Classroom observation is a vital tool for assessing teaching methods and student engagement, helping educators enhance instructional strategies. It provides real-time insights into classroom dynamics, allowing for targeted feedback and professional development. Explore the full article to discover effective techniques for conducting impactful classroom observations.
Table of Comparison
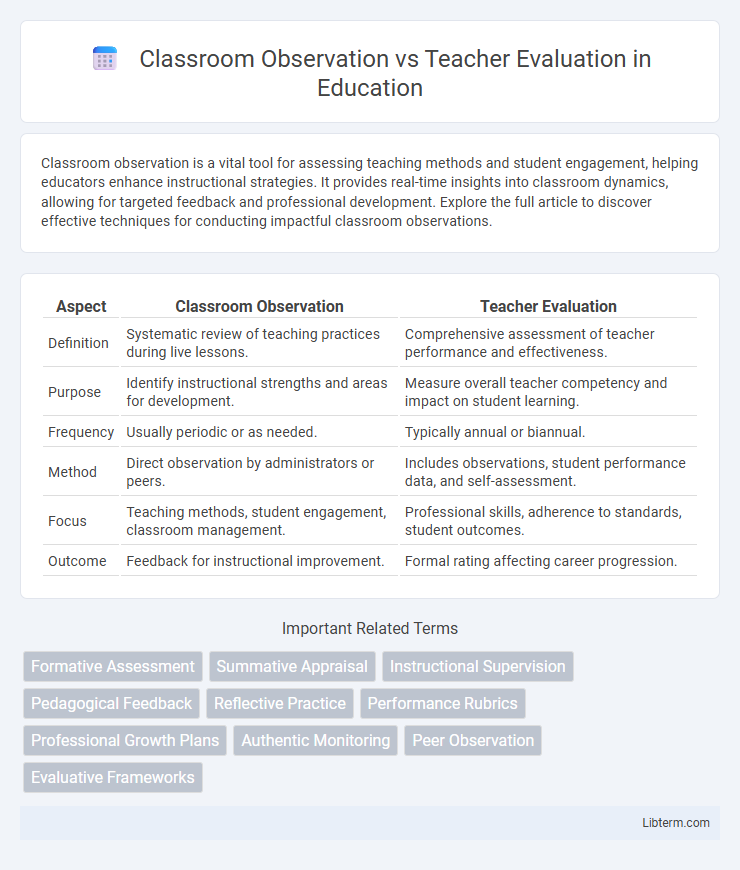
| Aspect | Classroom Observation | Teacher Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic review of teaching practices during live lessons. | Comprehensive assessment of teacher performance and effectiveness. |
| Purpose | Identify instructional strengths and areas for development. | Measure overall teacher competency and impact on student learning. |
| Frequency | Usually periodic or as needed. | Typically annual or biannual. |
| Method | Direct observation by administrators or peers. | Includes observations, student performance data, and self-assessment. |
| Focus | Teaching methods, student engagement, classroom management. | Professional skills, adherence to standards, student outcomes. |
| Outcome | Feedback for instructional improvement. | Formal rating affecting career progression. |
Introduction: Understanding Classroom Observation and Teacher Evaluation
Classroom observation involves systematically watching teachers' instructional methods and student interactions to gather real-time insights into teaching performance. Teacher evaluation is a comprehensive process that uses multiple data sources, including observations, student assessments, and feedback, to assess overall educator effectiveness. Understanding these distinct yet complementary components is essential for improving teaching quality and student outcomes.
Purpose of Classroom Observation
Classroom observation primarily aims to gather authentic insights into a teacher's instructional methods, student engagement, and classroom dynamics to support professional growth. It provides real-time, context-specific data that helps identify strengths and areas for improvement without formal judgment. This process fosters reflective teaching practices and enhances educational quality through continuous feedback.
Purpose of Teacher Evaluation
Teacher evaluation aims to assess educator effectiveness by measuring instructional quality, student engagement, and learning outcomes to support professional growth and accountability. It involves analyzing lesson planning, classroom management, and adherence to curriculum standards to provide actionable feedback. Unlike classroom observation, which offers a snapshot of teaching practices, teacher evaluation encompasses a comprehensive review of performance over time to inform personnel decisions and development plans.
Key Differences Between Classroom Observation and Teacher Evaluation
Classroom observation primarily involves the systematic monitoring of teaching practices within the learning environment to gather qualitative data on instructional methods and student engagement. Teacher evaluation encompasses a broader assessment process that includes classroom observations, but also integrates student performance metrics, professional development, and adherence to educational standards. Key differences lie in the scope, purpose, and criteria used, where classroom observation focuses on real-time instructional behavior, while teacher evaluation assesses overall effectiveness and growth over time.
Methods and Tools Used in Classroom Observation
Classroom observation methods include direct observation, video recordings, and peer reviews, utilizing tools such as observation checklists, rating scales, and digital platforms like TeachBoost or Swivl. These tools systematically capture instructional strategies, student engagement, and classroom management techniques, allowing for real-time feedback and data-driven insights. Unlike broader teacher evaluations, classroom observations emphasize qualitative data collection to inform targeted professional development and instructional improvement.
Criteria and Standards in Teacher Evaluation
Teacher evaluation criteria emphasize measurable standards such as subject knowledge, instructional strategies, student engagement, and classroom management effectiveness, providing a comprehensive assessment of teaching quality. Classroom observation serves as a tool within this framework, focusing on real-time teacher performance, adherence to curriculum standards, and interaction with students. Both processes rely on established benchmarks to ensure consistent, objective evaluations aligned with educational goals and professional development needs.
Benefits of Classroom Observation for Professional Growth
Classroom observation provides targeted insights into teaching methods, enabling educators to refine instructional skills and better address diverse student needs. It fosters reflective practice by offering real-time evidence of classroom dynamics and learner engagement, promoting continuous professional development. Observations support collaborative feedback, enhancing teacher confidence and driving measurable improvements in instructional quality.
Challenges and Limitations of Teacher Evaluation
Teacher evaluation faces challenges including subjectivity and bias, which can undermine the accuracy and fairness of assessments. The limited frequency of evaluations often fails to capture a teacher's full range of skills, creating gaps in feedback. Moreover, reliance on standardized metrics can overlook contextual factors like classroom dynamics and student diversity, limiting the evaluation's effectiveness.
Integrating Observation and Evaluation for Teacher Development
Integrating classroom observation and teacher evaluation fosters a comprehensive approach to professional growth, combining real-time instructional feedback with performance assessment metrics. Observation provides qualitative insights into teaching strategies and student engagement, while evaluation quantifies effectiveness through measurable outcomes and standards alignment. This synergy supports targeted development plans, enhancing instructional skills and promoting continuous improvement in educational practices.
Conclusion: Finding the Balance for Effective Teaching Assessment
Classroom observation and teacher evaluation must be balanced to create an effective teaching assessment system that supports professional growth and accountability. Integrating qualitative insights from observations with quantitative evaluation metrics ensures a holistic understanding of teacher performance. This balanced approach promotes continuous improvement and enhances student learning outcomes by recognizing both instructional strategies and measurable results.
Classroom Observation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com