Desertification refers to the degradation of land in arid and semi-arid areas, leading to the loss of vegetation, soil fertility, and biodiversity. This environmental issue is caused by factors such as climate change, deforestation, and unsustainable agricultural practices. Discover how desertification impacts your environment and what actions can help combat this growing problem in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
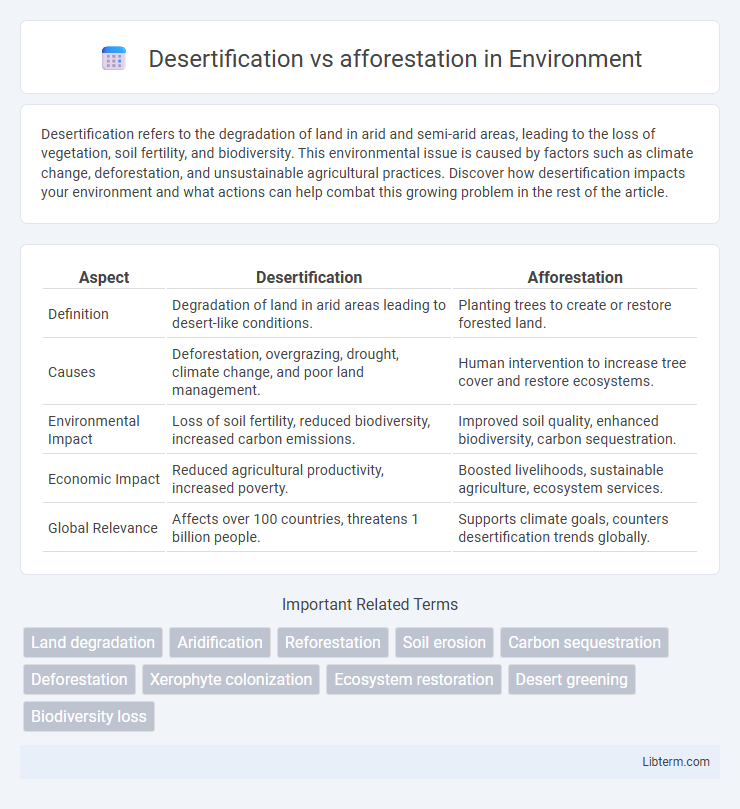
| Aspect | Desertification | Afforestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degradation of land in arid areas leading to desert-like conditions. | Planting trees to create or restore forested land. |
| Causes | Deforestation, overgrazing, drought, climate change, and poor land management. | Human intervention to increase tree cover and restore ecosystems. |
| Environmental Impact | Loss of soil fertility, reduced biodiversity, increased carbon emissions. | Improved soil quality, enhanced biodiversity, carbon sequestration. |
| Economic Impact | Reduced agricultural productivity, increased poverty. | Boosted livelihoods, sustainable agriculture, ecosystem services. |
| Global Relevance | Affects over 100 countries, threatens 1 billion people. | Supports climate goals, counters desertification trends globally. |
Understanding Desertification: Causes and Consequences
Desertification results from factors like prolonged drought, deforestation, and unsustainable land use, leading to soil degradation and loss of vegetation cover. This process reduces agricultural productivity, disrupts water cycles, and exacerbates food insecurity and biodiversity loss in affected regions. Combating desertification involves afforestation, which stabilizes soil, restores ecosystems, and improves carbon sequestration to mitigate environmental and socioeconomic impacts.
The Science Behind Afforestation
Afforestation involves planting trees in barren or deforested areas to restore ecosystems, enhance carbon sequestration, and prevent soil erosion. Scientific studies show that afforestation improves soil moisture retention, boosts biodiversity, and mitigates desertification by stabilizing microclimates. Satellite data confirm that afforested regions exhibit increased vegetation index and reduced land degradation compared to desertified zones.
Key Differences: Desertification vs Afforestation
Desertification refers to the degradation of land in arid and semi-arid areas, causing loss of vegetation, soil erosion, and reduced fertility, whereas afforestation involves planting trees to restore and increase forest cover, improving soil quality and biodiversity. Desertification results from factors such as drought, deforestation, and unsustainable farming, while afforestation actively combats these effects by stabilizing soil and enhancing local microclimates. The key difference lies in desertification being a destructive process leading to land degradation, while afforestation is a constructive environmental strategy aimed at land rehabilitation and carbon sequestration.
Impact of Desertification on Biodiversity
Desertification severely reduces biodiversity by degrading habitats and causing soil erosion, which leads to the loss of plant and animal species adapted to specific ecosystems. As vegetation cover diminishes, it disrupts food chains and reduces genetic diversity essential for ecosystem resilience. Afforestation counteracts these effects by restoring vegetation, improving soil quality, and providing habitats that support diverse species populations.
Afforestation as a Tool Against Land Degradation
Afforestation significantly combats land degradation by restoring vegetation cover, which improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and increases biodiversity. This process reduces the risk of desertification by stabilizing topsoil and curbing erosion caused by wind and water. Implementing afforestation projects contributes to carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change effects that exacerbate desertification.
Climate Change: Linking Desertification and Afforestation
Climate change accelerates desertification by intensifying droughts, reducing soil moisture, and disrupting natural vegetation cycles, leading to land degradation and loss of biodiversity. Afforestation combats these effects by planting trees that enhance carbon sequestration, stabilize soil, and restore ecosystems, thus mitigating climate impacts. Linking desertification and afforestation highlights the critical role of reforestation in reversing land degradation and promoting climate resilience.
Economic Effects: From Barren Lands to Forest Wealth
Desertification causes significant economic losses by reducing arable land productivity, leading to decreased agricultural yields and increased food insecurity that impact local and national economies. Afforestation reverses these effects by restoring soil fertility, enhancing biodiversity, and creating sustainable forest resources that boost timber production, ecotourism, and carbon credit opportunities. Investing in afforestation transforms barren lands into valuable economic assets, promoting rural development and long-term environmental resilience.
Global Success Stories: Reversing Desertification with Trees
Successful global initiatives in combating desertification through afforestation have transformed arid regions by planting millions of trees that restore soil fertility and improve water retention. Projects like China's Green Great Wall and Africa's Great Green Wall demonstrate significant progress in reversing land degradation, promoting biodiversity, and enhancing local livelihoods. These afforestation efforts contribute to climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon and stabilizing ecosystems in vulnerable desert-prone areas.
Community Involvement in Combating Desertification
Community involvement plays a crucial role in combating desertification by promoting sustainable land management practices that restore soil fertility and prevent land degradation. Local participation in afforestation projects enhances ecosystem resilience, increases vegetation cover, and provides alternative livelihoods that reduce pressure on fragile environments. Empowering communities with education and resources fosters long-term stewardship, ensuring successful reforestation efforts and sustainable desertification control.
Future Strategies: Integrating Afforestation for Sustainable Land Management
Integrating afforestation into future strategies offers a sustainable solution to combat desertification by restoring degraded land and enhancing soil fertility. Planting native tree species promotes biodiversity, improves water retention, and reduces soil erosion, directly counteracting desert expansion. Implementing community-based afforestation projects combined with advanced remote sensing technology enables effective land management and long-term environmental resilience.
Desertification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com