Deforestation causes significant loss of biodiversity, disrupts ecosystems, and contributes to climate change by increasing carbon dioxide levels. Protecting forests supports clean air, preserves wildlife habitats, and helps maintain the Earth's natural balance. Discover how you can help combat deforestation and protect our planet by reading the rest of this article.
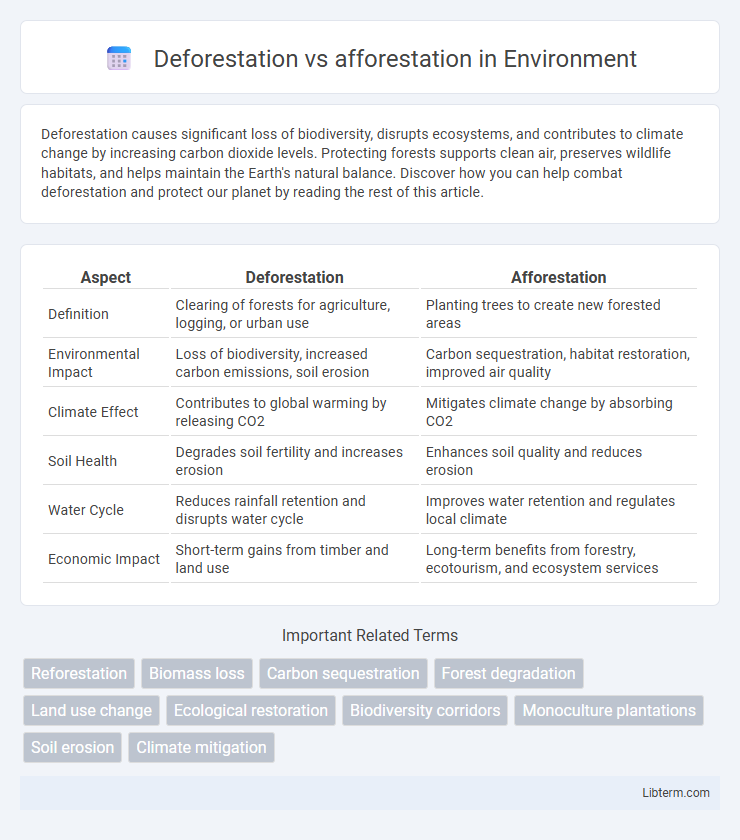
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Deforestation | Afforestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, or urban use | Planting trees to create new forested areas |
| Environmental Impact | Loss of biodiversity, increased carbon emissions, soil erosion | Carbon sequestration, habitat restoration, improved air quality |
| Climate Effect | Contributes to global warming by releasing CO2 | Mitigates climate change by absorbing CO2 |
| Soil Health | Degrades soil fertility and increases erosion | Enhances soil quality and reduces erosion |
| Water Cycle | Reduces rainfall retention and disrupts water cycle | Improves water retention and regulates local climate |
| Economic Impact | Short-term gains from timber and land use | Long-term benefits from forestry, ecotourism, and ecosystem services |
Understanding Deforestation and Afforestation
Deforestation involves the large-scale removal of forests, leading to habitat loss, increased carbon emissions, and biodiversity decline. Afforestation refers to the process of planting trees in previously non-forested areas, which helps sequester carbon dioxide, restore ecosystems, and improve air quality. Understanding these contrasting processes is essential for developing effective environmental policies and combating climate change.
Causes of Deforestation
Deforestation primarily results from agricultural expansion, logging for timber and fuelwood, and infrastructure development such as roads and urbanization. Commercial agriculture drives large-scale forest clearing, especially in tropical regions, while illegal logging accelerates forest degradation globally. The conversion of forests into farmland and pasture for livestock remains the most significant factor contributing to the loss of forest cover worldwide.
Key Drivers of Afforestation
Key drivers of afforestation include government policies promoting reforestation projects, economic incentives for carbon sequestration, and community-based initiatives aimed at restoring biodiversity. Technological advancements in satellite monitoring and seedling propagation enhance afforestation efficiency and success rates. Increased global awareness of climate change and the demand for sustainable land management further stimulate afforestation efforts worldwide.
Environmental Impacts of Deforestation
Deforestation causes significant environmental impacts, including loss of biodiversity, disruption of carbon cycles, and increased greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. The removal of trees leads to soil erosion, reduced water quality, and habitat destruction, threatening countless plant and animal species. In contrast, afforestation helps reverse these effects by restoring ecosystems, enhancing carbon sequestration, and improving air and water quality.
Benefits of Afforestation on Ecosystems
Afforestation enhances biodiversity by creating new habitats for numerous plant and animal species, which helps restore ecological balance. It plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration, reducing greenhouse gases and mitigating climate change impacts. Furthermore, afforestation improves soil quality and water retention, preventing erosion and supporting healthier ecosystems overall.
Deforestation’s Effects on Climate Change
Deforestation significantly accelerates climate change by increasing greenhouse gas emissions, as trees store carbon dioxide that is released when they are cut down and burned or left to rot. It reduces the planet's capacity to absorb CO2, leading to higher atmospheric carbon levels and global warming. Additionally, deforestation disrupts local weather patterns and decreases biodiversity, further destabilizing ecosystems and exacerbating climate impacts.
Afforestation and Carbon Sequestration
Afforestation plays a critical role in carbon sequestration by establishing new forested areas that absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide, mitigating climate change. Unlike deforestation, which releases stored carbon and reduces biodiversity, afforestation enhances carbon storage capacity and improves ecosystem resilience. Large-scale afforestation projects contribute significantly to global efforts in reducing greenhouse gas concentrations and restoring degraded landscapes.
Socioeconomic Implications of Deforestation
Deforestation significantly impacts socioeconomic conditions by disrupting livelihoods dependent on forests, such as agriculture, fishing, and ecotourism, leading to increased poverty and food insecurity in local communities. The loss of forest resources undermines traditional knowledge and cultural heritage while contributing to conflicts over land and resource access. Conversely, afforestation projects can create job opportunities, promote sustainable development, and restore ecosystem services essential for economic resilience.
Policy Approaches to Deforestation and Afforestation
Effective policy approaches to deforestation prioritize strict regulations on land use, enforcement of illegal logging bans, and promotion of sustainable agricultural practices to curb forest loss. Afforestation policies focus on incentives such as subsidies, tax benefits, and community engagement programs to encourage tree planting and restoration of degraded lands. Integration of monitoring technologies and international collaboration enhances compliance and the overall success of both deforestation control and afforestation initiatives.
Sustainable Solutions for Forest Management
Deforestation leads to biodiversity loss, climate change acceleration, and soil degradation, while afforestation helps restore ecosystems, sequester carbon, and improve air quality. Sustainable forest management integrates afforestation practices with reduced-impact logging, community engagement, and conservation policies to balance economic, environmental, and social goals. Innovations like remote sensing for monitoring and agroforestry systems optimize resource use and support long-term forest resilience.
Deforestation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com