | Teacher-led strategies, immediate feedback | Curriculum-integrated programs, long-term development |
Understanding Behavioral Management: Core Concepts
Behavioral management involves strategies and techniques aimed at modifying or controlling student behavior to create a productive learning environment. Core concepts include positive reinforcement, setting clear expectations, consistent consequences, and proactive interventions to prevent disruptive behavior. Understanding these principles helps educators maintain classroom order while promoting student accountability and engagement.
Defining Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) is an educational framework that cultivates students' skills in self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship building, and responsible decision-making. It integrates emotional intelligence into the learning process, promoting positive interactions and mental well-being. Unlike behavioral management, which focuses on controlling student conduct, SEL fosters intrinsic motivation and emotional regulation to support long-term personal and academic success.
Key Differences Between Behavioral Management and SEL
Behavioral Management primarily targets modifying observable actions through reinforcement strategies and clear consequences, while Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) emphasizes developing internal skills such as emotional regulation, empathy, and interpersonal communication. Behavioral Management relies on structured environments and behavioral cues to encourage compliance, whereas SEL fosters self-awareness and social skills to promote intrinsic motivation and positive relationships. The key difference lies in Behavioral Management addressing external behaviors directly, and SEL focusing on cultivating underlying emotional competencies that drive behavior.
Historical Evolution of Behavioral Management in Education
Behavioral management in education originated from early 20th-century behavioral psychology, emphasizing observable behaviors and reinforcement techniques, notably influenced by B.F. Skinner's operant conditioning. Over decades, this approach evolved through practices like token economies and behavior modification to address classroom discipline and improve student compliance. The shift towards Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) in recent years reflects an expanded focus on emotional regulation and interpersonal skills, contrasting with the traditional behaviorist model's focus on external behavior control.
The Development of Social-Emotional Learning Frameworks
The development of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) frameworks centers on cultivating essential emotional intelligence skills such as self-awareness, empathy, and responsible decision-making, contrasting with traditional Behavioral Management approaches that emphasize external behavior control and rule enforcement. SEL frameworks integrate evidence-based practices to foster intrinsic motivation and positive social interactions, promoting long-term emotional well-being and academic success. These frameworks are designed to be proactive, holistic, and inclusive, supporting student-centered environments that encourage growth through reflection and relationship-building rather than mere compliance.
Impact on Student Outcomes: Behavioral Management vs SEL
Behavioral Management techniques primarily aim to reduce disruptive behaviors and improve classroom order, leading to immediate improvements in student focus and academic performance. Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) fosters long-term emotional regulation, empathy, and interpersonal skills, which enhance students' resilience, motivation, and overall well-being. Research indicates that integrating SEL with behavioral management results in more positive student outcomes, including higher academic achievement, better mental health, and reduced disciplinary incidents.
Common Strategies in Behavioral Management
Common strategies in behavioral management include positive reinforcement, clear expectations, consistent consequences, and structured routines to promote desirable behaviors. Techniques such as token economies, behavior contracts, and frequent feedback help create an environment conducive to learning and self-regulation. These methods align with social-emotional learning goals by fostering self-awareness, responsible decision-making, and relationship skills among students.
Essential Practices in Social-Emotional Learning
Essential practices in Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) emphasize fostering self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making to create supportive learning environments. Behavioral management tends to focus on external control and modifying student behaviors through rules and consequences, whereas SEL encourages intrinsic motivation and emotional regulation to promote long-term positive outcomes. Integrating SEL practices such as explicit instruction, modeling, and reflective discussions enhances students' emotional intelligence and social competence more effectively than traditional behavioral management alone.
Integrating Behavioral Management and SEL in the Classroom
Integrating behavioral management and social-emotional learning (SEL) in the classroom enhances student engagement and fosters a positive learning environment by addressing both conduct and emotional development. Effective strategies include setting clear behavioral expectations while simultaneously teaching empathy, self-regulation, and interpersonal skills through SEL curricula such as CASEL frameworks. This holistic approach improves emotional well-being, reduces disciplinary incidents, and promotes academic success by supporting students' cognitive and social growth.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors for Educators
Effective decision-making in education requires evaluating behavioral management and social-emotional learning based on student needs, classroom dynamics, and school culture. Behavioral management emphasizes structured discipline and clear expectations to shape student behavior, while social-emotional learning fosters emotional intelligence, empathy, and interpersonal skills essential for long-term success. Educators should prioritize approaches that promote holistic development, considering factors like student emotional regulation, engagement levels, and the importance of building positive relationships.
Behavioral Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com