A carbon footprint label provides clear information on the greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product, helping consumers make environmentally conscious choices. These labels promote transparency and encourage manufacturers to reduce their carbon emissions throughout production. Discover how understanding carbon footprint labels can empower your sustainable shopping decisions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
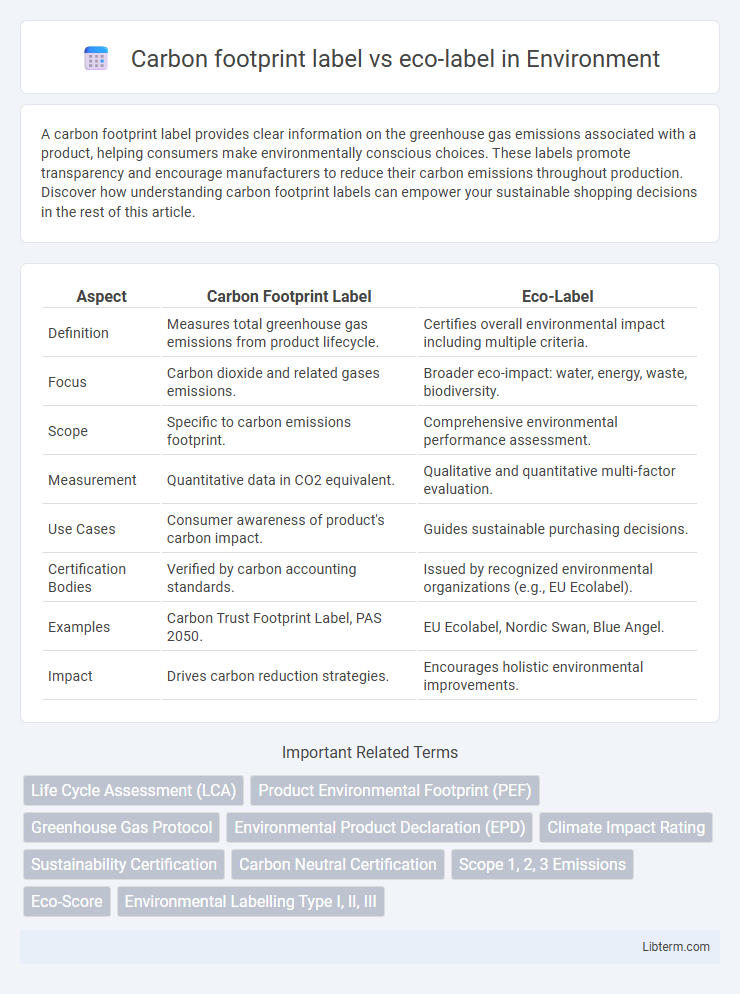
| Aspect | Carbon Footprint Label | Eco-Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures total greenhouse gas emissions from product lifecycle. | Certifies overall environmental impact including multiple criteria. |
| Focus | Carbon dioxide and related gases emissions. | Broader eco-impact: water, energy, waste, biodiversity. |
| Scope | Specific to carbon emissions footprint. | Comprehensive environmental performance assessment. |
| Measurement | Quantitative data in CO2 equivalent. | Qualitative and quantitative multi-factor evaluation. |
| Use Cases | Consumer awareness of product's carbon impact. | Guides sustainable purchasing decisions. |
| Certification Bodies | Verified by carbon accounting standards. | Issued by recognized environmental organizations (e.g., EU Ecolabel). |
| Examples | Carbon Trust Footprint Label, PAS 2050. | EU Ecolabel, Nordic Swan, Blue Angel. |
| Impact | Drives carbon reduction strategies. | Encourages holistic environmental improvements. |
Introduction to Carbon Footprint Labels and Eco-Labels
Carbon footprint labels quantify the total greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product's lifecycle, providing consumers with precise environmental impact data. Eco-labels, on the other hand, certify products meeting broader sustainability criteria, including resource use, biodiversity, and social responsibility, alongside carbon emissions. Both labeling systems aim to guide eco-conscious purchasing decisions but differ significantly in scope and measurement metrics.
