Alien encounters have fascinated humanity for decades, inspiring countless theories and stories about extraterrestrial life forms existing beyond Earth. From scientific searches using advanced telescopes to imaginative depictions in popular culture, the mystery of aliens continues to captivate our curiosity. Discover more about the possibilities of alien life and how it could impact your understanding of the universe in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
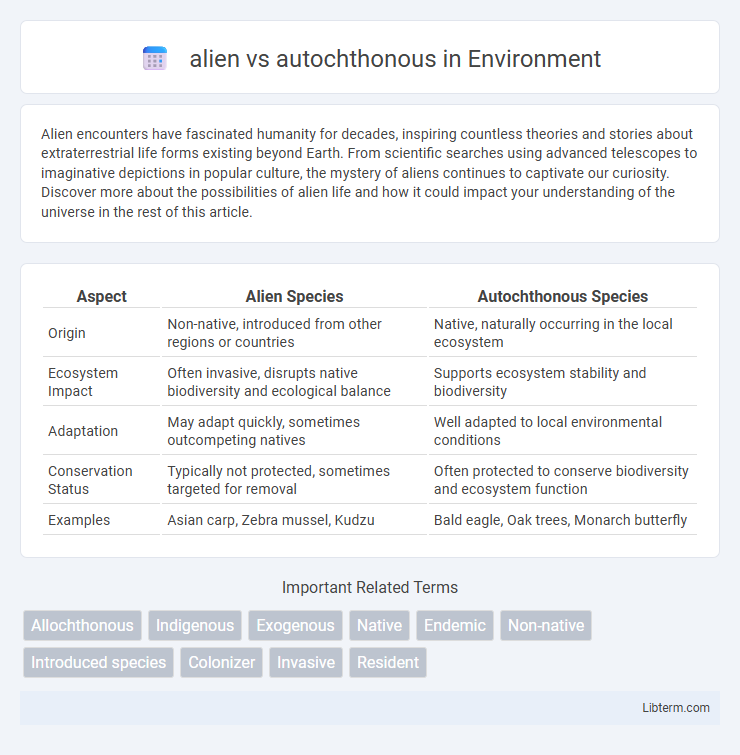
| Aspect | Alien Species | Autochthonous Species |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Non-native, introduced from other regions or countries | Native, naturally occurring in the local ecosystem |
| Ecosystem Impact | Often invasive, disrupts native biodiversity and ecological balance | Supports ecosystem stability and biodiversity |
| Adaptation | May adapt quickly, sometimes outcompeting natives | Well adapted to local environmental conditions |
| Conservation Status | Typically not protected, sometimes targeted for removal | Often protected to conserve biodiversity and ecosystem function |
| Examples | Asian carp, Zebra mussel, Kudzu | Bald eagle, Oak trees, Monarch butterfly |
Defining Alien and Autochthonous: Key Concepts
Alien species refer to organisms introduced to a new habitat beyond their native range, often through human activity, which may impact local ecosystems and biodiversity. Autochthonous species are native organisms that have evolved and persisted naturally within a specific geographical area, maintaining ecological balance and evolutionary adaptations. Distinguishing between alien and autochthonous species is crucial for conservation biology, ecosystem management, and understanding biogeographical patterns.
Historical Perspectives on Alien vs Autochthonous Entities
Historical perspectives on alien versus autochthonous entities often reflect the tension between indigenous populations and foreign settlers, shaping cultural and political landscapes over centuries. Autochthonous entities are recognized for their deep-rooted connection to a specific land, providing continuity and authenticity to historical narratives. Alien entities, introduced through migration, trade, or conquest, frequently challenge established norms and contribute to dynamic socio-cultural transformations.
Cultural Representations in Literature and Media
Alien and autochthonous identities in literature and media often symbolize the tension between foreign influence and indigenous roots, reflecting cultural conflicts and hybridity. Alien characters are frequently depicted as outsiders or invaders, embodying fears of otherness and displacement, while autochthonous figures represent native traditions, authenticity, and resistance to assimilation. Literary works and films use these opposing archetypes to explore themes of identity, belonging, and the power dynamics within postcolonial and multicultural societies.
Ecological Impacts: Alien Species vs Autochthonous Species
Alien species often disrupt native ecosystems by outcompeting autochthonous species for resources, leading to reduced biodiversity and altered habitat structures. Autochthonous species, adapted to local conditions, maintain ecological balance and support native food webs essential for ecosystem resilience. The introduction of alien species can cause cascading ecological impacts, including changes in nutrient cycling, habitat degradation, and increased vulnerability of autochthonous populations to extinction.
Societal Integration: Challenges and Opportunities
Alien populations often face language barriers, cultural differences, and limited access to social services, which hinder their societal integration. Autochthonous groups possess established social networks and cultural familiarity, providing them with advantages in education, employment, and political participation. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies promoting cross-cultural understanding and inclusive community programs to foster social cohesion and economic opportunities for alien populations.
Legal Frameworks Governing Alien and Native Status
Legal frameworks governing alien and autochthonous status establish criteria for individual rights, residency, and citizenship, differentiating between non-native aliens and indigenous populations. Statutes often define aliens as persons lacking inherent territorial affiliation, subjecting them to immigration controls and limited political participation, while autochthonous groups receive specific protections recognizing ancestral land rights and cultural heritage. International agreements, such as the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, reinforce these distinctions by promoting autonomy and safeguarding indigenous peoples' rights against displacement and marginalization.
Technological Influence on Identity Perception
Alien and autochthonous identities experience technological influence differently, as digital platforms often amplify the visibility of alien cultures while reinforcing autochthonous traditions through localized content. Algorithmic curation shapes identity perception by promoting dominant global narratives or preserving indigenous knowledge, impacting how individuals internalize cultural belonging. The interplay between augmented reality and social media enables hybrid identity expressions that blend alien and native elements, redefining authenticity in contemporary societies.
Case Studies: Notable Conflicts and Collaborations
Significant case studies in alien versus autochthonous interactions reveal both conflicts and collaborations shaping biodiversity and cultural landscapes. In the Mediterranean, invasive alien species like the lionfish have disrupted local fish populations, sparking ecological and economic disputes. Contrastingly, in New Zealand, collaborative efforts between indigenous Maori communities and scientists have successfully integrated traditional ecological knowledge to manage invasive species, promoting both conservation and cultural heritage preservation.
Philosophical Debates: Belonging and Otherness
Philosophical debates on alien versus autochthonous identities explore the tensions between belonging and otherness, questioning how individuals or groups integrate or remain distinct within societies. These discussions often emphasize the ontological and existential implications of being labeled as alien, highlighting issues of exclusion, identity formation, and cultural authenticity. The dialectic between alienness and autochthony interrogates notions of homeland, sovereignty, and the ethics of hospitality in multicultural and postcolonial contexts.
Future Outlook: Evolving Definitions and Relationships
The future outlook of alien versus autochthonous species centers on evolving definitions shaped by climate change, human activity, and ecological adaptation. Advances in genomics and biogeography will refine identification criteria, enhancing our understanding of species' origins and interactions. Anticipated shifts in species distribution necessitate dynamic frameworks to manage biodiversity, invasive species, and conservation efforts effectively.
alien Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com