Carbon offset involves compensating for your carbon emissions by funding projects that reduce or capture an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases, such as reforestation or renewable energy initiatives. This practice helps mitigate the impact of your carbon footprint and supports sustainable development worldwide. Discover how carbon offset programs can enhance your environmental responsibility in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
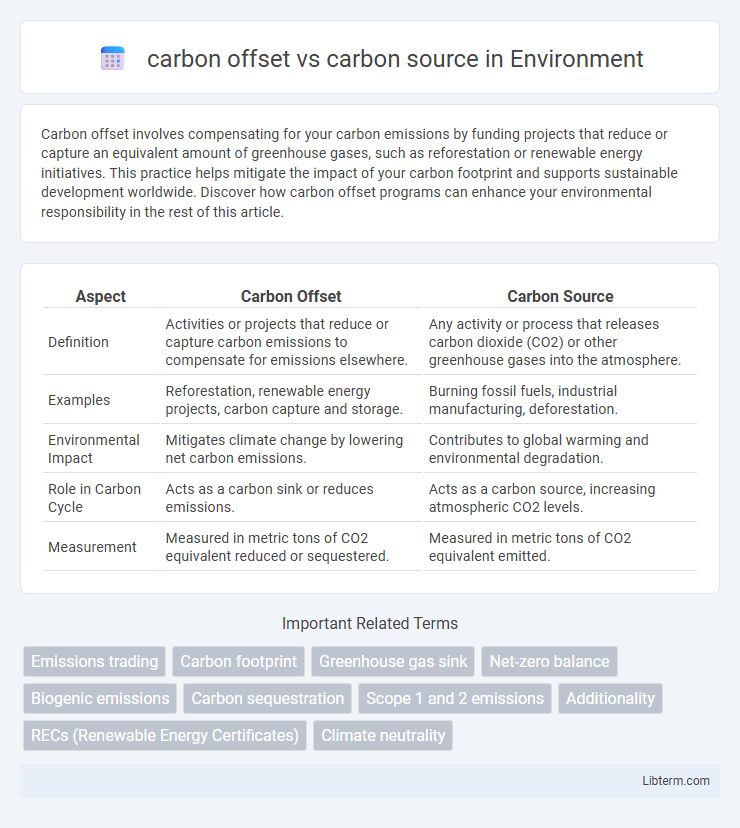
| Aspect | Carbon Offset | Carbon Source |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Activities or projects that reduce or capture carbon emissions to compensate for emissions elsewhere. | Any activity or process that releases carbon dioxide (CO2) or other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. |
| Examples | Reforestation, renewable energy projects, carbon capture and storage. | Burning fossil fuels, industrial manufacturing, deforestation. |
| Environmental Impact | Mitigates climate change by lowering net carbon emissions. | Contributes to global warming and environmental degradation. |
| Role in Carbon Cycle | Acts as a carbon sink or reduces emissions. | Acts as a carbon source, increasing atmospheric CO2 levels. |
| Measurement | Measured in metric tons of CO2 equivalent reduced or sequestered. | Measured in metric tons of CO2 equivalent emitted. |
Understanding Carbon Offsets
Carbon offsets represent measurable reductions or removals of greenhouse gas emissions that compensate for emissions produced elsewhere, effectively balancing carbon footprints. Understanding carbon offsets involves recognizing projects like reforestation, renewable energy, or methane capture that generate these credits to counteract carbon sources, which are activities or processes releasing CO2 into the atmosphere. Accurate carbon accounting ensures that offsets genuinely neutralize carbon sources, supporting climate change mitigation goals.
Defining Carbon Sources
Carbon sources are processes or activities that release greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Common carbon sources include fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial manufacturing. Understanding and quantifying these sources is essential for developing effective carbon offset strategies to mitigate climate change.
Key Differences Between Carbon Offset and Carbon Source
Carbon offsets represent measurable reductions in greenhouse gas emissions used to compensate for emissions produced elsewhere, often through projects like reforestation or renewable energy. Carbon sources, on the other hand, are processes or activities that release carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, such as fossil fuel combustion or deforestation. The key differences lie in their environmental impact: carbon offsets mitigate emissions, while carbon sources contribute to atmospheric carbon accumulation.
How Carbon Offsets Work
Carbon offsets function by compensating for greenhouse gas emissions through activities that reduce or remove an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, such as reforestation, renewable energy projects, or methane capture. These initiatives generate carbon credits, which can be purchased by individuals or companies to balance out their own carbon sources, effectively neutralizing their net emissions. Tracking and verifying these offsets through standardized protocols ensures that each credit corresponds to a quantifiable reduction in carbon footprint.
Types of Carbon Sources in Everyday Life
Carbon sources in everyday life primarily include the burning of fossil fuels such as gasoline and coal, which release significant amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Other common carbon sources include deforestation, which reduces carbon sequestration capacity, and agricultural activities that produce methane and nitrous oxide. Understanding these types of carbon sources is vital for developing effective carbon offset strategies to mitigate climate change impacts.
The Importance of Offsetting Carbon Emissions
Offsetting carbon emissions is essential for combating climate change by neutralizing the carbon released into the atmosphere through activities like fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, which act as carbon sources. Investing in projects such as reforestation, renewable energy, and carbon capture directly reduces the net carbon footprint, promoting sustainable environmental balance. Effective carbon offsetting helps organizations and individuals achieve carbon neutrality, mitigating global warming impacts and supporting international climate goals.
Measuring and Calculating Carbon Sources
Measuring and calculating carbon sources involves quantifying greenhouse gas emissions from activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes, using standardized units like CO2 equivalents. Accurate data collection relies on tools such as emission factors, satellite imagery, and life cycle assessment models to evaluate direct and indirect emissions. This precise measurement is crucial for developing effective carbon offset projects that aim to neutralize emissions by investing in renewable energy, reforestation, or carbon capture technologies.
Challenges in Balancing Offsets and Sources
Balancing carbon offsets and carbon sources presents challenges due to the complexity of accurately measuring emissions and ensuring offsets represent real, additional, and verifiable reductions. Variability in carbon accounting standards and the risk of double counting undermine the credibility and effectiveness of offset programs. Furthermore, reliance on offsets can delay essential systemic changes required to reduce primary carbon sources from fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes.
Best Practices for Reducing Carbon Sources
Reducing carbon sources involves minimizing fossil fuel combustion, enhancing energy efficiency, and transitioning to renewable energy like solar and wind power. Implementing sustainable agriculture, improving waste management, and promoting public transportation also significantly decrease carbon emissions. Businesses and individuals adopting these best practices contribute to lowering atmospheric carbon levels, thereby mitigating climate change impacts.
Future Trends in Carbon Offset Solutions
Future trends in carbon offset solutions emphasize scaling nature-based offsets like reforestation and soil carbon sequestration alongside emerging technologies such as direct air capture and carbon mineralization. Innovations in blockchain and AI enhance transparency, traceability, and verification of carbon credits, promoting market integrity and investor confidence. Increasing regulatory pressure and corporate net-zero commitments drive demand for high-quality, verifiable offsets that align with global climate goals.
carbon offset Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com