Defining Carbon Footprint Labels
Carbon footprint labels quantify the total greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product or service, measured in CO2 equivalents, to inform consumers about its environmental impact. These labels provide transparent, science-based data on carbon emissions from production, transportation, and disposal phases, enabling informed eco-conscious purchasing decisions. Unlike broader eco-labels that assess overall environmental performance, carbon footprint labels specifically target carbon emissions, fostering carbon reduction awareness and accountability.
What Are Eco-Labels?
Eco-labels are certification marks that indicate a product's environmental impact, helping consumers make sustainable choices by verifying eco-friendly attributes such as organic ingredients, energy efficiency, or ethical sourcing. Unlike carbon footprint labels, which quantify greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product, eco-labels provide a broader assessment of environmental benefits across multiple factors including water usage, pollution, and resource conservation. These labels are awarded by independent organizations following rigorous standards, promoting transparency and encouraging manufacturers to adopt greener practices.
Key Differences Between Carbon Footprint Labels and Eco-Labels
Carbon footprint labels specifically quantify the greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product or service throughout its lifecycle, providing consumers with data on environmental impact. Eco-labels represent broader environmental criteria, including sustainability, resource use, and ecological effects beyond just carbon emissions. The key difference lies in the scope: carbon footprint labels measure a singular environmental metric, while eco-labels encompass multiple aspects of environmental performance.
Certification Processes Compared
Carbon footprint labels measure the total greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product's lifecycle, requiring detailed data collection and verification by accredited third-party organizations, ensuring precise carbon quantification. Eco-labels encompass broader environmental criteria beyond carbon emissions, often including resource conservation, pollution reduction, and social responsibility, evaluated through comprehensive certification standards like ISO 14024 or the EU Ecolabel. The certification processes for carbon footprint labels are more specialized and focused on carbon accounting methodologies, while eco-label certifications involve multi-faceted environmental assessments, making their approval timelines and complexity vary significantly.
Benefits of Carbon Footprint Labels
Carbon footprint labels provide precise information about the greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product, enabling consumers to make environmentally conscious purchasing decisions. These labels help companies identify areas for improvement in their production processes, leading to reduced carbon emissions and enhanced sustainability. By fostering transparency and accountability, carbon footprint labels drive market demand toward low-impact products and promote global climate goals.
Advantages of Eco-Labels
Eco-labels provide clear visual cues that help consumers easily identify products meeting rigorous environmental standards, fostering informed purchasing decisions. They cover broader sustainability criteria beyond just carbon emissions, including resource conservation and social responsibility, enhancing overall environmental impact. Eco-labels also promote market transparency and encourage companies to adopt greener practices, driving widespread ecological benefits.
Challenges in Label Implementation
Challenges in implementing carbon footprint labels include accurately measuring and verifying emissions data across diverse products and supply chains, which demands standardized methodologies and transparency. Eco-labels face difficulties in maintaining credibility due to varying certification criteria and the risk of greenwashing, which can confuse consumers. Both labels struggle with balancing comprehensive environmental information and user-friendly design to ensure consumer engagement and trust.
Consumer Perception and Trust
Consumers often perceive carbon footprint labels as more transparent and quantifiable due to their focus on specific greenhouse gas emissions, whereas eco-labels tend to represent broader environmental standards, leading to varied trust levels. Studies indicate that carbon footprint labels can enhance trust among environmentally conscious buyers by providing clear, science-based metrics, while eco-labels may evoke skepticism because of inconsistent criteria across organizations. Trust in both label types significantly influences purchasing decisions, but clarity and verifiable impact measurements in carbon footprint labels generally foster higher consumer confidence.
Choosing the Right Label for Sustainability
Choosing the right label for sustainability involves understanding the specific focus of Carbon footprint labels, which quantify greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product, while eco-labels provide broader environmental certifications that include factors like resource use, waste management, and social responsibility. Carbon footprint labels enable consumers to make informed decisions by comparing the direct climate impact of products, crucial for reducing carbon emissions effectively. Eco-labels, such as the EU Ecolabel or Energy Star, offer comprehensive assurances of environmental performance, making them ideal for selecting products that support overall sustainable practices beyond just carbon reduction.
Carbon footprint label Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com