Natural products offer a wide range of benefits, including fewer synthetic chemicals and environmentally friendly ingredients that support your health and well-being. These items often provide superior nourishment and support sustainable practices that protect the planet. Explore the rest of this article to discover how natural choices can enhance your lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
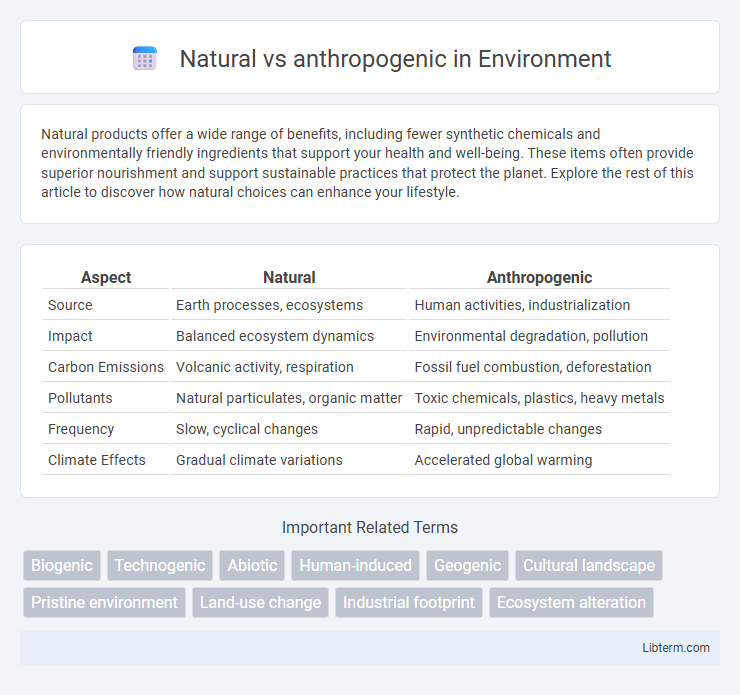
| Aspect | Natural | Anthropogenic |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Earth processes, ecosystems | Human activities, industrialization |
| Impact | Balanced ecosystem dynamics | Environmental degradation, pollution |
| Carbon Emissions | Volcanic activity, respiration | Fossil fuel combustion, deforestation |
| Pollutants | Natural particulates, organic matter | Toxic chemicals, plastics, heavy metals |
| Frequency | Slow, cyclical changes | Rapid, unpredictable changes |
| Climate Effects | Gradual climate variations | Accelerated global warming |
Introduction to Natural vs. Anthropogenic Phenomena
Natural phenomena originate from Earth's inherent processes such as volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, and earthquakes, driven by geological and atmospheric dynamics. Anthropogenic phenomena result from human activities including industrial emissions, deforestation, and urbanization, significantly impacting climate change and environmental degradation. Differentiating these sources is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies in environmental management.
Defining Natural Causes in the Environment
Natural causes in the environment refer to processes and phenomena that occur without human intervention, such as volcanic eruptions, wildfires, hurricanes, and earthquakes. These events shape ecosystems and climate patterns through natural cycles like the water cycle, volcanic activity releasing gases, and solar radiation variations. Understanding natural causes is crucial for distinguishing between environmental changes triggered by human activities and those resulting from Earth's inherent dynamics.
What Constitutes Anthropogenic Impacts?
Anthropogenic impacts refer to environmental changes caused directly or indirectly by human activities such as deforestation, industrial emissions, urbanization, and agriculture. These impacts often result in habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and biodiversity decline, distinguishing them from natural processes like volcanic eruptions or wildfires. Understanding the scope of anthropogenic influence is crucial for developing sustainable policies and mitigating long-term ecological damage.
Key Differences Between Natural and Human-Induced Changes
Natural changes occur through geological processes, volcanic eruptions, and climate cycles, shaping ecosystems over extended periods without direct human influence. Human-induced changes arise from industrial activities, deforestation, urbanization, and pollution, leading to rapid alterations in land use and atmospheric composition. Key differences include the timescale of impact, with natural changes typically unfolding gradually, while anthropogenic changes often cause immediate and widespread environmental consequences.
Examples of Natural Environmental Processes
Volcanic eruptions release ash and gases, significantly impacting air quality and climate patterns naturally. Hurricanes, formed by atmospheric and oceanic interactions, cause widespread flooding and ecosystem changes. Earthquakes result from tectonic plate movements, reshaping landscapes and influencing sediment distribution.
Major Anthropogenic Activities Affecting the Earth
Major anthropogenic activities affecting the Earth include deforestation, fossil fuel combustion, and industrial agriculture, which significantly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Urbanization and land-use changes disrupt ecosystems and reduce biodiversity, impacting natural carbon sinks. Pollution from manufacturing and waste management further degrades air, water, and soil quality, accelerating environmental degradation and posing risks to human health.
Interactions Between Natural and Human-Made Factors
Interactions between natural and anthropogenic factors significantly influence climate patterns, ecosystem stability, and resource distribution. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and industrial emissions exacerbate natural processes like wildfires, flooding, and soil erosion, creating complex feedback loops. Understanding these intertwined dynamics is crucial for developing sustainable environmental management and mitigating adverse impacts on biodiversity and human health.
Environmental Consequences of Anthropogenic Actions
Anthropogenic actions, such as deforestation, industrial emissions, and urbanization, contribute significantly to environmental degradation, leading to biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, and increased greenhouse gas concentrations. These human-induced changes accelerate climate change, disrupt ecosystems, and contaminate air and water resources, posing severe risks to both natural habitats and human health. Unlike natural environmental variations, anthropogenic impacts are often rapid, widespread, and less reversible, requiring urgent mitigation strategies to preserve ecological balance.
Importance of Distinguishing Natural from Anthropogenic Events
Distinguishing natural from anthropogenic events is crucial for accurate climate change assessments and effective environmental policy-making. Natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions and solar variability must be separated from human-induced activities like fossil fuel combustion and deforestation to attribute causes correctly. This differentiation enables targeted mitigation strategies and improved predictive models essential for sustainable resource management and disaster response.
Strategies for Mitigating Anthropogenic Effects
Strategies for mitigating anthropogenic effects emphasize reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy adoption, enhancing energy efficiency in industrial processes, and implementing carbon capture and storage technologies. Urban planning initiatives prioritize green infrastructure, such as afforestation and sustainable transportation systems, to decrease pollution and improve air quality. Environmental regulations and international agreements, like the Paris Agreement, play a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to limit human-driven climate change and protect natural ecosystems.
Natural Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com