The axillary region, commonly known as the armpit, plays a crucial role in lymphatic drainage and sweat secretion, impacting overall skin health and immune function. Proper hygiene and care of the axillary area help prevent infections, irritation, and unpleasant odors. Discover more about the importance of axillary health and how to maintain it effectively in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
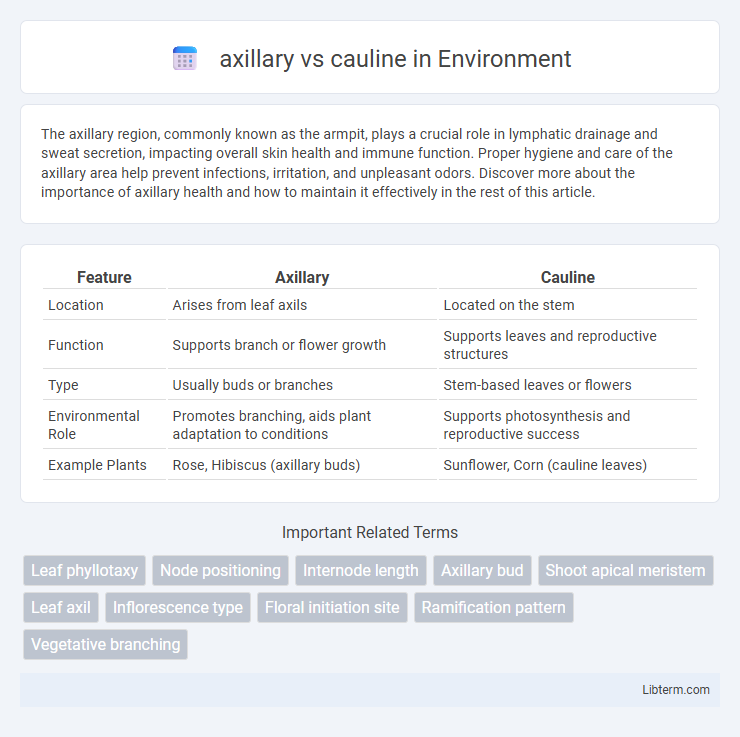
| Feature | Axillary | Cauline |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Arises from leaf axils | Located on the stem |
| Function | Supports branch or flower growth | Supports leaves and reproductive structures |
| Type | Usually buds or branches | Stem-based leaves or flowers |
| Environmental Role | Promotes branching, aids plant adaptation to conditions | Supports photosynthesis and reproductive success |
| Example Plants | Rose, Hibiscus (axillary buds) | Sunflower, Corn (cauline leaves) |
Introduction to Axillary and Cauline Structures
Axillary and cauline structures are key components in plant morphology, with axillary structures referring to those that arise from the axil--the angle between the stem and leaf--such as axillary buds and branches. Cauline structures, in contrast, grow directly from the stem itself and include features like cauline leaves and internodes. Understanding the differentiation between axillary and cauline parts is essential for studying plant growth patterns, branching architecture, and developmental biology.
Defining Axillary Position in Plants
The axillary position in plants refers to the location at the junction where the leaf joins the stem, specifically in the leaf axil, which is the angle between the upper side of the leaf and the stem. Axillary buds typically develop in these axils and can give rise to branches, flowers, or inflorescences, playing a crucial role in plant growth and morphology. In contrast, cauline structures are found directly on the stem itself, often relating to leaves or flowers emerging along the main stem rather than from axils.
Understanding Cauline Position in Botany
Cauline leaves are attached directly to the stem, growing along the main axis rather than at the base or leaf axils. This growth pattern contrasts with axillary leaves, which arise specifically from the axils, the junctions between stem and leaf petioles. Understanding the cauline position is essential for identifying plant morphology, as it influences leaf arrangement, photosynthetic efficiency, and overall plant architecture.
Morphological Differences: Axillary vs. Cauline
Axillary leaves emerge from the axils, the angle between the stem and a leaf, often producing buds or branches, whereas cauline leaves grow directly on the stem without forming from leaf axils. Morphologically, axillary structures tend to be associated with lateral buds that can develop into flowers or shoots, while cauline leaves typically display varied shapes and sizes along the stem, contributing to the overall plant architecture. These differences affect branching patterns and leaf arrangement, influencing photosynthesis efficiency and plant growth dynamics.
Functions of Axillary Structures
Axillary structures, including axillary buds and axillary branches, primarily function in plant growth and reproduction by generating lateral shoots that increase plant branching and leaf area for photosynthesis. These buds serve as meristematic sites enabling the development of flowers, fruits, or new stems, thereby facilitating adaptability and survival under varying environmental conditions. Unlike cauline leaves, which mainly support photosynthesis, axillary structures play a critical role in vegetative propagation and reproductive success.
Roles of Cauline Structures in Plant Growth
Cauline structures, found along the stem, play a critical role in supporting leaves, flowers, and branches, facilitating efficient nutrient transport and photosynthesis. These stem-based organs contribute to overall plant stability and adaptability by enabling lateral growth and resource allocation. Unlike axillary buds positioned in leaf axils, cauline elements are integral to extending the plant's vertical architecture and optimizing light capture for enhanced growth.
Examples of Axillary and Cauline Arrangements
Axillary leaf arrangements feature leaves or flowers growing from the axils, the angles between the upper side of a stem and a leaf or branch, commonly seen in plants like hibiscus and tomato. In contrast, cauline arrangements indicate leaves or branches growing directly on the stem, exemplified by sunflowers and corn, where the leaves are spaced along the main stem rather than clustered at nodes. These distinct phyllotaxy patterns are crucial for plant identification and influence photosynthesis efficiency based on leaf distribution.
Significance in Plant Identification and Taxonomy
Axillary and cauline leaf arrangements serve as critical diagnostic features in plant identification and taxonomy, revealing evolutionary relationships and species differentiation. Axillary leaves emerge from the leaf axils at stem nodes, while cauline leaves grow along the main stem, providing distinctive morphological markers. These characteristics assist botanists in classifying plants, understanding phylogenetic traits, and enhancing taxonomic accuracy.
Evolutionary Perspectives on Axillary and Cauline Traits
Axillary and cauline traits exhibit distinct evolutionary adaptations that reflect plant survival strategies in diverse environments. Axillary buds, located at leaf axils, often facilitate branching and reproductive structures, enhancing resource allocation and reproductive success. Cauline traits, involving stem-based structures, contribute to mechanical support and efficient hormone transport, promoting vertical growth and competitiveness for light.
Practical Applications in Horticulture and Agriculture
Axillary buds, located at the junction of stem and leaf, are exploited in horticulture for propagating plants through techniques like cuttings and layering, promoting bushier growth and higher yield. Cauline buds, found along the stem, are critical in pruning practices to encourage vertical growth and optimize light exposure, enhancing fruit and flower production. Understanding the differences between axillary and cauline buds facilitates precise manipulation of plant architecture, improving productivity in both agricultural and ornamental plant cultivation.
axillary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com