Streaming technology has revolutionized how you access and enjoy digital content, allowing instant playback of videos, music, and games without the need for downloads. This seamless delivery relies on efficient data compression and high-speed internet connections to provide uninterrupted experiences across various devices. Explore the rest of the article to understand how streaming impacts entertainment, work, and education in today's digital world.
Table of Comparison
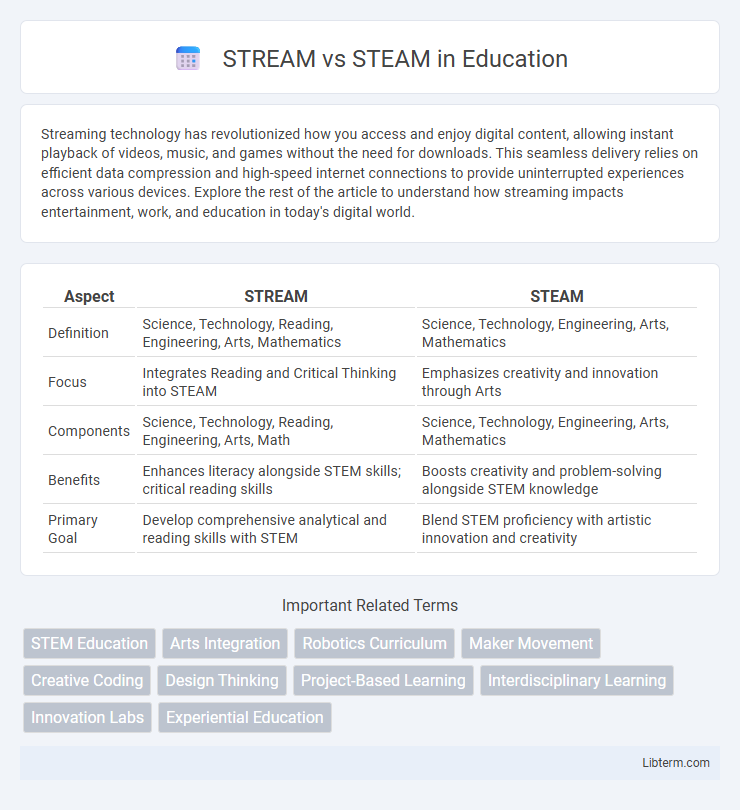
| Aspect | STREAM | STEAM |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics | Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics |
| Focus | Integrates Reading and Critical Thinking into STEAM | Emphasizes creativity and innovation through Arts |
| Components | Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, Math | Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics |
| Benefits | Enhances literacy alongside STEM skills; critical reading skills | Boosts creativity and problem-solving alongside STEM knowledge |
| Primary Goal | Develop comprehensive analytical and reading skills with STEM | Blend STEM proficiency with artistic innovation and creativity |
Introduction to STREAM and STEAM
STREAM integrates Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics to foster comprehensive interdisciplinary learning that enhances critical thinking and creativity. STEAM emphasizes the inclusion of Arts alongside Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics to promote innovative problem-solving and holistic education. Both frameworks aim to prepare students with versatile skills for future academic and career challenges by blending technical knowledge with artistic expression.
Defining STEAM: Origins and Components
STEAM education expands on the STREAM model by incorporating Arts alongside Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, fostering creativity and critical thinking. Originating in the early 2000s, STEAM aims to integrate artistic design and innovation into traditional STEM curricula to enhance problem-solving skills. This multidisciplinary approach promotes holistic learning, blending technical proficiency with visual and performing arts to prepare students for diverse career paths.
What is STREAM? An Expanded Approach
STREAM is an expanded educational framework that integrates Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, emphasizing interdisciplinary learning and creative problem-solving. This approach fosters critical thinking by incorporating literacy and the arts alongside traditional STEM subjects, enhancing student engagement and innovation. STREAM promotes holistic development by encouraging collaboration, communication, and real-world application of diverse skills.
Key Differences Between STEAM and STREAM
STEAM integrates Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, emphasizing creativity alongside technical skills, while STREAM expands this framework by adding Reading and Writing to enhance literacy and communication. The key difference lies in STREAM's inclusion of literacy components, which promotes comprehensive language development alongside STEM disciplines and arts. This fusion supports critical thinking and problem-solving through both analytical and expressive abilities, fostering well-rounded student competencies.
The Importance of the Arts in STEM Education
Integrating the arts into STEM education transforms it into STEAM, enhancing creativity and critical thinking essential for innovation and problem-solving. Art disciplines foster visual-spatial skills and empathetic understanding, bridging gaps between technical knowledge and human-centered design. Research shows students in STEAM programs demonstrate higher engagement, improved collaboration, and a stronger ability to develop innovative solutions across science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fields.
The Role of Reading in STREAM
Reading plays a critical role in STREAM education by enhancing comprehension and critical thinking skills essential for Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics subjects. Integrating reading into STREAM curricula supports vocabulary development, content mastery, and the ability to analyze complex concepts across disciplines. Effective reading strategies empower students to interpret technical texts, engage with scientific literature, and foster lifelong learning in innovative fields.
Benefits of Integrating STREAM/STEAM in Curriculum
Integrating STREAM (Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics) and STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics) in the curriculum enhances critical thinking and creativity by blending technical skills with artistic expression. This interdisciplinary approach promotes problem-solving, innovation, and collaboration, preparing students for future careers in diverse fields like robotics, digital media, and environmental science. Research indicates that STREAM/STEAM integration improves student engagement, retention rates, and academic performance, particularly in STEM subjects enriched by literacy and arts components.
STREAM and STEAM Best Practices
STREAM education integrates Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics to foster interdisciplinary learning and critical thinking skills. Best practices for STREAM include project-based learning, collaborative problem-solving, and incorporating creativity through art and reading to enhance engagement and innovation. STEAM emphasizes similar skills but prioritizes Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, often leveraging hands-on experiments and real-world applications to deepen understanding.
Challenges in Implementing STREAM and STEAM
Implementing STREAM and STEAM faces challenges including curriculum integration difficulties, limited teacher training in interdisciplinary approaches, and insufficient funding for resources like technology and arts materials. Schools often struggle balancing standardized testing requirements with creative and scientific exploration encouraged by STREAM/STEAM models. Overcoming these barriers requires targeted professional development, strategic resource allocation, and policy adjustments to support experiential, holistic learning frameworks.
The Future of Education: STREAM vs STEAM
STREAM education integrates Science, Technology, Reading, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, fostering a multidisciplinary approach that enhances critical thinking and creativity in students. STEAM emphasizes Arts alongside STEM subjects, promoting innovation and design thinking essential for future careers in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. Embracing STREAM prepares learners with a broader skill set, integrating literacy to improve comprehension and communication, driving the future of education toward holistic development.
STREAM Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com