Environmental standards establish guidelines and requirements to minimize the impact of human activities on the natural world, promoting sustainability and pollution reduction. Compliance with these standards ensures that businesses operate responsibly while protecting ecosystems and public health. Explore this article to understand how environmental standards affect your industry and contribute to a greener future.
Table of Comparison
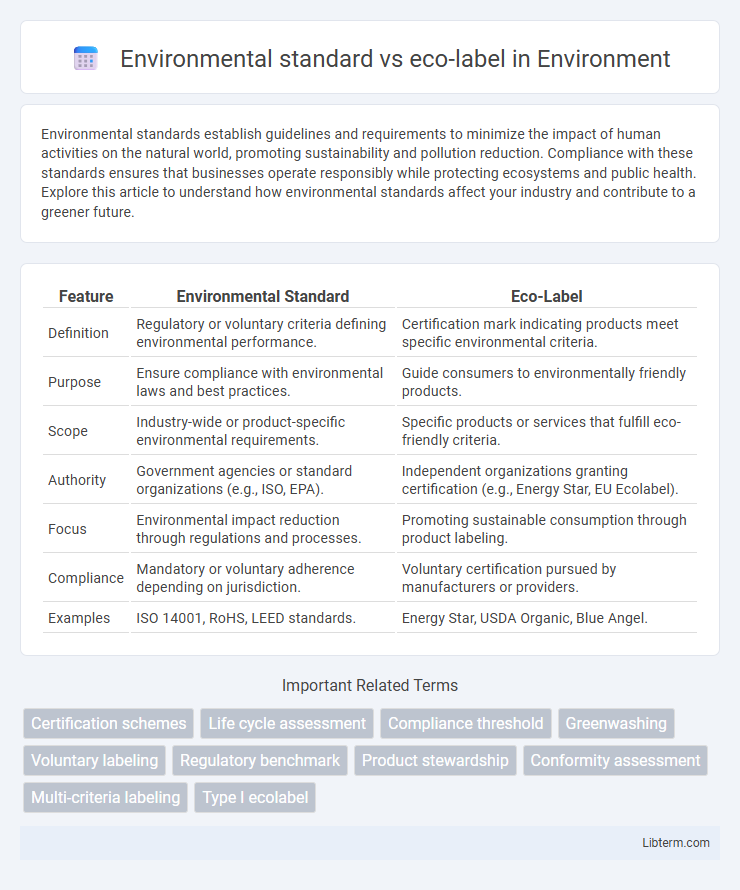
| Feature | Environmental Standard | Eco-Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulatory or voluntary criteria defining environmental performance. | Certification mark indicating products meet specific environmental criteria. |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance with environmental laws and best practices. | Guide consumers to environmentally friendly products. |
| Scope | Industry-wide or product-specific environmental requirements. | Specific products or services that fulfill eco-friendly criteria. |
| Authority | Government agencies or standard organizations (e.g., ISO, EPA). | Independent organizations granting certification (e.g., Energy Star, EU Ecolabel). |
| Focus | Environmental impact reduction through regulations and processes. | Promoting sustainable consumption through product labeling. |
| Compliance | Mandatory or voluntary adherence depending on jurisdiction. | Voluntary certification pursued by manufacturers or providers. |
| Examples | ISO 14001, RoHS, LEED standards. | Energy Star, USDA Organic, Blue Angel. |
Introduction to Environmental Standards and Eco-labels
Environmental standards define specific criteria and practices aimed at minimizing environmental impact through regulations or voluntary guidelines. Eco-labels are certifications awarded to products or services that meet these environmental standards, providing consumers with easily recognizable indicators of sustainability. Both tools promote eco-friendly choices by ensuring transparency and accountability in environmental performance.
Defining Environmental Standards
Environmental standards specify mandatory criteria for products, services, or processes to minimize their ecological impact, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks. These standards are developed by governmental bodies or international organizations and often serve as benchmarks for environmental performance and sustainability. In contrast, eco-labels are voluntary certifications that indicate a product or service meets certain environmental criteria, providing consumers with recognizable symbols of environmental responsibility.
Understanding Eco-labels
Eco-labels are certifications awarded to products that meet specific environmental standards, ensuring reduced ecological impact throughout their lifecycle. They provide consumers with clear, verified information about a product's sustainability, helping to promote environmentally responsible purchasing decisions. Understanding eco-labels involves recognizing certified marks such as Energy Star, Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), and Organic certification, each representing adherence to distinct environmental criteria.
Key Differences Between Environmental Standards and Eco-labels
Environmental standards establish specific criteria or regulations for product safety, emissions, or resource use to ensure environmental protection, often mandated by governments or international bodies. Eco-labels serve as voluntary certifications that identify products or services meeting these environmental standards, helping consumers make eco-friendly choices through recognizable logos. The key difference lies in environmental standards being formalized requirements, whereas eco-labels function as marketing tools that communicate compliance to end-users.
Goals and Objectives of Environmental Standards
Environmental standards aim to establish mandatory criteria for reducing pollution and conserving natural resources through measurable benchmarks, ensuring compliance and accountability in industry practices. These standards focus on achieving sustainability by setting quantifiable limits on emissions, waste management, and resource efficiency to protect ecosystems and public health. Eco-labels, in contrast, serve as voluntary certifications that inform consumers about products meeting specific environmental performance criteria, promoting market-driven ecological responsibility.
Purpose and Criteria of Eco-labels
Eco-labels serve to identify products and services that meet specific environmental performance criteria, promoting sustainability through consumer awareness and responsible purchasing. These criteria are often developed based on scientific assessments covering factors such as resource use, emissions, and overall environmental impact throughout a product's lifecycle. The purpose of eco-labels is to encourage manufacturers to improve environmental practices while providing transparent and reliable information that helps consumers make eco-conscious choices.
Certification Processes Compared
Environmental standards establish the specific criteria and benchmarks required for sustainable practices, while eco-labels represent the visible certification awarded to products meeting those standards. Certification processes for environmental standards typically involve rigorous audits, documentation review, and compliance verification conducted by accredited third-party bodies. Receiving an eco-label requires producers to demonstrate ongoing adherence to these standards through periodic reassessments and continuous improvements in environmental performance.
Impacts on Businesses and Consumers
Environmental standards establish regulatory requirements that businesses must meet to minimize ecological footprints, impacting operational costs and product development. Eco-labels serve as voluntary certifications that help consumers identify environmentally friendly products, influencing purchasing decisions and encouraging sustainable market practices. Both tools drive businesses toward greater sustainability while providing transparency and trust for eco-conscious consumers.
Global Examples of Environmental Standards and Eco-labels
Global environmental standards such as ISO 14001 provide comprehensive frameworks for organizations to manage their environmental responsibilities systematically. Prominent eco-labels like the EU Ecolabel and Energy Star serve as consumer-facing certifications that identify products meeting specific sustainability criteria. Both tools play crucial roles in promoting sustainable practices, with standards focusing on organizational processes and eco-labels emphasizing product-level environmental impacts.
Choosing Between Environmental Standards and Eco-labels
Choosing between environmental standards and eco-labels involves assessing their scope and transparency; environmental standards provide comprehensive, regulated criteria for sustainable practices, while eco-labels offer consumer-friendly certifications that highlight specific eco-friendly product attributes. Businesses aiming for robust compliance and operational improvements benefit from adhering to recognized environmental standards such as ISO 14001. Consumers seeking quick and reliable indicators of green products rely on trusted eco-labels like ENERGY STAR or the EU Ecolabel to guide environmentally conscious purchasing decisions.
Environmental standard Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com